+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
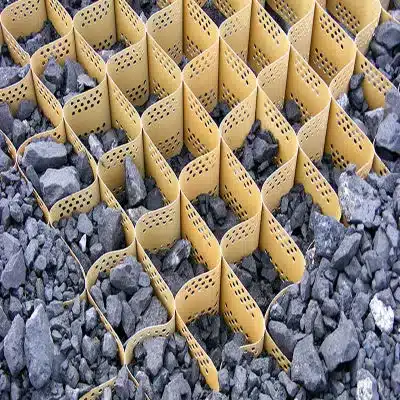
Geocells are an innovative and versatile solution in the field of geotechnical engineering, particularly valuable for soil stabilization on slopes. Known as velocity slope geocells when used to mitigate the effects of water or wind erosion on slopes, these cellular confinement systems play a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of soil structures in various environmental conditions. This article explores the concept of geocells, addressing common questions regarding their application and advantages, particularly for slope protection.
What is the maximum slope for geocell installation?
The maximum slope for geocell installation typically ranges from 45 degrees to 60 degrees, depending on the specific design and configuration of the geocells. Geocells are cellular confinement systems made from interconnected polymeric strips or grids filled with soil, aggregate, or other infill materials. They are used to stabilize slopes, control erosion, and provide structural support in various geotechnical applications.
The slope angle at which geocells can be effectively installed depends on factors such as:
- Geocell Design: Different geocell designs may have varying capabilities in terms of slope stabilization. Some geocells are designed specifically for steeper slopes and can accommodate angles closer to 60 degrees.
- Soil or Fill Type: The type of infill material used with the geocells can influence the maximum slope angle. Coarser and more angular materials generally provide better interlock and stability within the geocells.
- Site Conditions: Factors such as site drainage, environmental conditions, and the presence of vegetation can affect the stability and performance of geocells on slopes.
In practical applications, it’s important to consult with geotechnical engineers or manufacturers to determine the appropriate geocell design and installation methods for specific slope angles and site conditions.
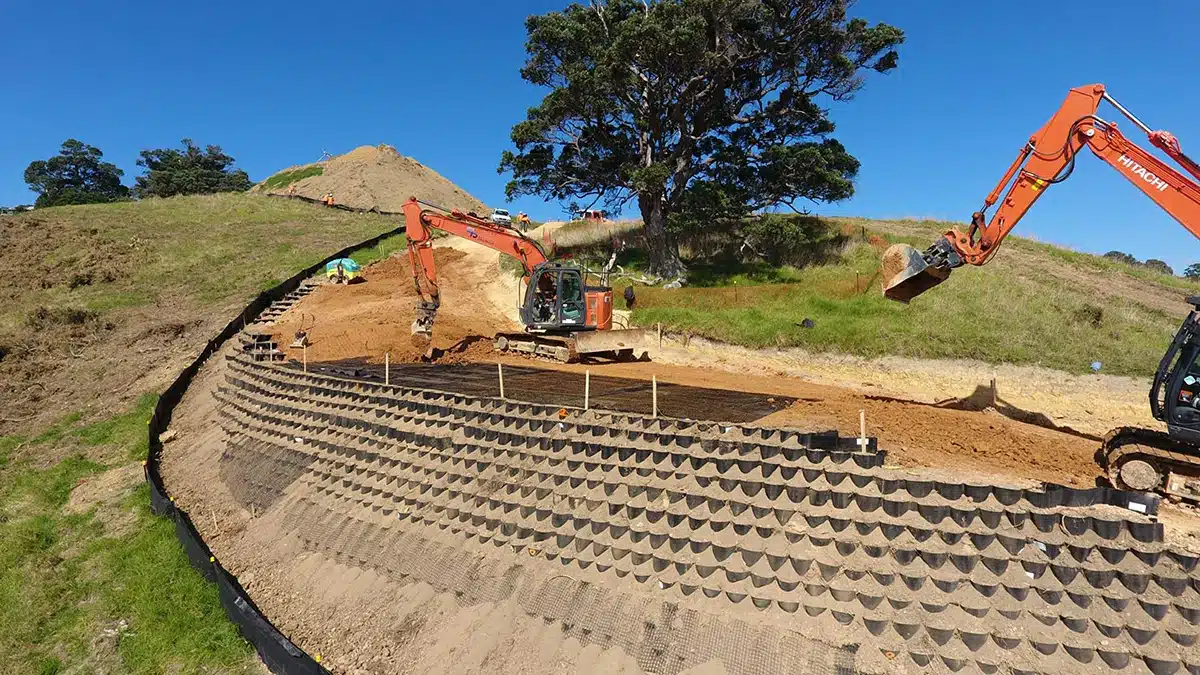

What is a geocell for slope protection?
A geocell is a three-dimensional, honeycomb-like cellular structure made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or other durable materials. It is used extensively in civil engineering and geotechnical applications for slope protection among other purposes. Specifically for slope protection:
- Reinforcement: Geocells are filled with soil, aggregate, or concrete to create a stable structure that reinforces slopes against erosion and landslides.
- Erosion Control: They help in stabilizing soil on slopes by preventing erosion caused by rainfall, surface runoff, or wind.
- Vegetation Support: Geocells provide a stable base for vegetation growth on slopes, allowing plants to take root and further stabilize the soil.
- Ease of Installation: They are relatively easy to install and can conform to various slope angles and shapes, making them versatile for different terrain conditions.
Overall, geocells enhance the stability and longevity of slope structures, offering a sustainable solution for erosion control and slope protection in civil engineering projects.
What is the difference between geogrid and geocell?
Although both geogrids and geocells are used for soil reinforcement, they differ significantly in their structure and function. Geogrids are open, net-like structures that reinforce soil by providing tensile strength, primarily used in the stabilization of roads and foundations. On the other hand, geocells are deep, three-dimensional mesh structures that confine and stabilize soil, making them ideal for applications involving slope protection and erosion control. This distinction highlights that while the geogrid is typically two-dimensional, the geocell provides a more pronounced confinement effect, which is beneficial on varied and unstable terrains.
Can you stack geocells?
Yes, geocells can be stacked to create deeper layers for more significant soil stabilization needs, such as high retaining walls or in areas with very soft soils. The panels can be stacked and filled to create a gravity-retaining structure. When stacking geocells, it’s essential to ensure they are securely interconnected and adequately anchored to withstand the loads and stresses of the environment. Proper installation and layering are crucial for maintaining the integrity and effectiveness of the stacked geocell structure.
Velocity slope geocells offer a robust and eco-friendly solution for protecting slopes from erosion and instability. By understanding their maximum slope limits, applications for slope protection, and differences from other soil stabilization technologies like geogrids, professionals can better leverage these tools in environmental and civil engineering projects. Moreover, the ability to stack geocells provides added flexibility and adaptability in managing more challenging terrains and projects. With ongoing advancements in material science and engineering techniques, geocells continue to represent a critical component in sustainable development and soil conservation strategies.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















