+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
In the realm of railway infrastructure development, engineers constantly seek innovative solutions to address challenges like soil stabilization, erosion control, and load distribution. One such groundbreaking technology that has gained traction in recent years is the geocell. Geocells, also known as cellular confinement systems, are three-dimensional honeycomb-like structures made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or other durable materials. They have emerged as a versatile and effective tool for enhancing the performance and longevity of railway tracks and embankments. Approved by Network Rail as the solution to improve and regulate track bed stiffness, and reduce both maintenance and installation time and cost, geocells offer a sustainable solution to longstanding challenges. In this article, we delve into the world of geocells in railway engineering, exploring their purpose, applications, construction details, and key differentiators from other geosynthetic materials like geogrids.
What is the purpose of a Geocell?
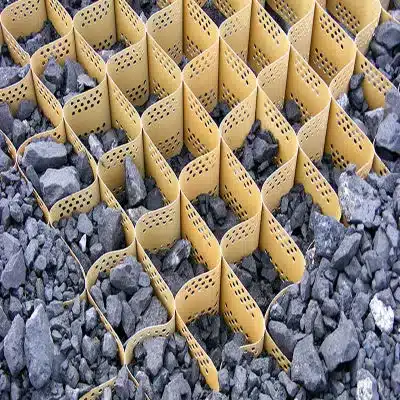
Geocells, also known as cellular confinement systems, are three-dimensional honeycomb-like structures made from various materials such as high-density polyethylene (HDPE). The primary purpose of geocells is to provide reinforcement and stabilization to soil in various civil engineering applications. Here are some key purposes and benefits of using geocells:
- Soil Confinement: Geocells confine and stabilize soil within their interconnected cells, preventing lateral movement and enhancing load distribution. This confinement improves the load-bearing capacity of weak soils.
- Erosion Control: By stabilizing soil particles, geocells reduce erosion caused by water flow, thereby protecting slopes and embankments from erosion damage.
- Load Support: Geocells distribute applied loads over a wider area, reducing stress on underlying soils and increasing the load-bearing capacity of the ground. This makes them useful in applications such as road and railway embankments, parking lots, and even retaining walls.
- Vegetation Support: In environmental applications, geocells can be filled with soil and used to support vegetation growth on slopes, promoting green infrastructure and ecological restoration.
- Quick Installation: Geocells are lightweight and easy to transport, allowing for rapid deployment and installation in various terrain conditions.
Overall, geocells are versatile geosynthetic products that play a crucial role in stabilizing soils, preventing erosion, and enhancing the performance of civil engineering projects.
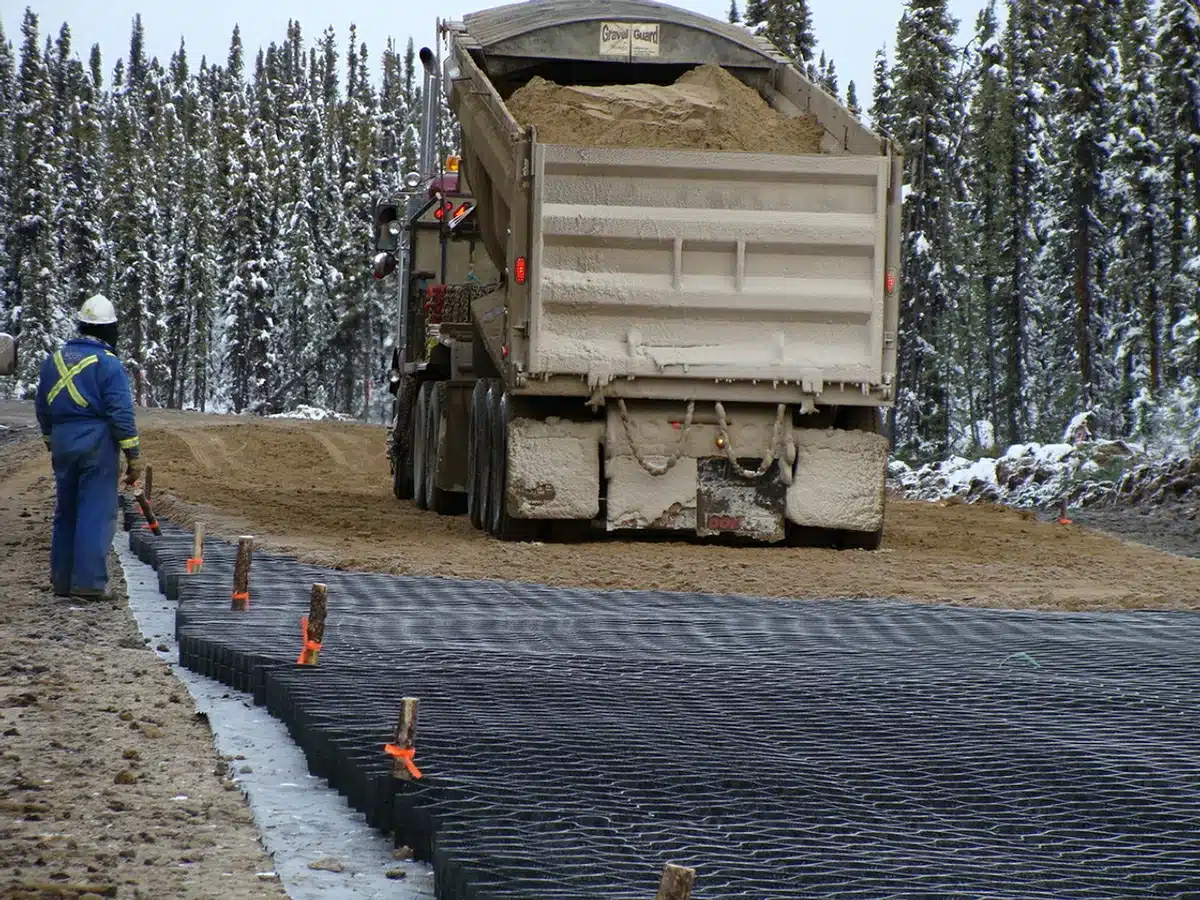

When to use Geocell?
