+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
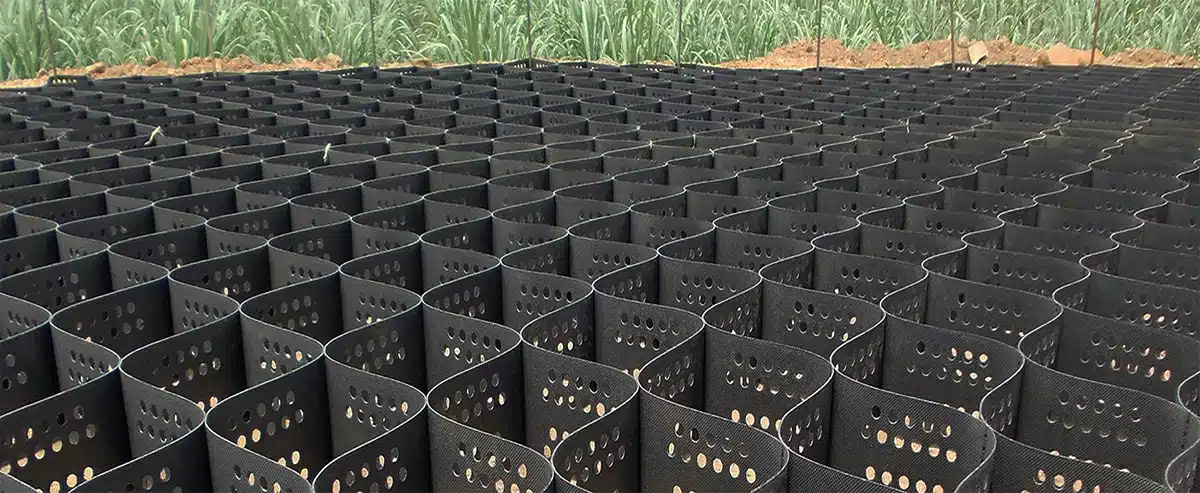
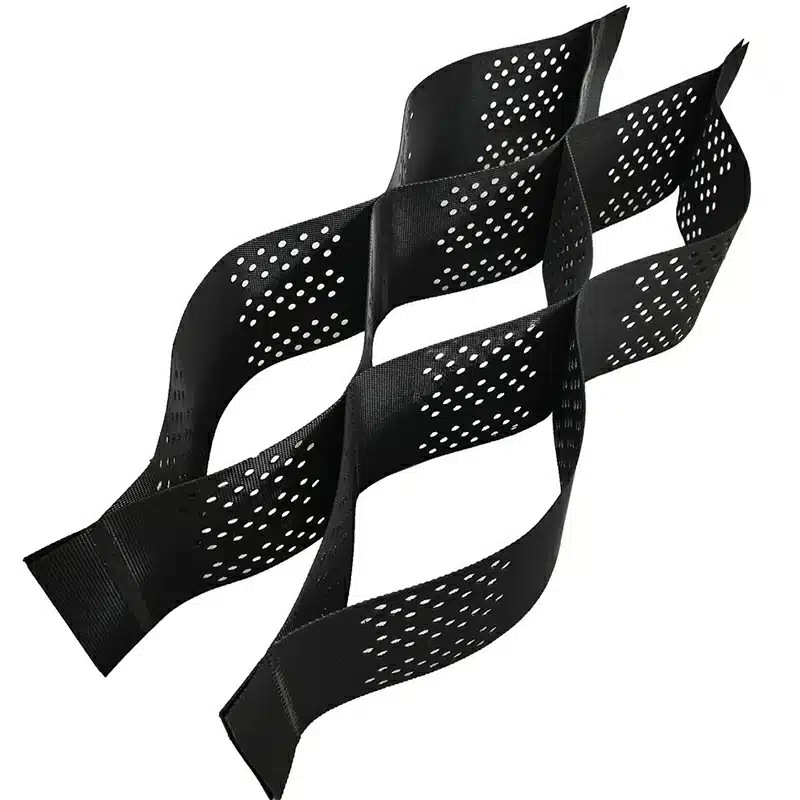
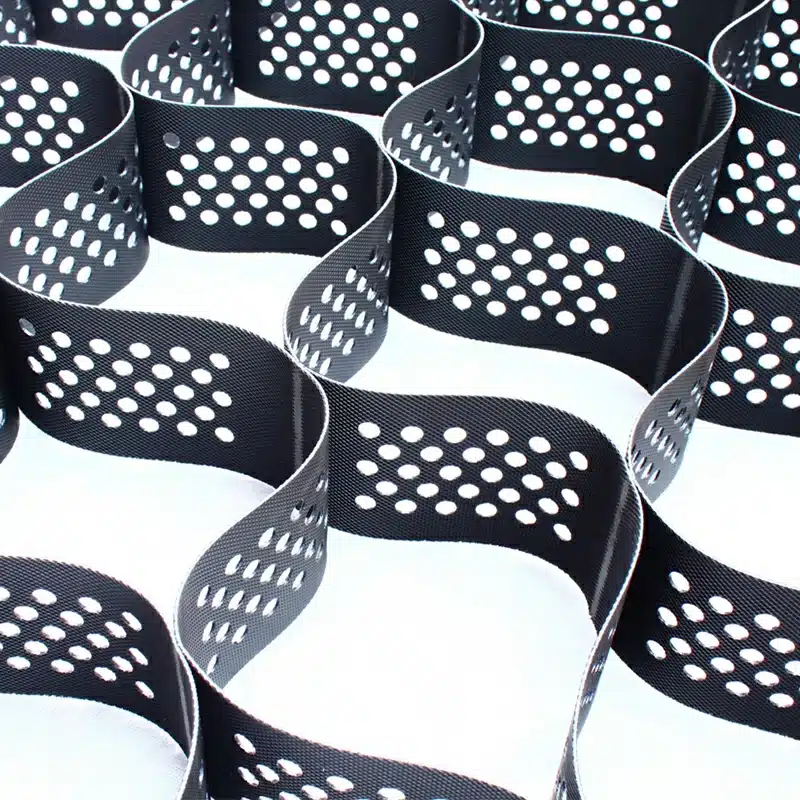
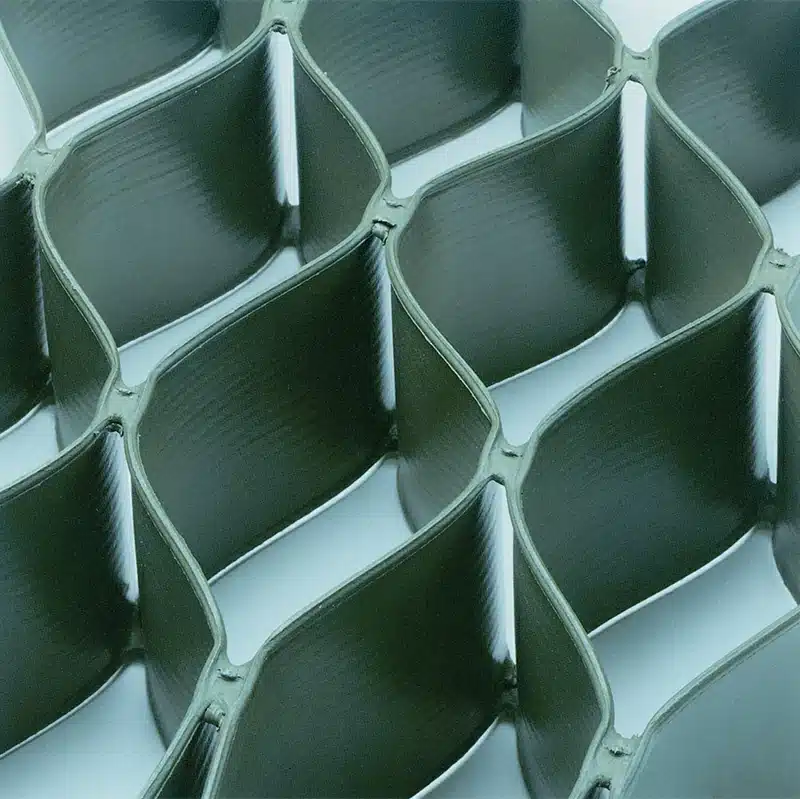
Geocells are a type of geosynthetic material widely used in construction and civil engineering projects. They consist of a honeycomb-like structure made from polymer strips that are joined together to form flexible, three-dimensional cells. These cells can be filled with soil, gravel, or other materials to create a stable and reinforced structure. The versatility of geocells makes them an essential tool in various applications, particularly to protect slopes from erosion and help stabilize the surface, as well as in erosion control, slope stabilization, and load support. This article explores the uses, benefits, and characteristics of geocells, as well as how they compare to other geosynthetic materials like geogrids.
