+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
Geocell-reinforced foundations are revolutionizing civil engineering projects by providing increased stability and strength to support heavy structures. In this article, we will explore what geocell foundations are, how geocell reinforcement works, their significance in civil engineering, and the key differences between geogrids and geocells.
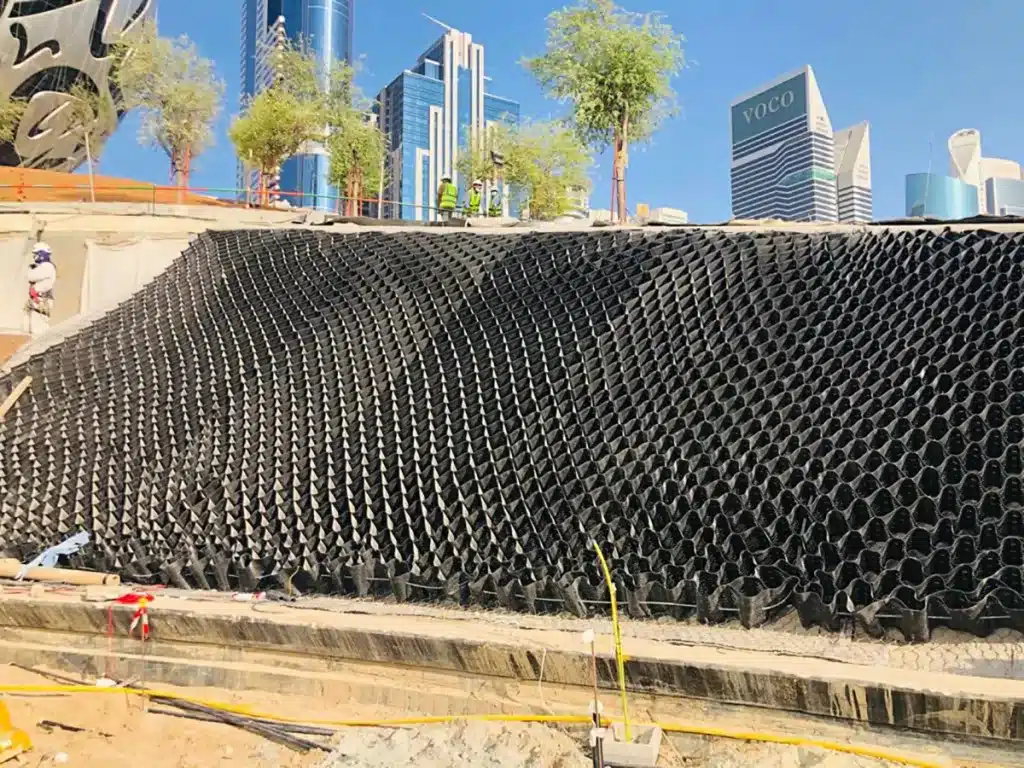

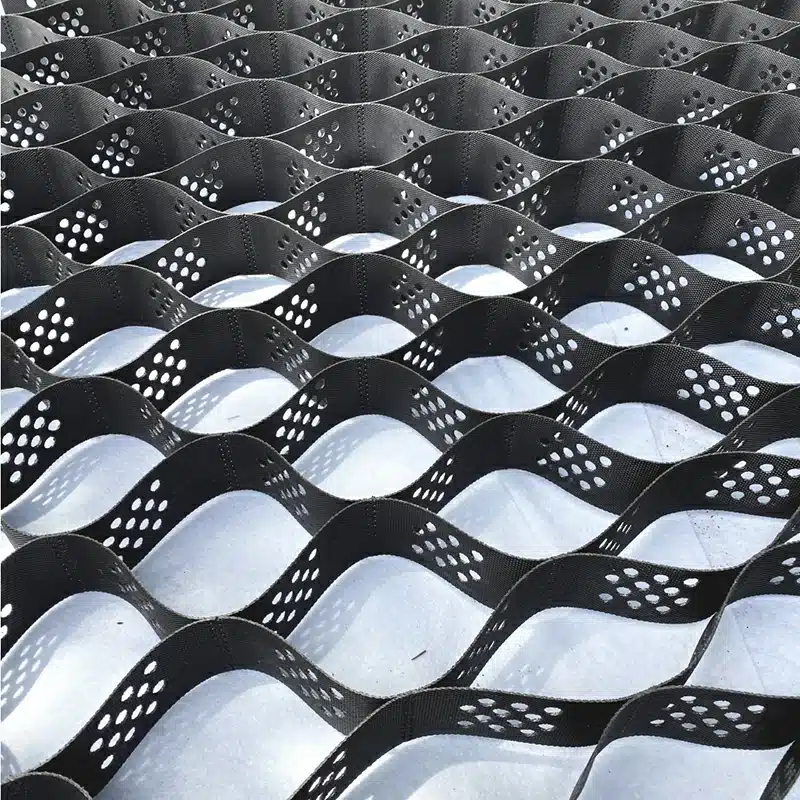
What is a Geocell Foundation?
