+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
In recent years, the use of geocell technology in pond construction and maintenance has gained significant attention. This article delves into the world of geocells, exploring their applications, varieties, and benefits, particularly in the context of pond environments. By understanding how geocells work and the different types available, we can appreciate their role in sustainable water body management.
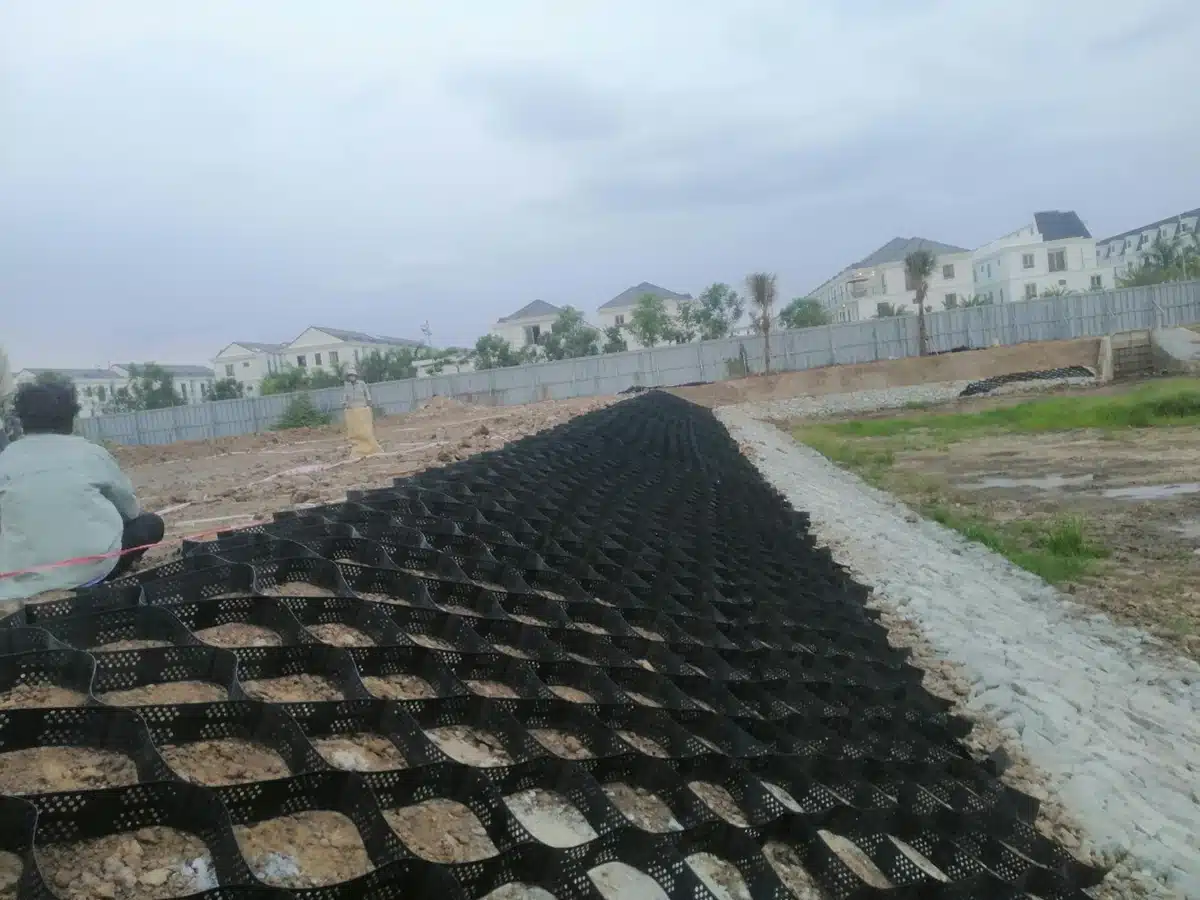

What is Geocell Used For?
