+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
Geonet fabric is revolutionizing the construction industry, offering a sustainable and cost-effective solution for various projects. In this article, we’ll delve into what geonet fabric is made of, the difference between geotextile and geonet, and explore the diverse applications of this innovative material.
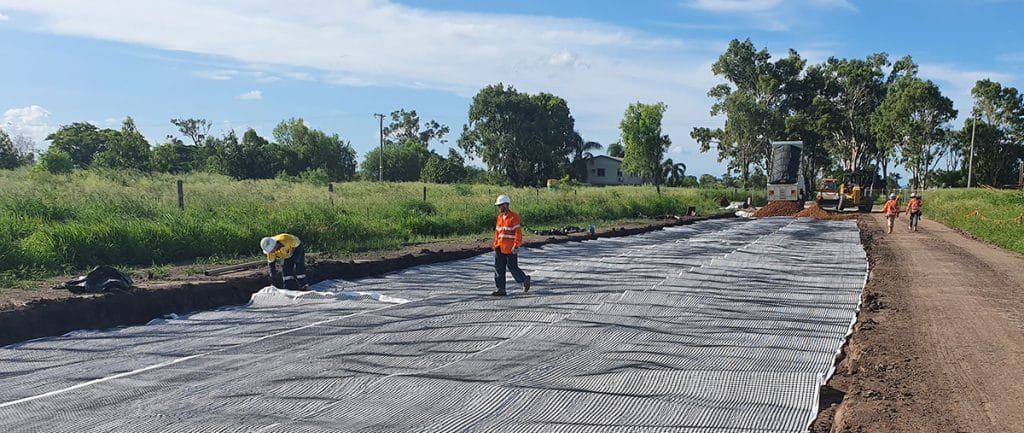