When deployed, geocells confine the infill material within their interconnected cells, providing lateral support and distributing loads more evenly across the foundation. This confinement reduces the lateral movement of the soil, increases shear strength, and minimizes settlement. The result is a stable and durable foundation that can withstand significant loads and environmental stresses.
Key Benefits
- Enhanced Load Distribution: Geocell foundations distribute loads over a wider area, reducing pressure on underlying soils.
- Improved Soil Stabilization: They reinforce weak soils, increasing their bearing capacity and stability.
- Erosion Control: The structure helps prevent soil erosion, especially on slopes and embankments.
- Material Efficiency: Geocells allow the use of locally available or recycled materials as infill, reducing the need for high-quality aggregates.
- Environmental Sustainability: By reducing the need for extensive excavation and imported materials, geocell foundations contribute to more sustainable construction practices.
Common Applications
- Road and Pavement Construction: Providing a stable base for roads, especially in areas with soft subgrades.
- Slope and Channel Protection: Preventing erosion and stabilizing slopes.
- Retaining Walls: Enhancing the structural integrity of retaining structures.
- Railway and Airport Infrastructure: Supporting heavy loads and reducing maintenance needs.
In summary, geocell foundations offer a versatile and effective solution for ground stabilization, particularly in challenging soil conditions. Their ability to improve load distribution and soil strength makes them a valuable tool in modern construction and civil engineering projects.
What is Geocell Reinforcement?
- Road and Pavement Construction: Providing a stable and durable foundation for roads, highways, and pavements, particularly in areas with soft or weak subgrades, while reducing rutting and settlement.
- Slope and Channel Protection: Stabilizing slopes and channels by confining soil and aggregates, minimizing erosion, and improving resistance to water flow and surface runoff.
- Retaining Walls: Enhancing the stability and load-bearing performance of retaining structures by improving soil confinement and reducing lateral earth pressures.
- Railway and Airport Infrastructure: Supporting heavy dynamic loads from trains and aircraft, improving bearing capacity, and lowering long-term maintenance requirements.
In summary, geocell foundations provide a versatile and high-performance solution for ground stabilization in challenging soil conditions. By improving load distribution, soil strength, and durability, they play a crucial role in modern construction and civil engineering projects.
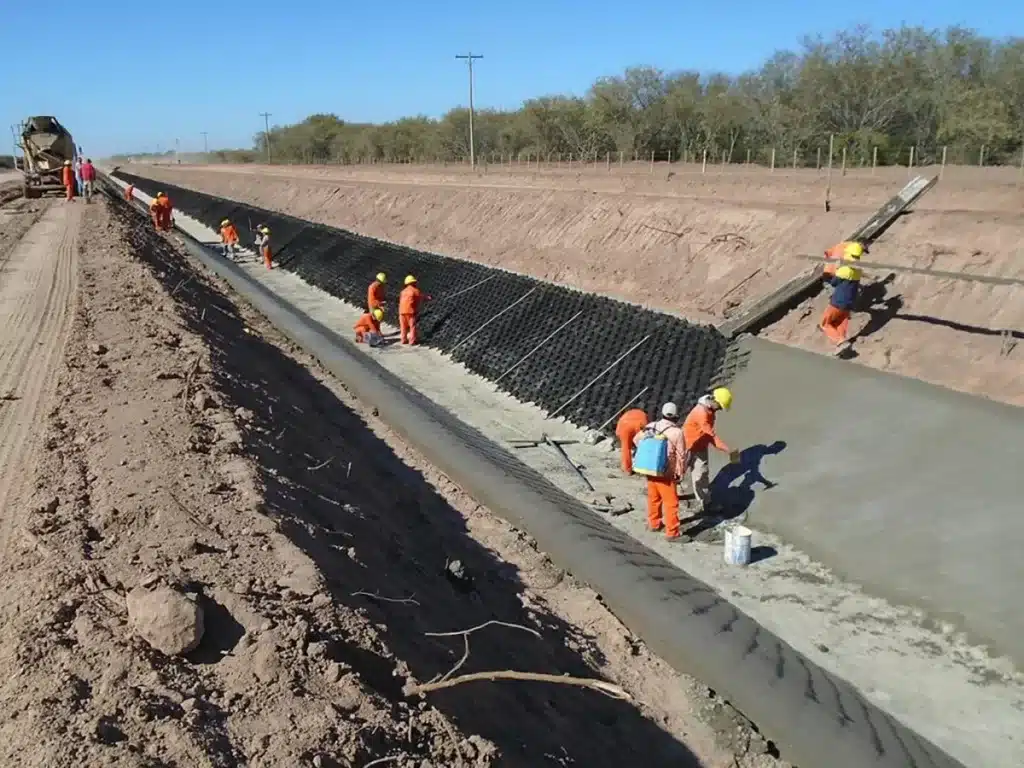

What is a Geocell in Civil Engineering?