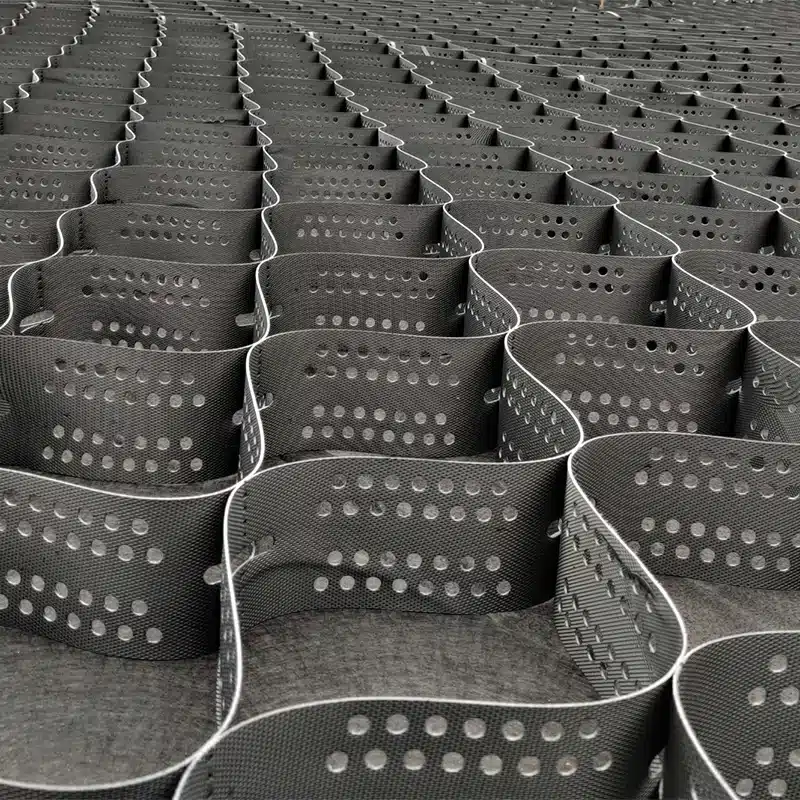
Geocell is a versatile material used in various applications within construction and civil engineering projects, thanks to its unique structure and properties. It consists of a three-dimensional honeycomb-like network of interconnected cells made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE), polypropylene, or other polymers. These cells can be filled with different materials, such as soil, sand, gravel, or concrete, depending on the application. Here are some of the primary uses of Geocell:
- Soil Stabilization: Geocell is widely used to stabilize soils in areas prone to erosion or where the soil lacks the strength to support structures or traffic. The confinement provided by the Geocell structure increases the load-bearing capacity of the soil and reduces deformation under load.
- Slope Protection: On slopes, Geocell can prevent soil erosion caused by water runoff and wind. It helps in retaining soil and vegetation on slopes, promoting natural vegetation growth by trapping seeds and moisture within its cells.
- Road and Railway Construction: In road and railway construction, Geocell is used to stabilize the subgrade layer of roads and railway tracks. It improves the performance and longevity of roads and railways by distributing loads more evenly and reducing the risk of rutting and structural failure.
- Retaining Walls: Geocell can be used to construct flexible, cost-effective retaining walls. Filled with soil or another granular material, these walls can support lateral loads, making them suitable for landscaping and erosion control applications.
- Channel Protection: For channels and waterways, Geocell helps protect the banks and beds against erosion. It can be used to stabilize the banks and provide a robust foundation for vegetation.
- Load Support: In areas with weak soils, Geocell can be used to distribute loads more evenly over a larger area, reducing the pressure on the underlying soil. This is particularly useful for parking lots, airport runways, and other areas subject to heavy loads.
- Landscaping: In landscaping projects, Geocell can be used to create stable and durable surfaces for pedestrian and vehicle traffic, as well as to construct green retaining walls and embankments.
The versatility and effectiveness of Geocell in improving soil strength, preventing erosion, and supporting loads make it a valuable tool in a wide range of construction and civil engineering projects.
What are the Different Types of Geocells?
