+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
Geocomposites, combining geosynthetics like geotextiles, geomembranes, and geogrids, are transforming modern engineering with their versatile uses. They provide innovative solutions for soil stabilization, drainage, erosion control, and environmental protection, becoming essential in construction and civil engineering for efficient, cost-effective, and eco-friendly approaches.

What are geocomposites used for?
Geocomposites are multifunctional materials engineered to address various geotechnical challenges. They find extensive use in civil engineering, construction, and environmental projects, including applications for drainage from a basal layer in case of embankments and for drainage behind retaining walls and/or bridge abutments. Here are some key applications:
- Soil Reinforcement: Geocomposites enhance the stability of slopes and embankments by reinforcing drainage from a basal layer in the case of embankments and for drainage behind retaining walls and/or bridge abutments. They help prevent soil erosion and landslides, making them invaluable for infrastructure projects like highways and railways.
- Drainage: Geocomposites are employed for efficient subsurface drainage, facilitating the removal of excess water from the soil for drainage from a basal layer in the case of embankments and for drainage behind retaining walls and/or bridge abutments. This prevents saturation and ensures structural integrity in retaining walls, landfills, and sports fields.
- Environmental Protection: In environmental projects, geocomposites act as barriers to contain hazardous materials, such as landfill liners or pond liners, safeguarding surrounding ecosystems and groundwater.
- Erosion Control: Geocomposite mats and blankets offer erosion control solutions on riverbanks, shorelines, and construction sites. They help prevent soil loss and maintain environmental stability.
- Pavement Systems: Geocomposites are used to improve the performance of pavements. They distribute loads, reduce rutting, and enhance the durability of road surfaces.
What is geocomposite material?
A geocomposite consists of a combination of one or more geosynthetics, specifically a geogrid, a geotextile, a geomembrane, and/or a geonet, with another material. Geocomposites are engineered materials comprising geosynthetics, such as geotextiles, geomembranes, and geogrids, bonded together through various methods, including heat sealing and needle punching. This combination results in a composite material that exhibits enhanced properties compared to individual geosynthetics.
The primary components of a geocomposite include:
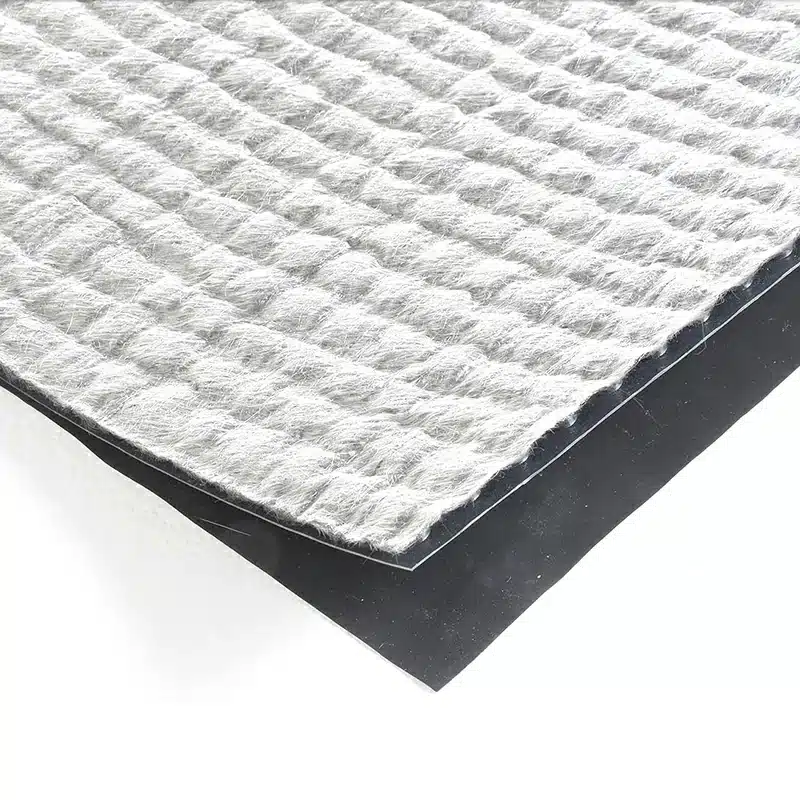
- Geotextiles: These are permeable fabrics designed to separate, filter, reinforce, and protect soils. Geotextiles are used primarily for applications requiring separation, filtration, reinforcement, and drainage. They enhance drainage, reduce soil erosion, and provide structural support.
- Geomembranes: Impermeable sheets that act as barriers against fluid or gas migration. They are used in containment systems and environmental protection projects.
- Geogrids: Grid-like structures made of polymers or other materials. Geogrids improve soil stability, distribute loads, and reinforce weak subsoils.

What is an example of a geocomposite?