What Are Geocells Used For?
Geocells are used in a variety of civil engineering and construction applications to improve the structural integrity and durability of soil and aggregate materials. They are versatile tools that find common applications in erosion control, soil stabilization on flat ground and steep slopes, channel protection, and structural reinforcement for load support and earth retention. Some of the most common uses of geocells include:
- Erosion Control: Geocells are effective in preventing soil erosion by confining and stabilizing the soil within their cells. This is particularly useful in areas with steep slopes or where water runoff is a concern.
- Slope Stabilization: Geocells provide additional support to slopes, reducing the risk of landslides or slope failure. They help distribute the load evenly and prevent soil movement.
- Load Support: In applications like road construction or railway track beds, geocells are used to distribute the weight of heavy loads over a larger area, reducing the pressure on the underlying soil and preventing rutting and settlement.
- Retaining Walls: Geocells can be used in the construction of retaining walls by reinforcing the soil behind the wall and providing additional stability.

What Is the Difference Between Geogrid and Geocell?
While both geogrids and geocells are geosynthetic materials used in construction, they serve different purposes and have distinct structures. In summary, geogrids primarily provide tensile reinforcement to soils, enhancing their stability, while geocells confine and stabilize granular materials within their cells, creating a rigid structure. Geogrids are grid-like and focus on reinforcement, while geocells are cellular structures that confine fill material.
- Structure: Geogrids are grid-like structures made from polymers, featuring large apertures between the ribs. In contrast, geocells are three-dimensional honeycomb-like structures that form cells when expanded.
- Function: Geogrids are primarily used for soil reinforcement, enhancing the tensile strength of the soil. They are often used in road construction, embankment reinforcement, and retaining walls. Geocells, on the other hand, are used for load distribution, erosion control, and slope stabilization. The three-dimensional structure of geocells allows them to confine and stabilize soil, making them ideal for applications where lateral soil movement is a concern.
- Application: Geogrids are commonly used in planar applications, such as reinforcing the base of roads or retaining walls, whereas geocells are used in both planar and three-dimensional applications, such as slope stabilization and erosion control.
What Is Geocell in Slope Protection?
In slope protection, geocells play a crucial role in preventing soil erosion and slope failure. Employed to protect slopes from erosion and assist in stabilizing the surface, geocells are laid out and filled with soil, gravel, or other materials to create a stable and reinforced structure. The honeycomb structure of the geocell confines the fill material, reducing the likelihood of soil movement and erosion caused by water runoff or wind. This is particularly important in areas with steep gradients or where slopes are subjected to heavy rainfall or other environmental stresses.
Geocells also enhance the overall stability of the slope by distributing the load evenly across the surface, reducing the stress on any one point and preventing localized failures. This makes geocells an ideal solution for slope protection in road embankments, riverbanks, and other areas prone to erosion.
What Are the Characteristics of a Geocell?
Geocells possess several key characteristics that make them effective in various construction and engineering applications:
Flexibility: Geocells are made from flexible polymer materials, allowing them to conform to the contours of the terrain. This adaptability makes them suitable for use on uneven or irregular surfaces.
- High Tensile Strength: The polymer strips that makeup geocells are designed to withstand significant tensile forces, providing strong reinforcement to the confined materials. This reinforcement increases the base course’s stiffness and strength while lowering surface permanent deformation.
- Durability: Geocells are resistant to chemical degradation, UV radiation, and other environmental factors, ensuring long-term performance even in harsh conditions.
- Permeability: The open structure of geocells allows for water drainage, reducing the risk of water buildup and associated issues like soil liquefaction or erosion.
- Ease of Installation: Geocells are lightweight and can be easily transported and installed on-site, making them a cost-effective solution for many projects.
Geocells are versatile geosynthetic materials used in various construction and civil engineering applications, including erosion control, slope stabilization, load support, and retaining wall construction. Their unique honeycomb structure allows them to confine and stabilize soil or aggregate materials, making them an effective solution for enhancing the durability and stability of soil structures. Understanding the differences between geocells and other geosynthetic materials like geogrids can help in selecting the right solution for specific project needs. With their flexibility, durability, and ease of installation, geocells are a valuable tool in modern construction and engineering.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