Geocells come in various types, primarily distinguished by the materials used, their design features, and whether they are non-perforated geocells or perforated geocells. The most common types include:
- High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) Geocells (Non-Perforated and Perforated): Known for their durability and chemical resistance, HDPE geocells are widely used in pond applications. The non-perforated geocell is ideal for water retention and structural support, while the perforated version is used for drainage and vegetation support.
- Polypropylene Geocells (Non-Perforated and Perforated): These are lighter and more flexible compared to HDPE, suitable for projects requiring adaptability to uneven surfaces. Both non-perforated and perforated polypropylene geocells cater to different needs, with the former providing solid support and the latter aiding in drainage and root growth.
- Textile-based Geocells (Perforated): Made from woven or nonwoven fabrics, these are often used for erosion control and vegetation support on pond banks. The perforated nature of these geocells allows for water and nutrient flow, promoting healthy plant growth.
- Biodegradable Geocells (Non-Perforated and Perforated): Ideal for temporary applications, these geocells gradually decompose, making them an eco-friendly option. They are available in both non-perforated forms for structural stability and perforated forms for environmental restoration projects.
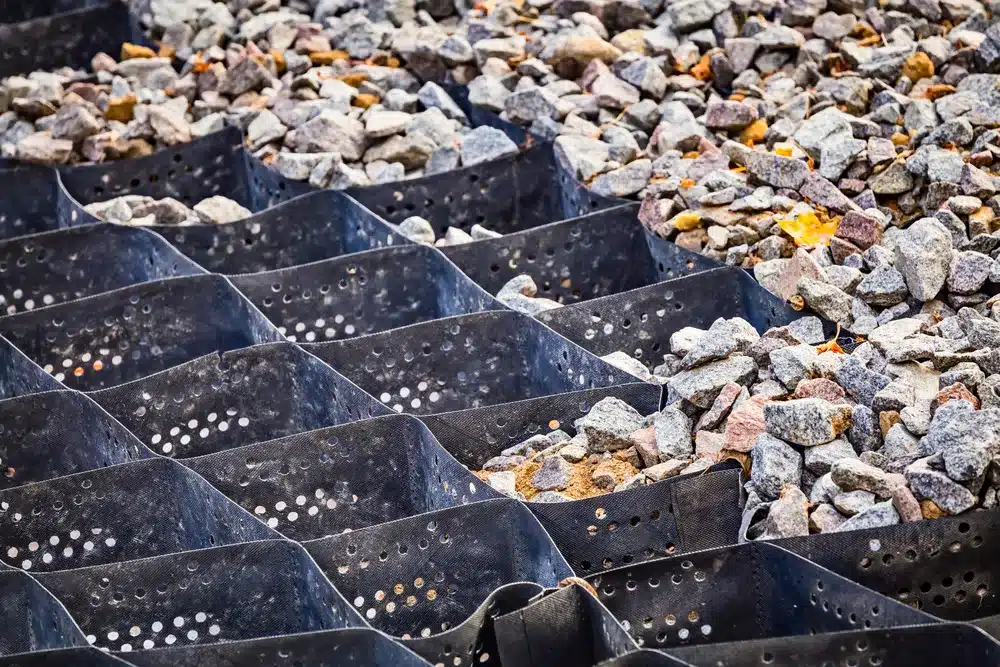

How Do Geocells Contribute to Environmental Sustainability?
Geocells are an innovative technology used in civil engineering that contributes significantly to environmental sustainability in several ways. Here’s how they help:
- Erosion Control: Geocells are effective at controlling erosion on slopes and in channel linings. They confine the soil which can prevent it from being washed away by water flow. This is especially important in preserving natural landscapes and preventing sediment from entering waterways.
- Soil Stabilization: They stabilize soils by confining the material in their honeycomb-like structures, which enhances the load-bearing capacity of sub-grade soils. This stabilization is crucial for the construction of roads and pavements, especially in areas with weak soils, and reduces the need for non-renewable resources like aggregate and concrete.
- Vegetation Growth: Geocells can be filled with soil and used to support vegetation on slopes and in arid areas, promoting green cover and aiding in the restoration of natural habitats. This can help in carbon sequestration and lowering local temperatures.
