+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
Geocells vs. Geogrids are both essential materials in the field of soil stabilization and reinforcement, often used in construction, civil engineering, and environmental applications. These materials are designed to improve the load-bearing capacity of weak soils, enhance drainage, and prevent erosion. However, their composition, functionality, and ideal use cases differ.
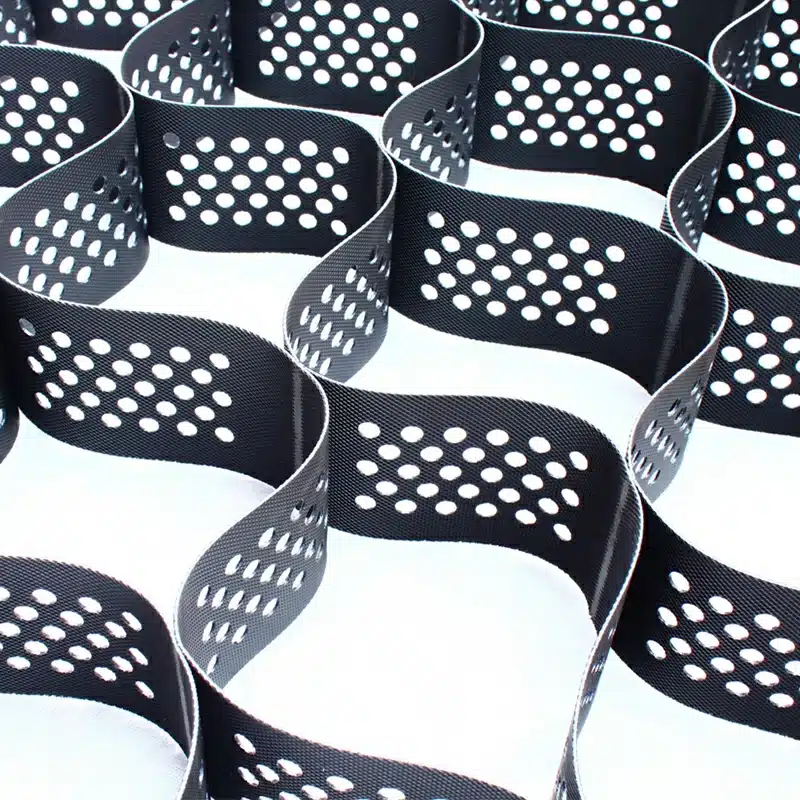
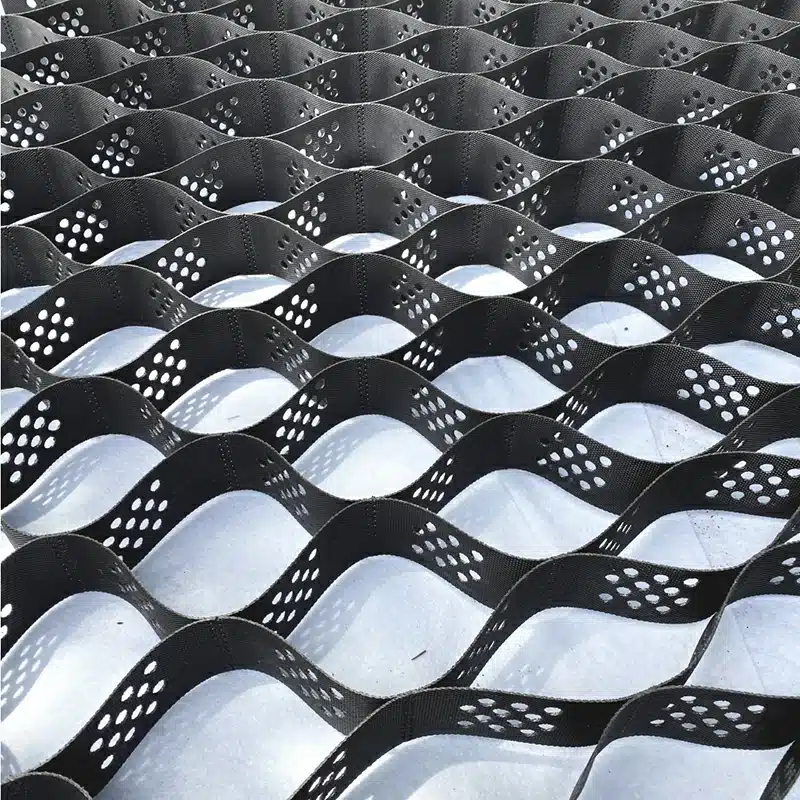
Geocells are three-dimensional, honeycomb-like structures made from polymer materials, which expand and form a grid-like pattern when filled with soil or gravel. This structure creates a confinement effect, which enhances the stability and strength of the soil beneath.