A geocomposite is a product made from a combination of geosynthetic materials, designed for various civil engineering and environmental applications. These materials typically include a combination of geotextiles, geonets, geomembranes, geogrids, and/or geosynthetic clay liners. Each component in a geocomposite serves a specific function such as filtration, drainage, reinforcement, separation, or containment.
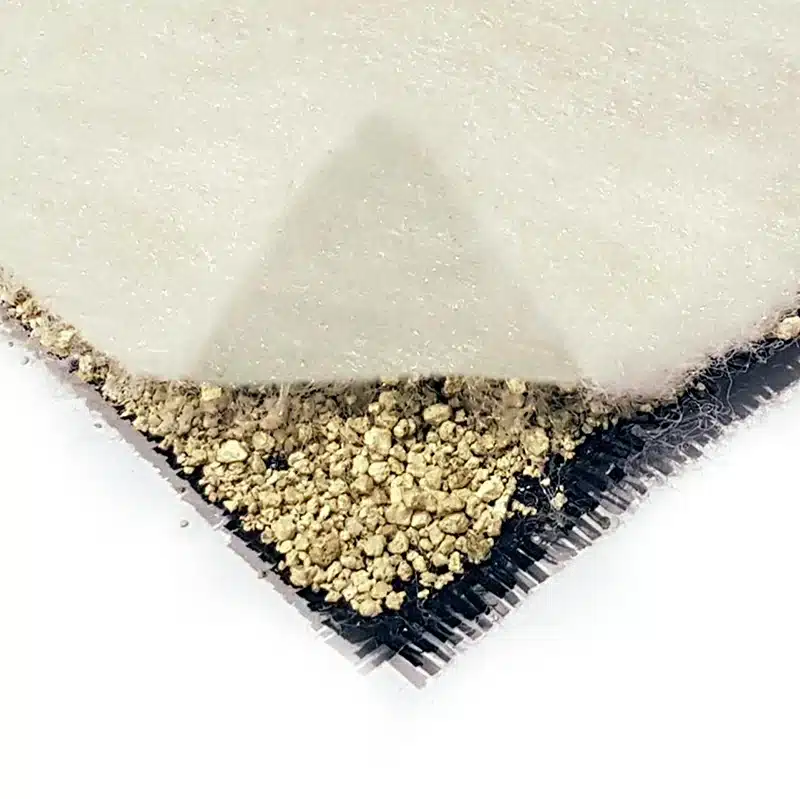
An example of a geocomposite is a drainage geocomposite. This type of geocomposite often consists of a geonet core sandwiched between two layers of geotextile. The geonet provides a channel for water flow, while the geotextiles perform filtration functions, preventing soil particles from clogging the geonet. This kind of geocomposite is commonly used in landfill liners, road construction, and behind retaining walls to facilitate efficient drainage and prevent water buildup and related problems.
What are the different types of geocomposites?
Geocomposites are engineered materials made by combining different types of geosynthetics. These combinations are designed to offer multiple functions such as separation, reinforcement, filtration, drainage, and containment. The types of geocomposites are generally categorized based on the combination of geosynthetics used and their intended applications. Here are some common types:
- Geotextile-Geonet Composites: These are often used for drainage applications. The geonet acts as a drainage core, allowing for the passage of fluids, while the geotextile, usually on one or both sides, provides filtration to prevent soil particles from clogging the drainage core.
- Geotextile-Geomembrane Composites: Combining a geomembrane (for impermeability) with a geotextile (for protection, separation, or filtration) results in a composite material often used in landfill liners, pond liners, and other containment applications.
- Geogrid-Geotextile Composites: These composites combine the reinforcing properties of geogrids with the separation and filtration properties of geotextiles. They are commonly used in road construction, especially over soft soils, and in retaining wall applications.
- Geosynthetic Clay Liner (GCL) Composites: GCLs are a type of geocomposite that combines geotextiles with bentonite clay. These are primarily used as a sealing layer in landfill liners, containment, and groundwater protection.
- Geomembrane-Geogrid Composites: These are used for reinforcement and containment, combining the high tensile strength of geogrids with the impermeability of geomembranes.
- Geotextile-Geocell Composites: Geocells provide a three-dimensional confinement system, and when combined with geotextiles, they can be used for soil stabilization, erosion control, and reinforcement applications.
- Geotextile-Geopipe Composites: These are used for effective drainage and filtration, where the pipe carries away the water, and the geotextile acts as a filter.
- Geocomposite Drainage Layers: These are multi-layered composites, often including a combination of geonets, geotextiles, and sometimes geomembranes, designed specifically for high-capacity drainage applications.
Each type of geocomposite is designed to address specific engineering challenges, and the choice of a particular geocomposite depends on factors such as soil type, environmental conditions, load requirements, and the specific application’s needs.
By categorizing geocomposites into drainage geocomposites, reinforcement geocomposites, and fluid barrier geocomposites, it becomes easier to understand their specific functions and applications in various engineering and environmental projects.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