In civil engineering, geocells are versatile tools used in construction for erosion control, soil stabilization, channel protection, and structural reinforcement for load support and earth retention. These cost-effective solutions enhance the performance of foundations, retaining walls, embankments, and green infrastructure projects. The application of geocells in civil engineering extends the lifespan of structures while lowering maintenance expenses.
What is the Difference Between Geogrid and Geocell?
Geogrids and geocells, both geosynthetic materials used in civil engineering, have distinct characteristics:
- Geogrids: Geogrids are flat sheets or grids made of synthetic materials like polyester or polypropylene, commonly used for soil reinforcement, especially in retaining walls and slopes. They offer tensile strength to the soil and are typically installed horizontally.
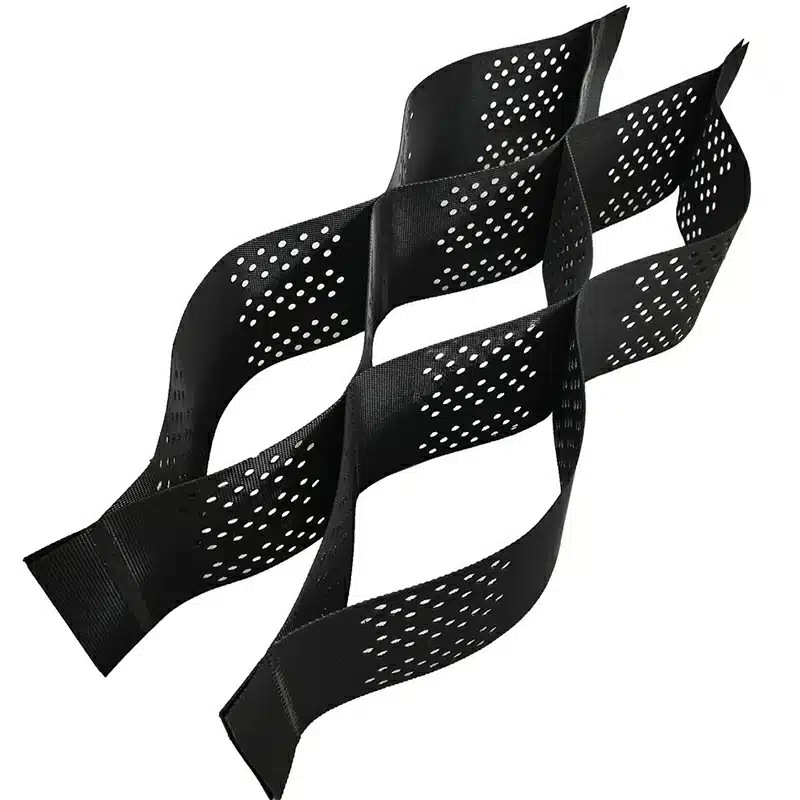
- Geocells: Geocells, as previously mentioned, are deep, three-dimensional cellular structures. They are versatile and find applications in soil stabilization, load support, and erosion control. Geocells form a three-dimensional matrix, providing both vertical and lateral confinement for fill material.
In essence, geogrids primarily strengthen soil horizontally, while geocells, with their three-dimensional mesh structure, offer strength and stability in both horizontal and vertical directions. This versatility makes geocells suitable for a broader range of applications, including foundations.
In conclusion, geocell-reinforced foundations have emerged as a game-changer in civil engineering, offering enhanced stability, load-bearing capacity, and erosion control. By understanding the concept of geocell foundations and their reinforcement techniques, civil engineers can harness the full potential of these innovative solutions to create more durable and resilient infrastructure.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















