+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
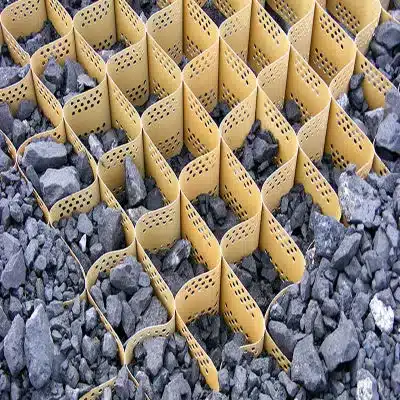
Geocells are an innovative and versatile technology widely used in civil engineering to stabilize and protect soils. Particularly effective in erosion control applications, these three-dimensional honeycomb-like structures confine materials to prevent soil displacement and promote vegetation growth. This article explores the applications of geocells, their uses in various environments, their specific role in erosion control, and alternatives to geocells in landscape management.
What are the applications of GeoCells?
Geocells are employed in a wide range of applications, primarily focused on improving ground stability and erosion control. Their versatility is showcased in various sectors including road construction, landfills, mining operations, and green infrastructure projects. Key applications include:
- Road Construction: They stabilize the subgrade to improve the load-bearing capacity of roads, ensuring long-term durability essential for heavy traffic conditions.
- Slope Protection: Geocells help hold the earth and prevent landslides or washouts on slopes, which is crucial in mining operations where earth stability is a frequent concern.
- Channel Protection: They are used to line drainage channels to prevent erosion, commonly seen in landfills and urban infrastructure projects to manage runoff effectively.
- Retaining Walls: Geocells can be stacked to form flexible, permeable, and durable retaining structures, beneficial in both urban and natural settings for managing earth and water.
- Landscaping: They provide soil stabilization in parks and gardens, enhancing vegetation without erosion, a core component of green infrastructure projects designed to integrate ecological functionality in urban environments.
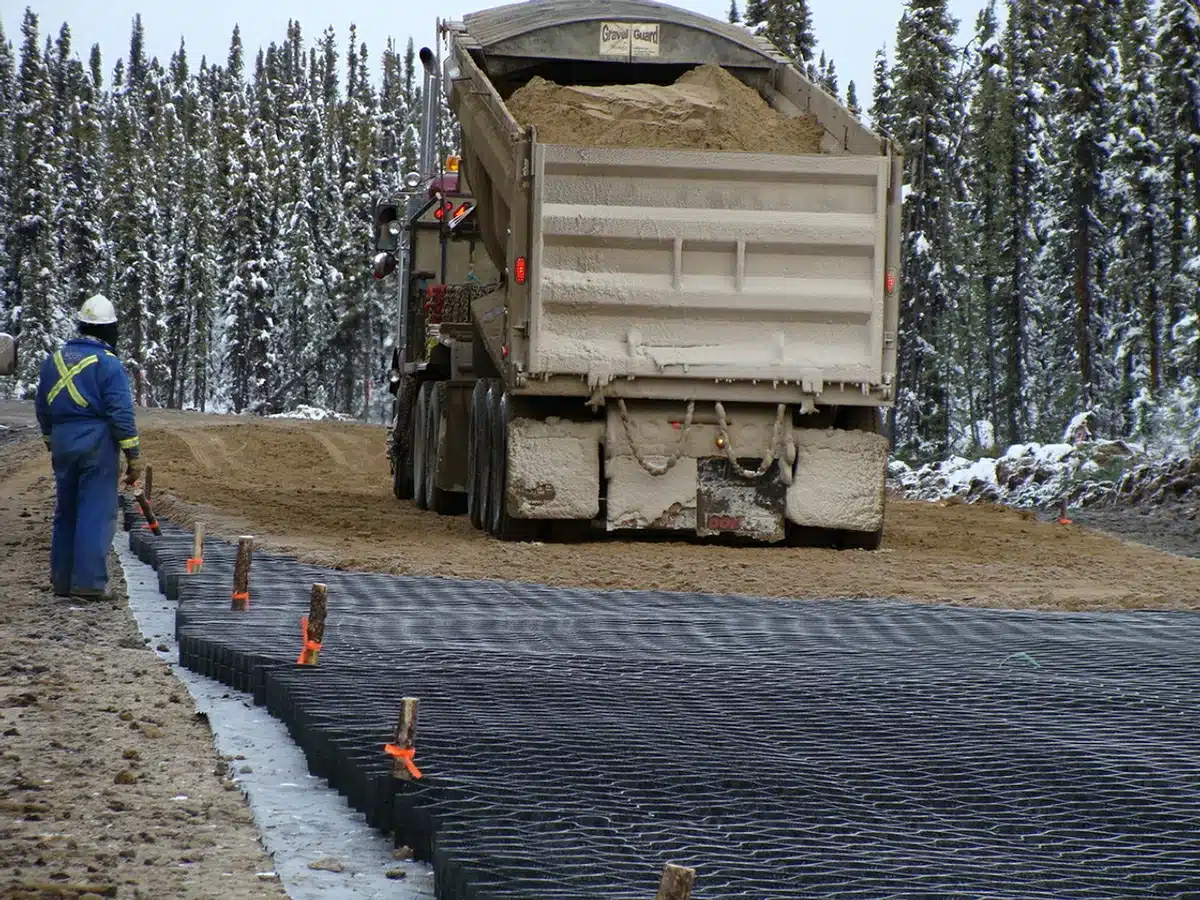

Where are geocells used?
Geocells find their utility in diverse settings, each demanding unique environmental and structural resilience. Their applications span construction for erosion control, soil stabilization on flat ground and steep slopes, channel protection, and structural reinforcement for load support and earth retention:
- Infrastructure Projects: Highways, railways, and airports utilize geocells for foundation stability and longevity, enhancing structural reinforcement for load support crucial for such heavily trafficked areas.
- Environmental Conservation Areas: Erosion-prone areas, like riverbanks and coastal zones, benefit from geocells in maintaining landscape integrity through construction for erosion control and soil stabilization on steep slopes.
- Agricultural Lands: They are used to stabilize irrigation channels and prevent soil erosion in farming terrains, ensuring channel protection and soil stabilization on flat ground which are vital for crop success.
