+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
Leachate carrier geonets are an essential component in landfill management, playing a pivotal role in preventing environmental contamination. In this article, we will explore the world of geonets, their transmissivity, and how they contribute to safeguarding our environment.
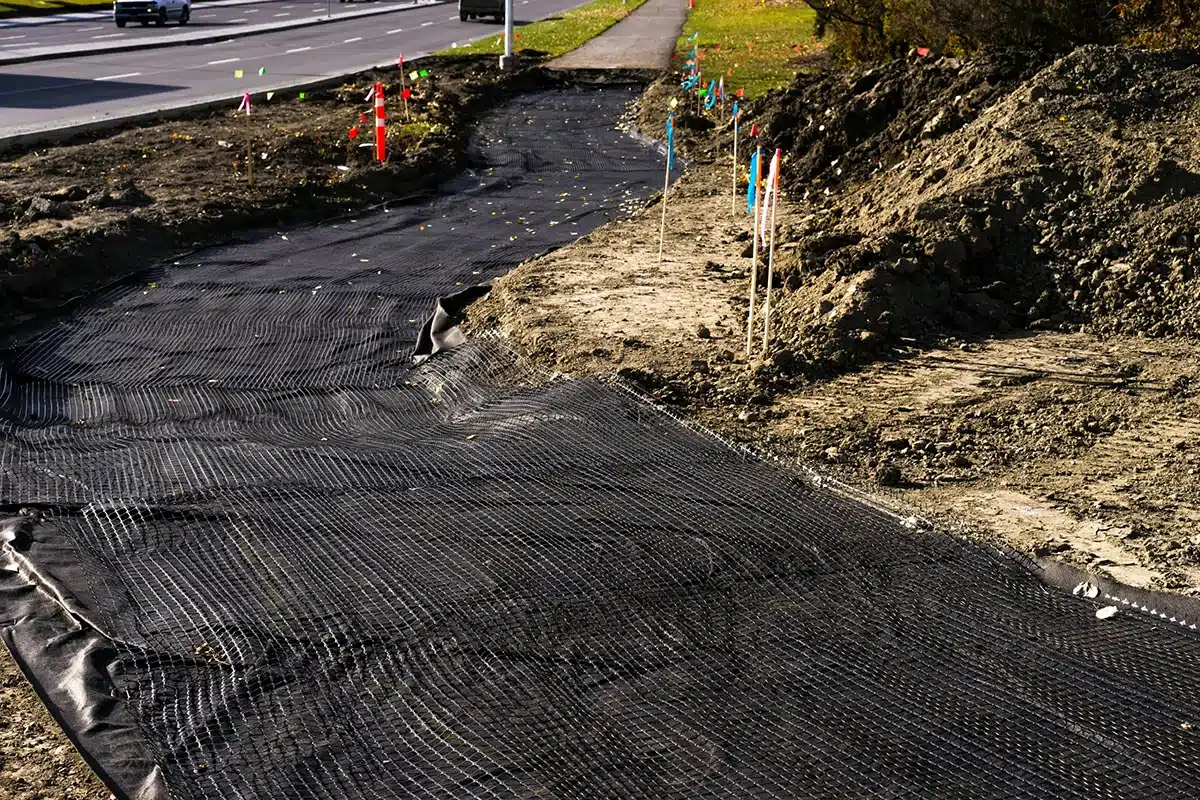

What is a Geonet?
