+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
The use of geogrid for roads has transformed the way engineers design and reinforce road infrastructure. This geosynthetic solution enhances soil stability, reduces material costs, and increases the lifespan of paved and unpaved roads.
What is geogrid, and how is it used in road construction?
- Soil Stabilization: Geogrids are installed between soil layers to improve load distribution and limit soil movement, especially over weak or soft subgrades.
- Base Reinforcement: When placed beneath the aggregate base or sub-base, geogrids reduce rutting, extend road service life, and allow for thinner pavement structures.
- Improved Load-Bearing Capacity: By forming a reinforced composite layer, geogrids increase pavement bearing capacity, making them ideal for heavy traffic and industrial areas.
- Erosion Control: On slopes and embankments, geogrids help retain soil and reduce erosion caused by water runoff or traffic vibration.
- Cost Efficiency: Geogrids lower the demand for high-quality fill materials and reduce construction and maintenance costs by improving overall road durability.
- Typical Applications: Geogrids are widely used in highways, rural roads, airport runways, and parking lots where long-term performance and soil reinforcement are essential.
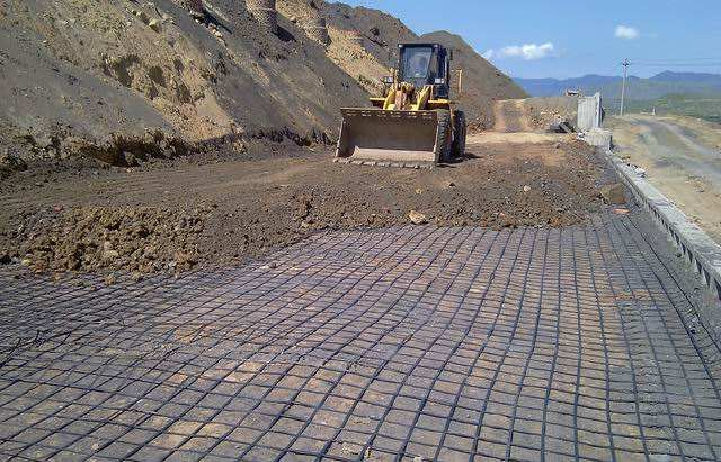

What are the main benefits of using geogrid in road projects?
Using geogrid for roads offers several advantages:
- Extended road lifespan: Geogrid reinforcement can increase pavement service life by up to 50% (Geosynthetics Institute, 2022).
- Cost savings: It reduces the required thickness of base layers, leading to lower construction and material costs.
- Improved load-bearing capacity: Geogrids help distribute loads more evenly, reducing deformation and maintenance needs.
These benefits make geogrids a cost-effective and high-performance solution in modern road engineering.
What types of geogrid are commonly used for roads?
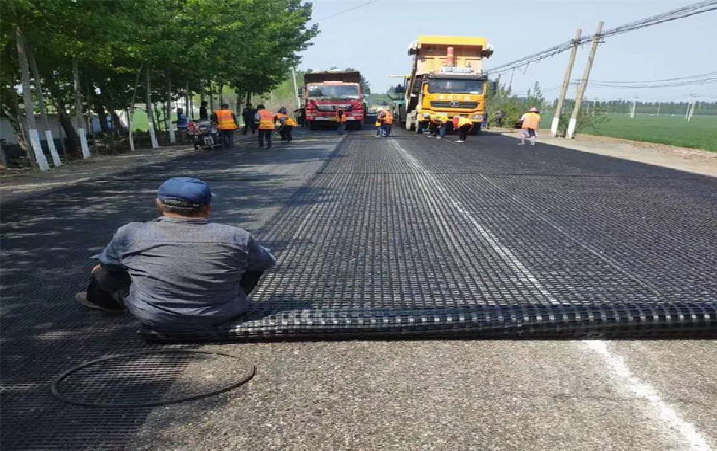

There are two primary types:
- Uniaxial geogrids: Designed for applications requiring strength in one direction, ideal for retaining walls and embankments.
- Biaxial geogrids: Provide equal strength in both directions, commonly used under roadways and parking areas.
For road projects, biaxial geogrids are most prevalent due to their ability to stabilize in both longitudinal and transverse directions. Innovations have also introduced triaxial geogrids, which offer improved performance in dynamic loading conditions.
How does geogrid usage impact sustainability in road construction?
In road construction, the main types of geogrid are:
- Uniaxial Geogrids:
- Designed to provide high strength in a single direction.
- Typically used in retaining walls, embankments, or applications where reinforcement is needed primarily along one axis.
- Biaxial Geogrids:
- Offer equal strength in both longitudinal and transverse directions.
- Commonly used beneath roadways, parking lots, and pavements to stabilize soil and distribute loads evenly.
- Triaxial Geogrids (innovative option):
- Provide improved performance under dynamic loading.
- Optimize load distribution and reduce deformation, ideal for high-traffic roads and heavy-duty pavements.
Choosing the correct type ensures optimal reinforcement, extends road lifespan, and improves durability and sustainability.
The strategic use of geogrid for roads is not just a matter of structural reinforcement—it’s an investment in long-term performance, cost-efficiency, and sustainability. As infrastructure demands grow globally, geosynthetics like geogrids will continue to play a vital role in smart, resilient road construction.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