- Urban Planning: In city landscapes, geocells help manage stormwater and reduce sediment runoff, playing a key role in structural reinforcement for earth retention and effective water management.
What is a GeoCell for erosion?
In the context of erosion covered, a geocell is a geosynthetic material that confines soil in its cells to prevent erosion by water or wind. The cells confine the infill material, creating a stable layer that protects the slope from erosion. When filled with soil, sand, or aggregate, geocells create a stable base that distributes weight evenly, reducing pressure on the soil and maintaining surface integrity. This structure is particularly effective on slopes and in areas exposed to high levels of surface runoff, as it retains earth materials and supports plant growth, thus establishing a natural barrier against erosion.
What is the alternative for geocells?
While geocells are a preferred solution for many soil stabilization needs, there are alternatives that can also be effective, depending on the project requirements. For more complex or difficult areas, geogrids provide more stabilization and are often a better solution:
- Geotextiles: These permeable fabrics, when used alone or in conjunction with other materials such as geogrids, help with soil filtration, separation, and stabilization, enhancing the overall effectiveness in challenging environments.
- Gabions: Made from wire mesh and filled with rock, gabions serve as a bulkier, yet effective, alternative to manage erosion, especially in retaining walls and shoreline structures where additional stability is required.
- Riprap: Consisting of large stones placed along shorelines or riverbanks, riprap is a simple, natural solution to reduce water erosion, and when combined with geogrids, can offer enhanced stabilization.
- Bioengineering Techniques: Combining vegetation with structural support, such as coir mats or vegetative geogrids, offers an eco-friendly alternative that enhances landscape aesthetics and sustainability, particularly effective in areas needing robust structural reinforcement.
Geocells are a robust and environmentally friendly solution to soil stabilization challenges, particularly effective in erosion control applications. Their adaptability across various environments—from agricultural fields to urban infrastructures—demonstrates their critical role in contemporary landscape management. While alternatives like geotextiles and gabions offer different benefits, geocells remain a top choice for projects requiring efficient, reliable, and sustainable soil confinement solutions. By integrating geocell technology, we can better protect and preserve our natural and built environments against the forces of erosion.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