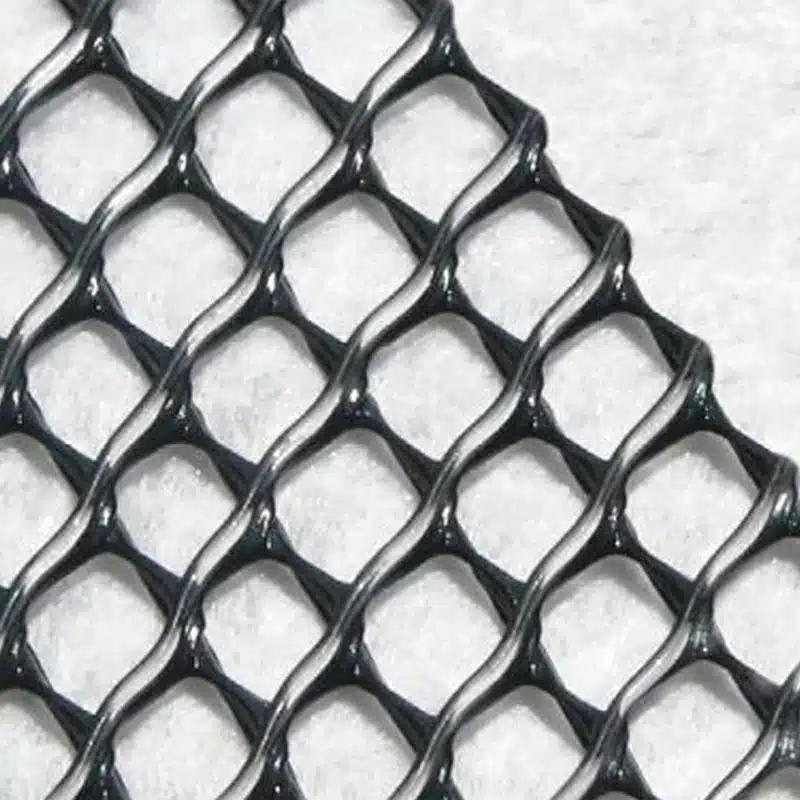
A geonet, or geosynthetic drainage net, is a crucial part of modern landfill systems. It’s a specialized material with a unique three-dimensional structure, made of high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or polypropylene. This structure offers several benefits:
- Efficient Liquid Movement: Geonets, with their interconnected ribs and grid-like design, are designed for effective drainage of liquids like leachate within landfills. This swift drainage helps maintain landfill stability and reduces the risk of contamination.
- Reinforcement: Geonets are often combined with other geosynthetic materials to reinforce landfill structures, preventing deformation and settling over time.
- Eco-Friendly: Geonets are environmentally friendly and can be recycled and reused in various construction projects, contributing to sustainability.
What is the Transmissivity of Geonet?
A geonet, also known as a geosynthetic drainage net, is a vital component of modern landfill and environmental engineering systems. It is a specially engineered material featuring a rigid three-dimensional drainage structure, typically manufactured from high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or polypropylene. This structure provides several key advantages:
- Efficient Liquid Movement: Geonets use interconnected ribs and an open grid design to create continuous in-plane flow channels. This allows leachate and other liquids to drain rapidly, reducing hydraulic pressure, improving landfill stability, and lowering the risk of environmental contamination.
- Structural Support & Reinforcement: Geonets are commonly used in combination with geomembranes and geotextiles to form integrated drainage systems. This layered approach enhances structural stability and helps prevent long-term deformation and settlement under heavy loads.
- Sustainable & Durable Solution: Made from chemically resistant polymers, geonets offer long service life and can be recycled or reused in certain construction applications, supporting sustainable waste management and infrastructure development.

How are Geonets Installed in Landfills?
The installation of geonets in landfills involves a series of well-defined steps:
- Site Preparation: Before installation, the landfill area is carefully prepared, ensuring a stable base and proper grading.
- Geonet Placement: Geonets are rolled out on the prepared surface, forming a network of drainage channels. They are secured in place using staples or other appropriate methods.
- Covering and Overlapping: Multiple layers of geonets may be installed, and they should be overlapped to ensure continuous drainage pathways. The top layer is typically covered with a protective geotextile fabric.
- Waste Layer: After geonet installation, waste materials are added to the landfill, and geonets are placed between the different waste layers.
- Final Cover: The landfill is capped with a final cover system, which may include additional geosynthetic materials to further protect against leachate migration.
How Does Leachate Carrier Geonets Benefit the Environment?
Leachate carrier geonets offer several environmental benefits. Firstly, they help in the efficient management of leachate, the liquid that drains from a landfill, by facilitating its proper containment and removal. This prevents leachate from contaminating soil and groundwater, thus safeguarding ecosystems and drinking water sources. Additionally, geonets aid in the stabilization and reinforcement of landfill slopes, reducing erosion and minimizing the risk of landslides or collapses. Moreover, by promoting better drainage and filtration, these geonets enhance the overall performance and longevity of landfill structures, contributing to sustainable waste management practices.
In conclusion, leachate carrier geonets are an integral part of responsible landfill management. They help safeguard our environment, prevent contamination, and ensure the long-term stability of landfill structures. Understanding their role and transmissivity is crucial for implementing effective waste management practices while minimizing environmental impact.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















