+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
Composite geonets stand as innovative marvels within geosynthetic engineering, offering multifunctional capabilities in diverse geotechnical applications. Comprising multiple layers intricately designed for optimal performance, composite geonets redefine the landscape of modern engineering solutions. These versatile structures serve as pivotal components in various civil and environmental projects, providing efficient drainage, soil stabilization, erosion control, and waste management functionalities. Their unique composition and adaptable properties make composite geonets indispensable in enhancing structural integrity, mitigating environmental risks, and ensuring sustainable solutions across a spectrum of engineering challenges.
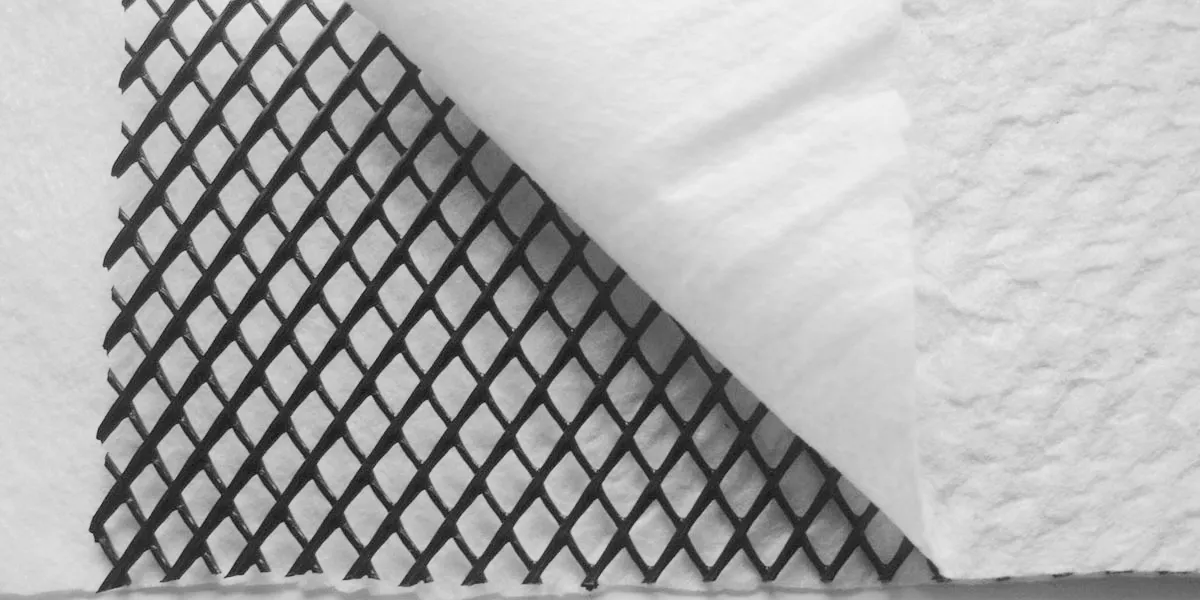
What does composite geonet consist of?
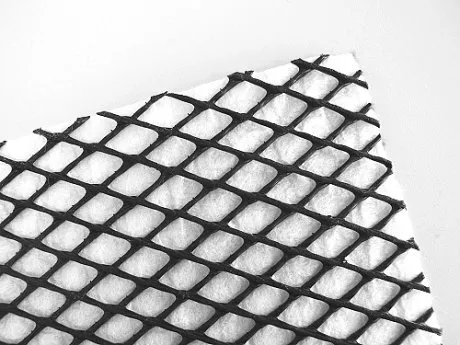
Composite geonets are specialized geosynthetic materials used primarily in civil engineering and environmental applications for drainage and stabilization purposes. A composite geonet typically consists of several layers, each serving a specific function. The composition usually includes:
Geonet Core:
The central part of a composite geonet is the geonet itself, which is a net-like structure made from a synthetic polymer, usually polyethylene or polypropylene. This core is designed with a unique ribbed or lattice structure to provide excellent in-plane drainage capability, allowing fluids like water or gases to pass through while providing good structural strength.
Geotextile Layers:
The geonet core is often sandwiched between layers of geotextile. Geotextiles are permeable fabrics that, when used in association with soil, have the ability to separate, filter, reinforce, protect, or drain. These layers can be made from various materials, including woven or non-woven polypropylene or polyester. The geotextile layers serve multiple purposes:
| Filtration | They prevent soil particles from clogging the geonet channels, ensuring consistent drainage performance. |
| Separation | They keep different soil layers separate, which is crucial in many construction applications to maintain the integrity and functionality of the materials. |
| Protection | They provide additional mechanical protection to the geonet, enhancing durability and lifespan. |
| Bonding | The geotextile layers are usually bonded to the geonet core through various methods such as heat bonding, needle punching, or adhesive bonding. This bonding is crucial to maintain the structural integrity of the composite geonet and ensure that the layers function together effectively. |
Composite geonets are used in a variety of applications, including landfill liners, road construction, drainage systems, erosion control, and earth reinforcement. Their design allows for efficient drainage and filtration, while also providing strength and stability to the soil or other materials with which they are used. The specific composition and design of a composite geonet can vary depending on the manufacturer and the intended application.

