+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
Hillside erosion is a pervasive issue that threatens soil stability and landscape integrity, particularly in areas prone to heavy rains or lacking vegetation. Ground covers, specifically innovative geocell technology, provide a robust solution to mitigate this issue. Designed for both residential and commercial applications, a variety of different pocket sizes and heights are available to suit the specific application. This article explores the efficacy of geocells as a ground cover option for hillside erosion control, addressing their application, suitability for various slopes, and optimal materials for enhanced performance.
What is the maximum slope for geocell?
General Guidelines:
- The maximum slope angle for geocell installation typically ranges between 1:1 (45 degrees) and 1:1.5 (34 degrees).
- This range can vary based on the type of geocell, soil conditions, and external factors such as vegetation and load-bearing requirements.
Factors Affecting Maximum Slope Angle:
- Soil Type: Different soils (clay, sand, gravel) have varying shear strengths which influence slope stability.
- Geocell Properties: The material, height, and cell size of the geocell can affect its performance on slopes.
- External Loads: Additional loads, such as vehicular traffic or construction activities, can reduce the allowable slope angle.
- Environmental Conditions: Weather conditions, such as heavy rain or freeze-thaw cycles, can impact slope stability.
Performance and Stability Impacts:
- Proper geocell installation enhances slope stability by providing confinement to the infill material, reducing erosion, and improving load distribution.
- Higher slope angles may require additional stabilization measures such as anchors or vegetation.
Best Practices:
- Conduct thorough site assessments to determine soil characteristics and slope conditions.
- Follow manufacturer guidelines and consult with geotechnical engineers for specific project requirements.
- Incorporate additional stabilization techniques as necessary for steeper slopes.
Geocell installations are versatile but must be carefully designed to match the specific site conditions and requirements. Understanding the factors influencing the maximum allowable slope angle is crucial for ensuring the stability and performance of the geocell system.
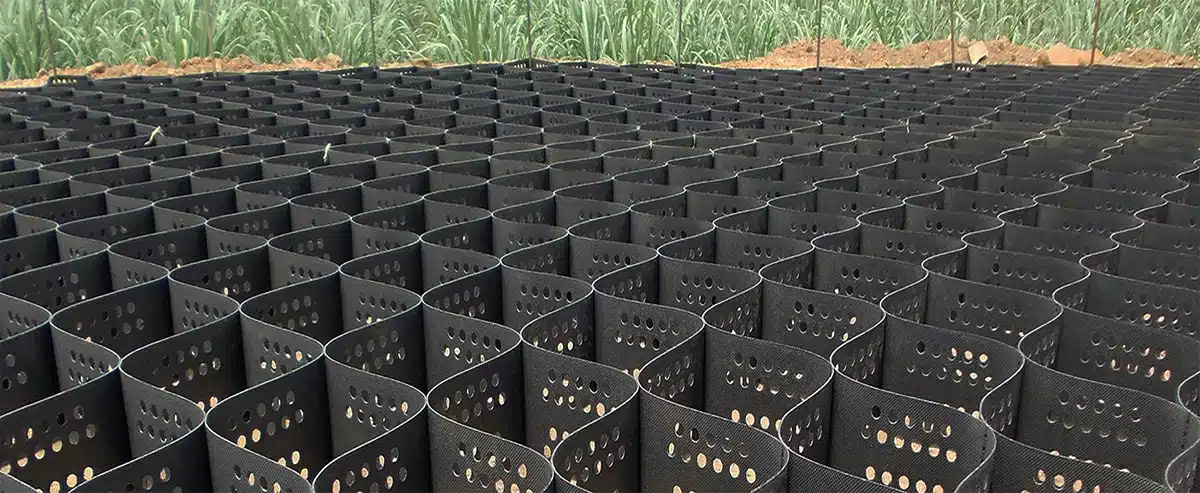

What is geocell in slope protection?
Definition and Structure
- Geocell: A geocell is a three-dimensional, honeycomb-like cellular confinement system made from polymer materials such as high-density polyethylene (HDPE).
- Structure: It consists of interconnected cells that can be expanded to form a strong, flexible mat when filled with soil, gravel, or other infill materials.
Materials
- Polymer Base: Typically constructed from high-density polyethylene (HDPE) for durability and flexibility.
- Infill Materials: Soil, sand, gravel, concrete, or other locally available materials can be used to fill the cells.
Installation Process
- Site Preparation: Clear the area of debris and level the slope if necessary.
- Anchoring: Secure the geocell at the top of the slope to anchor it in place.
- Expansion: Expand the geocell sections and anchor them along the slope.
- Filling: Fill the cells with the chosen infill material, ensuring even distribution and compaction.
- Covering (optional): A protective layer of vegetation or further infill may be added to enhance stability.
Effectiveness in Preventing Erosion and Landslides
- Erosion Control: Geocells reinforce the soil structure, reducing surface runoff and soil erosion.
- Slope Stabilization: The cellular confinement improves load distribution, which increases slope stability and reduces the risk of landslides.
- Environmental Benefits: Geocells promote vegetation growth, further stabilizing the slope and enhancing the ecosystem.
Geocells are an effective solution for slope protection, offering structural reinforcement, erosion control, and improved slope stability. Their versatility in materials and ease of installation make them a preferred choice in various civil engineering and environmental projects.
What is the best gravel for geocell?
The best gravel for use within a geocell system is angular crushed stone with a size range of 0.75 to 1.5 inches. This size ensures optimal interlocking of the gravel pieces, which enhances the overall structural integrity of the geocell system. Angular gravel is preferred over rounded gravel, such as Pea Gravel, because it provides better friction and interlock, reducing internal movement and offering superior erosion control on slopes.
When to use Geocell?
Geocell should be used in scenarios where soil stabilization and erosion control are critical, such as on steep slopes, in areas with loose soil, or where vegetation alone cannot prevent soil degradation. It is particularly beneficial in infrastructure projects like road embankments, hillside gardens, and around water bodies where soil erosion can lead to significant environmental and structural issues. Employed to protect slopes from erosion and help stabilize the surface, geocell installations are also ideal in areas that require immediate stabilization and quick vegetation support.
Geocells offer an effective and environmentally friendly solution for controlling erosion on hillsides. Their adaptability to different slopes and conditions, ability to hold various types of fill materials, and enhancement of slope stability make them a go-to choice for engineers and landscape architects. By choosing the right type of geocell and corresponding materials like angular gravel, the longevity and durability of slope protection can be significantly improved, ensuring sustainable land management practices.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















