+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
Geocomposite liners are essential components in the field of civil engineering, environmental protection, and construction. These innovative materials are a combination of geosynthetic materials used in civil engineering applications, integrating two or more geosynthetic components, such as geotextiles, geomembranes, and drainage layers. This combination creates a versatile, durable, and highly effective solution for various infrastructure projects. The integration of different layers enhances the liner’s performance, making it ideal for applications such as landfill liners, erosion control, and water management systems. This article will dive into the core aspects of geocomposite liners, including their differences from geotextiles, their functions, uses, and applications.
What is the difference between geotextile and geocomposite?
Here’s the comparison in table format in English:
| Feature | Geotextile | Geocomposite |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A permeable textile material made from synthetic fibers (e.g., polypropylene, polyester) | A composite material made by combining geotextiles with other materials (e.g., drainage cores, geomembranes) |
| Types | Woven, Nonwoven | Varies based on combination (e.g., geotextile + drainage core or geomembrane) |
| Main Functions | Separation, Filtration, Reinforcement | Drainage, Waterproofing, Filtration, Separation |
| Structure | Single-layer textile material | Multi-layer material, combining geotextiles with other components (e.g., drainage, waterproof layers) |
| Applications | – Soil separation- Filtration- Reinforcement (e.g., in roads, embankments) | – Drainage (e.g., roads, landfills)- Waterproofing (e.g., landfill liners)- Filtration and Separation |
| Materials Used | Synthetic fibers (e.g., polypropylene, polyester) | Geotextile + other materials (e.g., geonets, geomembranes) |
| Durability | Generally durable depending on type (woven/nonwoven) | Highly durable with enhanced properties due to composite structure |
| Water Permeability | High permeability for filtration | Permeability depends on the combination of materials used, often designed for drainage or waterproofing |
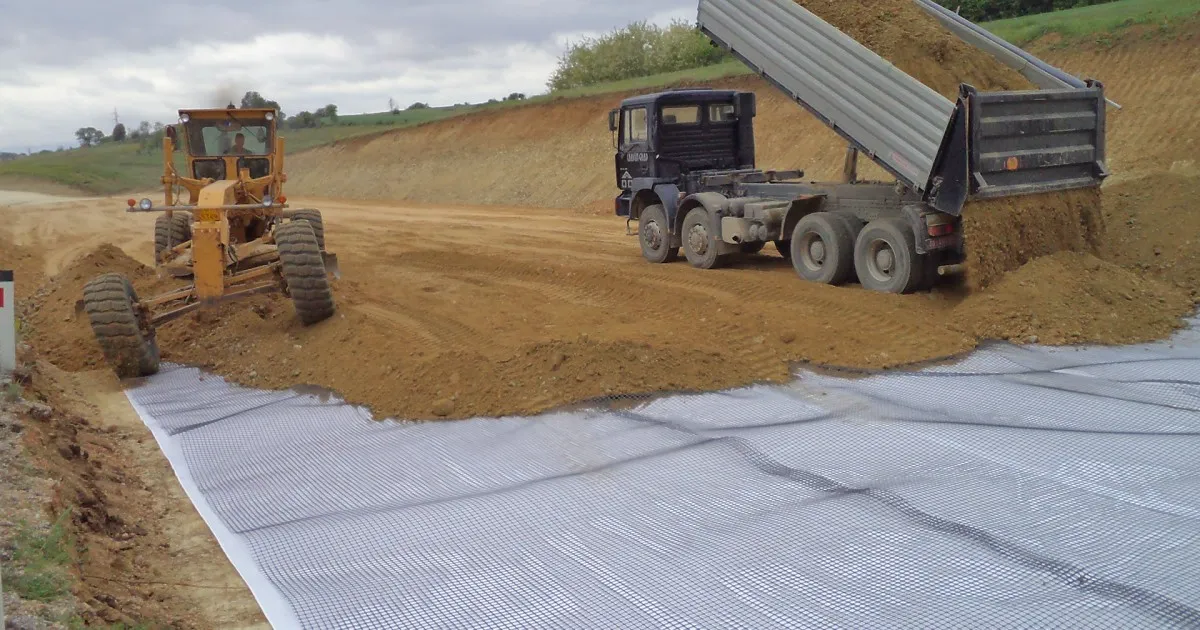

What Is a Geocomposite Used For?
A geocomposite is used in engineering applications where multiple geotechnical functions must be achieved simultaneously within a single, integrated system. By combining two or more geosynthetic materials—such as geotextiles, geomembranes, geonets, or drainage cores—geocomposites deliver higher performance than single-layer products.
Primary uses of geocomposites include:
- Landfill and waste containment systems: Geocomposites are widely used in landfill liners and caps. When combined with geomembranes, they help control leachate migration, gas venting, and groundwater protection, while geotextile layers provide filtration and protection to prevent damage to impermeable membranes.
- Drainage and water management: Geocomposite drainage layers replace traditional granular drainage systems. They efficiently collect and convey water in applications such as roadways, retaining walls, tunnels, foundations, and green roofs, while significantly reducing excavation depth and material volume.