What are the applications of Composite geonet?
The versatile applications of composite geonets span various civil and environmental engineering endeavors, showcasing their significance in multiple areas:
- Drainage Systems: These geonets serve as effective components in drainage systems within construction projects, enabling optimal water flow. They play a pivotal role in mitigating soil erosion and preserving the structural integrity of diverse infrastructures such as railway systems, road foundations, and slope drainage.
- Landfills and Waste Management: Composite geonets are integral in waste containment strategies, functioning as a critical layer for drainage in landfills. They significantly contribute to enhancing leachate collection efficiency, thereby preventing contamination in landfill areas and adjacent zones.
- Soil Stabilization: Within civil engineering, composite geonets prove invaluable for stabilizing slopes, embankments, and roadways. They achieve this by enhancing soil drainage and fortifying the ground structure, which is crucial for maintaining the stability of infrastructure elements like railway systems and road foundations.
What are the different types of geocomposites?
Geocomposites encompass various types, each designed with specific characteristics and functions. Common types of geocomposites include:
- Geotextile-Geonet Composites: These combine geotextile and geonet materials to offer both filtration and drainage properties.
- Geonet-Geotextile-Geocomposite: This type integrates multiple layers of geotextile and geonet for enhanced filtration, drainage, and reinforcement.
- Geogrid-Geotextile Composites: Geogrids combined with geotextiles provide reinforcement and filtration capabilities suitable for road construction and soil stabilization.
- Geomembrane-Geonet Composites: These incorporate a geomembrane layer with a geonet for applications requiring high impermeability and drainage efficiency.
What is the difference between geotextile and geonet?
Geotextiles and geonets are both important components in the field of geosynthetic materials, used extensively in civil engineering and environmental applications. While they are sometimes used together, they have distinct properties and serve different primary functions.
Geotextile
Material and Structure:
Geotextiles are permeable fabrics made from synthetic fibers like polypropylene, polyester, or sometimes natural fibers. They can be woven, non-woven, or knitted. The choice between woven and non-woven depends on the required application.
Primary Functions:
- Separation: Preventing the mixing of different soil layers.
- Filtration: Allowing water to pass through while preventing soil erosion.
- Reinforcement: Increasing soil stability.
- Protection: Providing a cushion to protect geomembranes or other materials from damage.
- Drainage: Facilitating the flow of fluids within the plane of the fabric.
Applications:
Used in road construction, drainage systems, erosion control, landfill liners, and as protective layers in various construction projects.
Geonet
Material and Structure:
Geonets are typically made from polyethylene or polypropylene and have a net-like structure with interconnected ribs or strands. This design creates in-plane channels for fluid flow.
Primary Functions:
- Drainage: Providing high-capacity, in-plane drainage for liquids and gases. Geonets are specifically designed to transport fluids and gases within their structure.
- Confinement: Sometimes used to confine or stabilize loose materials.
Applications:
Primarily used in drainage applications, such as within landfill liners, road subgrades, and behind retaining walls, where high-capacity drainage is required.
Key Differences
- Functionality: The most significant difference is their primary function. Geotextiles are versatile, focusing on separation, filtration, reinforcement, protection, and drainage. Geonets are more specialized, and primarily used for high-capacity drainage.
- Structure and Material: Geotextiles are fabric-like, and available in woven or non-woven forms, while geonets have a distinct net-like, open structure.
- Drainage Capacity: Geonets generally offer greater in-plane drainage capacity compared to geotextiles.
In many engineering projects, geotextiles and geonets are used in conjunction to leverage the strengths of both materials. For example, a geonet might be used for its superior drainage capabilities, sandwiched between layers of geotextile to provide filtration and protection.
Composite geonets, combining the functionalities of both geotextiles and geonets, offer a versatile solution catering to diverse engineering needs, integrating filtration, reinforcement, and drainage properties in one material.
Composite geonets, a subset of geocomposites, represent a versatile solution within geosynthetic materials. These structures, comprising multiple layers, serve diverse purposes in various engineering applications. They are engineered to deliver enhanced functionalities that cater to specific geotechnical and environmental needs.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