- Water Conservation: In areas prone to drought, geocells help in water retention and slow down water runoff, allowing for better infiltration and moisture retention in the soil. This is beneficial for agricultural practices and can reduce the need for irrigation.
- Recycled Materials: Many geocells are made from recycled plastics, which helps reduce the amount of waste that ends up in landfills. By using recycled materials, the production of geocells also contributes to reducing the environmental impact associated with new material extraction and processing.
- Durability and Reduced Maintenance: The durability of geocells means that structures last longer and require less maintenance. This reduces the frequency of repairs and rebuilds, which in turn minimizes the environmental impact associated with construction activities.
- Reduction in Carbon Footprint: By improving the load-bearing capacity of roads and reducing the need for traditional pavement materials like asphalt and concrete, geocells can significantly reduce the carbon footprint of construction projects.
Overall, geocells are a versatile and sustainable solution in modern engineering that helps mitigate environmental impact through erosion control, resource conservation, and the use of recycled materials.
What are the Installation and Maintenance Considerations for Geocells in Pond Applications?
Installing and maintaining geocells for pond applications involves several key considerations to ensure they function effectively and last a long time. Here’s a breakdown of the essential aspects to consider:
Installation Considerations
Site Preparation: The first step involves preparing the site where the geocells will be installed. This typically includes removing vegetation, leveling the ground, and ensuring proper drainage. It’s crucial to create a stable and uniform subgrade to prevent uneven settlement or deformation of the geocells.
- Sizing and Layout: Before installation, plan the layout of the geocells according to the size and shape of the pond. It’s important to select the correct cell size and depth based on the specific needs of the application, such as expected load and soil type.
- Material Handling: Geocells are usually transported to the site in a collapsed form and then expanded into their honeycomb structure on-site. Care must be taken during handling to avoid damage to the cells.
- Anchoring and Connection: Proper anchoring of geocells is critical to withstand forces from water and soil. The cells must be securely interconnected to form a continuous structure, and they might need to be pinned or staked to the ground to prevent movement.
- Filling: Once laid and anchored, geocells need to be filled with appropriate materials such as soil, sand, or gravel. The filling process should ensure that cells are evenly filled to avoid differential settling and to provide uniform support and filtration.
- Vegetation: In some cases, establishing vegetation within the geocells can help with erosion control and aesthetic integration with the surrounding environment. Choosing the right type of vegetation is crucial for the success of the installation and its long-term stability.
Maintenance Considerations
- Inspection: Regular inspections are necessary to check for any signs of damage or wear, such as tears, punctures, or deformation of the geocells. It’s also important to check for sediment build-up or erosion within the cell structure.
- Repair: Any damaged areas should be repaired promptly to prevent further deterioration. This might involve replacing sections of the geocell or refilling areas where the fill material has settled or washed away.
- Vegetation Management: If vegetation is part of the geocell system, regular maintenance including watering, weeding, and pruning may be required to keep the vegetation healthy and effective at erosion control.
- Debris and Sediment Control: It’s important to regularly clean any debris that accumulates within the geocells to prevent clogging and to maintain effective drainage. Sediment accumulation can also reduce the efficiency of the geocells and should be periodically removed.
By addressing these installation and maintenance considerations, geocells can provide effective and durable solutions for pond applications, enhancing the stability, load distribution, and aesthetic qualities of the area.
Geocell technology offers a revolutionary approach to pond construction and maintenance. Its applications range from soil stabilization to erosion control, making it an invaluable tool in creating and preserving healthy pond ecosystems. With various types available, including HDPE, polypropylene, textile-based, and biodegradable options, geocells cater to diverse needs and environmental considerations. Their contribution to sustainability, coupled with the practical aspects of installation and maintenance, underscores the importance of geocells in modern environmental management and landscaping practices. As we continue to seek eco-friendly and efficient solutions, geocell for ponds stands out as a prime example of innovation meeting nature conservation.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