- Erosion control and slope stabilization: In slope and embankment applications, geocomposites provide reinforcement, filtration, and controlled drainage, reducing pore water pressure and preventing soil loss caused by surface runoff or subsurface flow.
- Infrastructure and transportation projects: Geocomposites are used beneath roads, railways, and paved areas to enhance soil separation, load distribution, and subsurface drainage, improving long-term structural performance and reducing maintenance requirements.
- Environmental protection systems: In hydraulic and environmental projects, geocomposites help manage liquid and gas flow, protect sensitive soils, and support sustainable construction practices by minimizing raw material use and environmental disturbance.
In summary, geocomposites are used wherever drainage, filtration, separation, reinforcement, and containment must work together as a unified system. Their multifunctional design makes them essential in modern civil engineering, offering efficient, durable, and cost-effective solutions to complex ground and environmental challenges.
What is a geocomposite drainage layer?
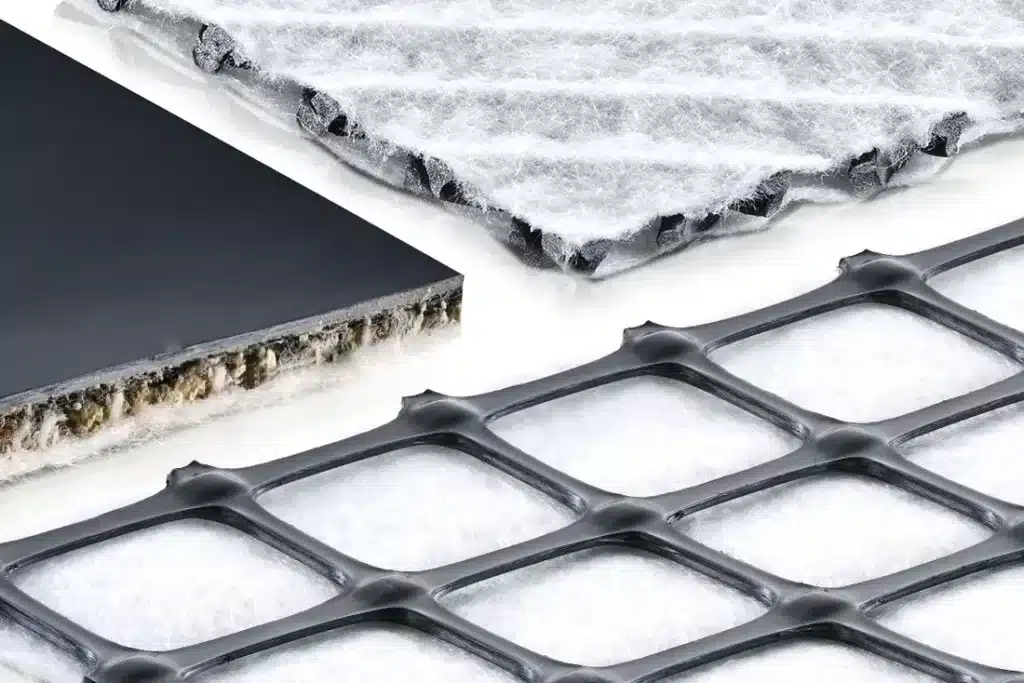
A geocomposite drainage layer is a type of geocomposite material specifically designed to facilitate water movement while providing filtration. It is made up by associating, during production, a draining core layer (it can be either a mat, a net, or a molded element) between two layers of geotextiles. This configuration ensures optimal water flow while maintaining structural integrity.
This type of geocomposite is widely used in applications where proper water management is essential, such as under drainage systems in landfills, tunnels, and roads. The geotextile serves as a filter to prevent clogging of the drainage layer, allowing water to pass through efficiently while retaining fine particles and preventing soil erosion.
What are the applications of geocomposite?
Geocomposites have a broad range of applications across various industries due to their ability to combine multiple functionalities. Some common applications include:
- Landfill lining: Geocomposites are used as protective liners in landfills to contain leachate and prevent contamination of surrounding groundwater.
- Stormwater management: In drainage systems, geocomposites facilitate the movement of water while preventing soil migration, thus protecting the system from clogging ensuring efficient water flow, and helping control the movement of liquids or gases.
- Road construction: Used for soil reinforcement, geocomposites provide structural support to roads, highways, and embankments, improving durability and preventing erosion.
- Slope protection and erosion control: Geocomposites are used to prevent soil erosion on slopes by reinforcing the soil and allowing for efficient drainage.
Geocomposite liners are powerful materials that offer a range of benefits in modern construction and environmental management. By combining geotextiles, geomembranes, and drainage layers, geocomposites provide versatile solutions for projects such as landfill management, erosion control, water drainage, and more. Their unique ability to perform multiple functions makes them an indispensable tool in civil engineering, offering cost-effective and sustainable solutions to complex challenges. Understanding their applications and advantages can help professionals make informed decisions when choosing materials for large-scale infrastructure projects.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