Geocells are beneficial in various civil engineering and environmental applications where soil stabilization, erosion control, and load support are critical. Here are some specific situations and conditions where geocells are commonly used:
- Soft Soil Stabilization: Geocells are effective in stabilizing soft or weak soils by confining them within the cells, thereby increasing their load-bearing capacity. This is useful in areas with poor soil conditions where traditional construction methods might not provide adequate support.
- Slope and Embankment Stabilization: Geocells can be used to stabilize slopes and embankments, reducing erosion and preventing soil movement. They help maintain the integrity of slopes against natural forces such as rainfall and runoff.
- Road and Railway Construction: Geocells are used in the construction of roads, highways, and railways to reinforce the subbase and improve the load-bearing capacity of the ground. They help distribute loads evenly, reducing settlement and extending the lifespan of the pavement structure.
- Retaining Walls: Geocells are employed in the construction of retaining walls to enhance stability and prevent soil erosion. They provide structural support and can be filled with soil or aggregate to create a stable foundation for the wall.
- Erosion Control: Geocells are effective in erosion control applications along riverbanks, shorelines, and steep slopes. They stabilize soil particles and prevent erosion caused by water flow, protecting the environment and infrastructure.
- Green Infrastructure: Geocells filled with soil can support vegetation growth on slopes and embankments, promoting green infrastructure and ecological restoration projects.
- Load Support in Landfills: Geocells are used in landfill applications to provide support for heavy equipment and landfill caps. They help distribute the weight of the landfill materials and protect the underlying soil and groundwater from contamination.
In summary, geocells are versatile and can be used in various situations where soil stabilization, erosion control, load support, and environmental protection are priorities. Their effectiveness makes them a valuable solution in both infrastructure projects and environmental restoration efforts.
What is geocell details?
Geocells consist of interconnected cells or chambers formed by welding or ultrasonic bonding sheets of HDPE or other polymer materials. This innovative design improves soil stabilization, facilitates efficient load transfer, and provides robust erosion control, ensuring the longevity and performance of railway infrastructure. These cells are typically filled with locally available soil, aggregate, or concrete, and compacted to achieve the desired density and strength. Geocell panels are modular in design, allowing for easy transportation, handling, and installation on-site. The height, thickness, and cell geometry of geocells can vary depending on project requirements and design specifications. Advanced geocell systems may feature perforated walls for enhanced drainage or textured surfaces to improve interface friction with surrounding materials.
What is the difference between geogrid and geocell?
While both geogrids and geocells are geosynthetic materials used in civil engineering, they serve distinct functions and exhibit different structural properties. Geogrids are flat, grid-like sheets made from materials like polyester or polypropylene, designed primarily for soil reinforcement and slope stabilization. They function by distributing loads and reducing tensile stresses in soil structures. The geocell is a deep, three-dimensional mesh structure, while the geogrid is typically two-dimensional. In contrast to geogrids, geocells are composed of interconnected cells, providing confinement and lateral support to soil or aggregate infill. Geocells offer superior load-bearing capacity, soil confinement, and erosion control compared to geogrids, making them more suitable for applications requiring heavy-duty reinforcement and stability, such as railway embankments.
In summary, geocells have revolutionized the field of railway engineering by offering a versatile, cost-effective, and sustainable solution for soil stabilization, erosion control, and load support. Their unique three-dimensional design and structural integrity make them indispensable in enhancing the performance and longevity of railway tracks and embankments. By understanding the purpose, applications, construction details, and differentiating factors of geocells compared to other geosynthetic materials, railway engineers can make informed decisions to optimize the design and construction of railway infrastructure for years to come.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