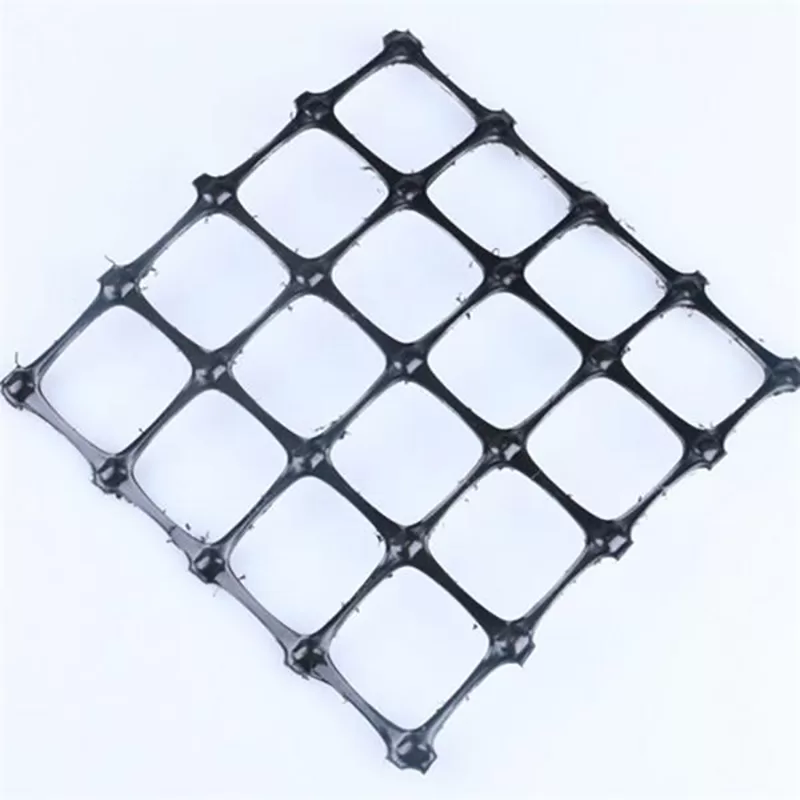
Geogrids are typically two-dimensional grid materials, often made from polymers, fiberglass, or steel, designed to reinforce soil by providing tensile strength and support. They are generally used to distribute loads evenly across the surface and prevent soil shifting.

Detailed Comparison:
Definition and Composition:
- Geocells: Typically made from HDPE (high-density polyethylene) or similar materials, geocells are flexible, expandable, and used to create a cellular structure that confines the soil, reducing lateral movement.
- Geogrids: These are either biaxial or uniaxial grids made from polymers, glass, or metal, designed to resist stretching and shifting under load.
Common Applications:
- Geocells: Often used in soil stabilization, slope protection, road construction, and erosion control. They are especially beneficial in areas with soft soils that require reinforcement to handle heavy loads.
- Geogrids: Primarily used for road and railway subgrade stabilization, retaining walls, and reinforcing embankments.
Performance Characteristics:
- Load Distribution: Both materials help distribute loads, but geogrids typically excel at horizontal load distribution due to their tensile strength. Geocells, on the other hand, excel at vertical load distribution due to their confinement properties.
- Drainage Capabilities: Geocells, due to their 3D structure, often provide better drainage as water can flow through the cells, reducing the risk of waterlogging. Geogrids typically offer less drainage but provide better reinforcement.
- Durability: Both materials are highly durable, though geogrids, especially those made from fiberglass or steel, can offer superior strength in harsher conditions.
Cost Considerations and Availability:
- Geocells: Generally more expensive due to their complex manufacturing process and material properties. They may also require specialized installation.
- Geogrids: Usually more affordable and widely available, with various types suited for different construction needs.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability:
- Geocells: These can reduce the amount of material required for construction, as they stabilize the soil without the need for heavy aggregates. Their design can also reduce soil erosion, making them more sustainable for environmental projects.
- Geogrids: Although geogrids can be more resource-intensive, their longevity and reusability contribute to sustainability. The reduction in material usage for projects like roadbeds can also reduce overall environmental impact.
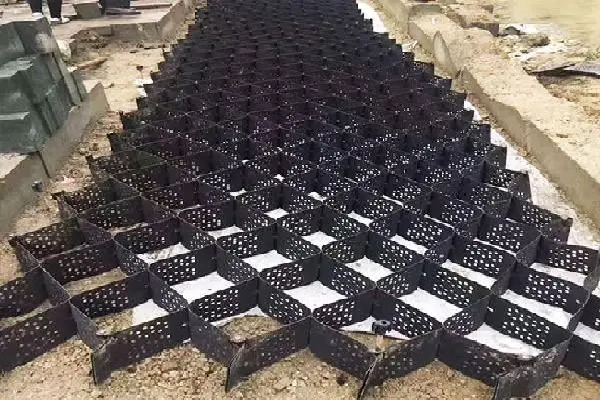

In conclusion, both geocells and geogrids have unique strengths in the soil stabilization and reinforcement market. Geocells are ideal for applications where load distribution and drainage are critical, while geogrids are more suitable for applications requiring tensile strength and load-bearing over a larger surface area. For construction projects where environmental sustainability and cost are key considerations, geogrids may be a more practical choice. However, for projects requiring complex soil stabilization or erosion control, geocells are likely to offer superior performance.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