What is Geonet Made Of?
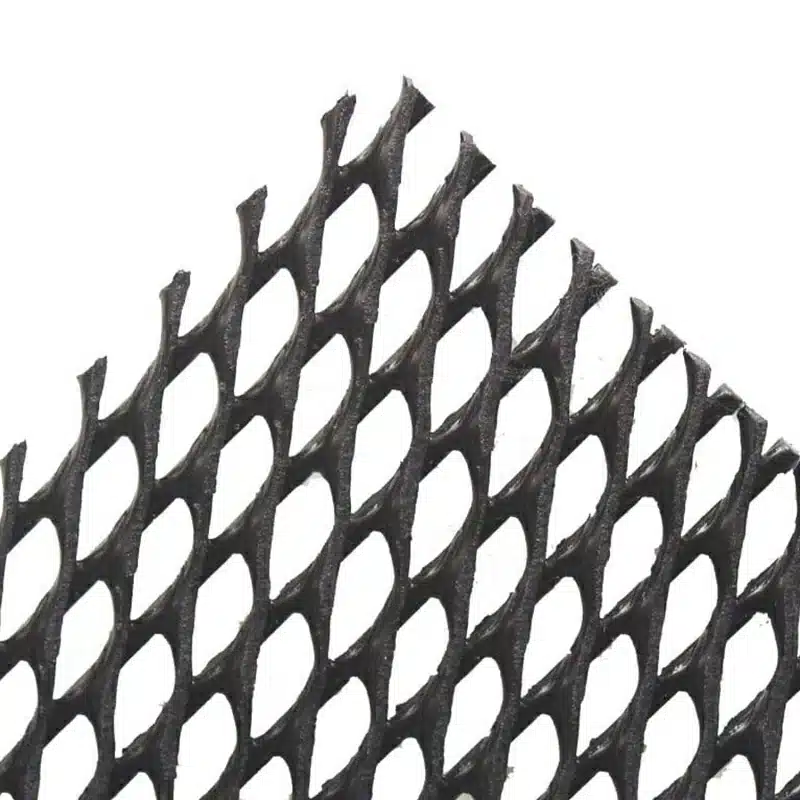
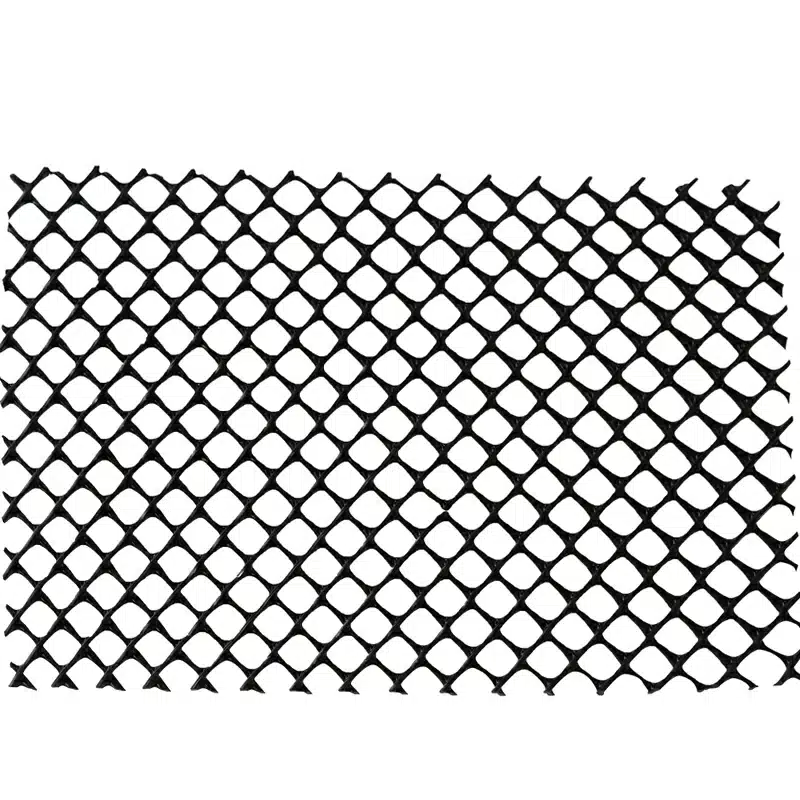
Geonets are primarily manufactured from high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or polypropylene (PP), two geosynthetic-grade polymers selected for their mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and long-term durability in harsh environmental conditions. These thermoplastic resins are extruded into intersecting ribs that form a structured bi-planar or tri-planar network, enabling in-plane fluid drainage under compressive loads.
- HDPE Geonets provide elevated tensile stiffness, creep resistance, and chemical compatibility, making them suitable for demanding landfill, mining, and environmental containment systems where leachate or gas drainage is required.
- PP Geonets offer lower density, improved flexibility, and lighter handling characteristics, which can be advantageous in architectural or landscape drainage such as green roofs, foundation drainage, or road subsurface systems.
Additive formulations may include UV stabilizers, antioxidants, and thermal stabilizers to extend service life during exposure to temperature fluctuations, soil chemistry, and mechanical loads.
Material selection is governed by drainage transmissivity, compressive strength, and environmental exposure conditions to ensure geonet performance throughout the design life of the civil or environmental project.
What is Geonet?
Un geonet es un material geosintético tridimensional fabricado a partir de polímeros como polietileno de alta densidad (HDPE) o polipropileno (PP). Su estructura de malla o rejilla permite un flujo eficiente de agua y proporciona estabilidad al suelo o material circundante, siendo ideal para aplicaciones de drenaje y refuerzo del terreno.
Estructura y tipos de geonets:
- Unidireccional: Las nervaduras o hilos corren en una sola dirección, ofreciendo drenaje lineal.
- Bidireccional: Las nervaduras cruzan en dos direcciones, aumentando la resistencia y la capacidad de drenaje.
Diferencias clave con geotextiles:
| Propiedad | Geotextil | Geonet |
|---|---|---|
| Estructura | Plano, tejido o no tejido | Tridimensional, rejilla abierta |
| Función principal | Estabilización del suelo, separación y filtración | Drenaje y conducción de agua |
| Complemento | Puede actuar solo | Generalmente se combina con geotextil para filtración y protección |
Aplicaciones principales:
- Drenaje: Bajo carreteras, pavimentos, taludes y vertederos.
- Muros de contención: Reduce presión hidrostática y refuerza el suelo.
- Control de erosión: En taludes, riberas y pendientes.
- Cubiertas verdes y techos verdes: Facilita la evacuación del agua y promueve el crecimiento vegetal.
En resumen, mientras los geotextiles proporcionan soporte estructural y control de erosión, los geonets se especializan en drenaje eficiente y, combinados con geotextiles, forman sistemas geosintéticos de alto rendimiento en ingeniería civil y ambiental.
What is the Difference Between Geotextile and Geonet?
The main distinction lies in their structure and primary roles. Geotextiles are flat fabrics primarily designed for soil stabilization and erosion control. They provide tensile strength and safeguard against soil erosion.
In contrast, geonets are three-dimensional structures used primarily for drainage and filtration. The geonet core provides the main function of drainage, while the nonwoven geotextiles provide the main functions of filtration, separation, and protection. Their high flow rate makes them perfect for applications where efficient water management and filtration are crucial. Geonets significantly improve the overall performance of geosynthetic systems in hydraulic applications.

What is a Geonet Used For?
Geonets have a wide range of applications in civil and environmental engineering, including:
- Landfill Liners: Geonets play a vital role in landfill liners, preventing leachate from seeping into the surrounding soil and groundwater. Their excellent drainage capacity ensures effective liquid removal within landfills.
- Retaining Walls: Geonets aid in drainage and soil reinforcement behind retaining walls. They reduce hydrostatic pressure, enhancing the stability and durability of these structures.
- Erosion Control: Geonets are employed to control soil erosion in embankments, slopes, and riverbanks. They support vegetation growth and efficiently manage water runoff.
- Road Construction: Geonets are valuable in road construction, helping with drainage to mitigate the risk of water-related damage to roads, highways, and related infrastructure.
- Green Roofs: Geonets are also utilized in green roof systems to facilitate water drainage and promote healthy vegetation growth. These versatile materials find application in road construction, road widening, asphalt work, building construction and foundations, retaining walls, dams, artificial ponds, water reservoirs, and many more engineering projects.
In conclusion, geonet fabric is a versatile and sustainable solution for various construction and environmental projects. Its unique three-dimensional structure, along with its durability and drainage capabilities, makes it an essential component in modern engineering practices. By understanding the composition and applications of geonets, you can harness their benefits to maximize efficiency and sustainability in your projects.

Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















