+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
In the quest for sustainable waste management solutions, the importance of efficient landfill design cannot be overstated. Among the myriad of technologies and materials employed to enhance the functionality and environmental safety of landfills, geocomposite drainage layers stand out for their effectiveness and versatility. This article delves into the intricacies of geocomposite drainage layers used in landfills, exploring their definition, purpose, properties, and the pivotal role they play in modern waste management practices.
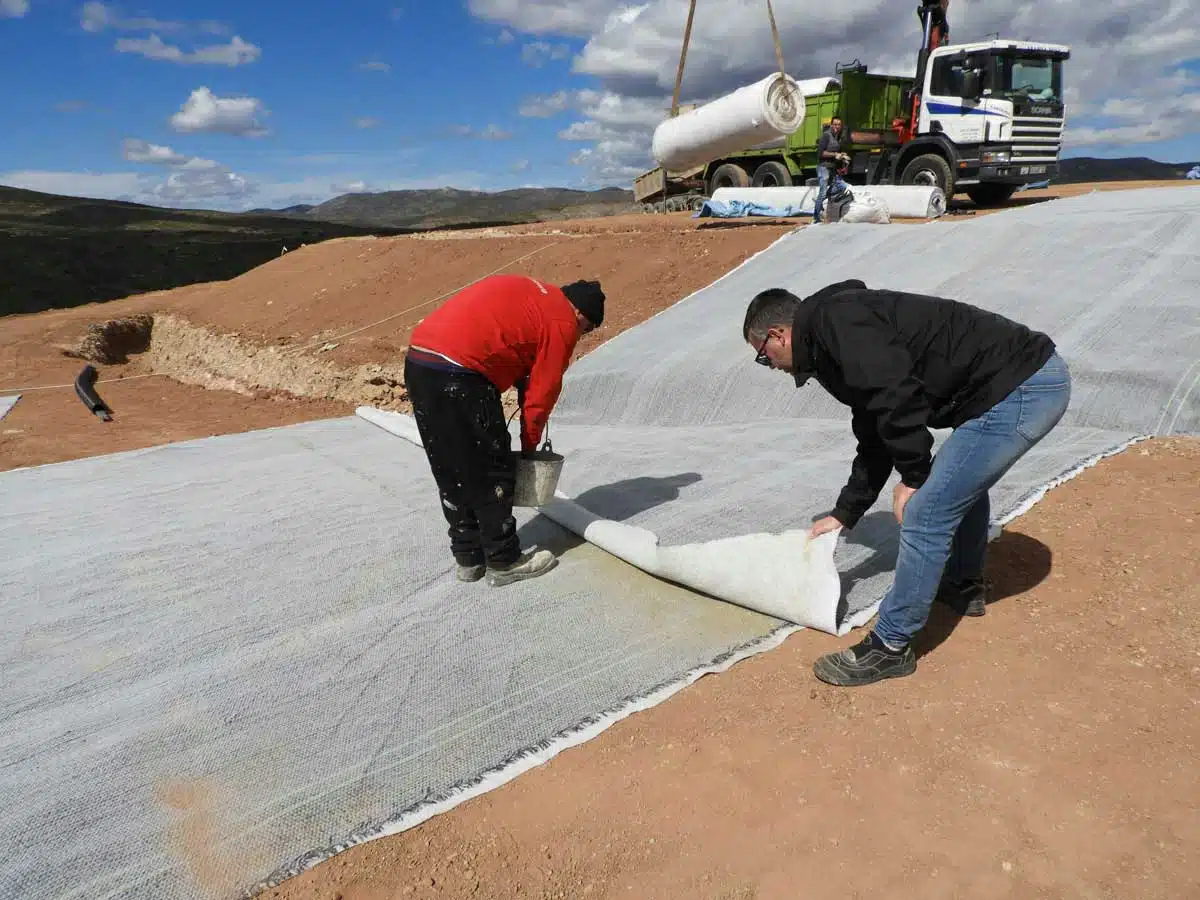

What is a Drainage Layer in a Landfill?
Purpose and Function:
- Purpose: The drainage layer in a landfill is designed to collect and channel leachate—a liquid that has percolated through waste material—away from the landfill to prevent it from contaminating surrounding soil and groundwater.
- Function: It serves to facilitate the removal of leachate, ensuring that it can be safely treated or disposed of, thereby preventing environmental pollution and maintaining the structural integrity of the landfill.
Composition:
- Materials Used: Typically composed of granular materials like gravel or sand, or synthetic materials such as geonets and geotextiles.
- Permeability: These materials are chosen for their high permeability, allowing liquids to pass through easily while providing structural support.
Installation Process:
- Base Preparation: The base of the landfill is first prepared and compacted.
- Liner Placement: A liner system, usually made of clay or synthetic materials, is installed to prevent leachate from escaping into the ground.
- Drainage Layer Installation: The drainage layer is placed on top of the liner. For granular materials, this involves spreading and leveling gravel or sand. For synthetic materials, geonets or geotextiles are rolled out and secured in place.
- Collection Pipes: Perforated pipes may be installed within the drainage layer to collect and transport leachate to a treatment facility.
Leachate Management:
- Collection: The drainage layer captures leachate and directs it towards collection points.
- Transport: The collected leachate is transported via pipes to a storage area or directly to a treatment plant.
- Treatment: Leachate is treated to remove harmful contaminants before being safely discharged or reused.
Environmental Protection:
- Contamination Prevention: By efficiently collecting and removing leachate, the drainage layer prevents it from infiltrating the surrounding soil and groundwater, thus protecting the environment from contamination.
- Compliance: Proper leachate management ensures that the landfill complies with environmental regulations and standards.
What is a Geocomposite Drainage Layer?
A Geocomposite Drainage Layer is a modern engineering material designed to facilitate effective drainage and water management in various civil engineering and construction applications. Here is a detailed explanation:
Composition
A Geocomposite Drainage Layer typically consists of multiple components combined to optimize drainage performance:
- Geotextiles: Non-woven or woven fabrics that filter soil particles while allowing water to pass through.
- Geonets: Plastic mesh structures that provide a pathway for water flow.
- Geogrids: Reinforcing materials that add structural stability.
- Core: A polymer core, often in the form of a cuspated or dimpled sheet, which provides a void space for water to flow.
Purpose
The primary purposes of a Geocomposite Drainage Layer include:
- Drainage: Efficiently directing water away from structures to prevent water accumulation and potential damage.
- Filtration: Preventing soil particles from clogging the drainage system while allowing water to pass.
- Protection: Safeguarding waterproofing membranes and other underlying materials from mechanical damage and punctures.
- Stabilization: Reinforcing soil structures to maintain integrity and prevent erosion.
Applications
Geocomposite Drainage Layers are used in a variety of applications, such as:
- Landfills: Managing leachate and protecting liners.
- Road and Railway Construction: Preventing water buildup and maintaining the stability of the subgrade.
- Retaining Walls: Ensuring proper drainage to reduce hydrostatic pressure.
- Green Roofs: Facilitating water drainage while protecting the roof structure.
- Building Foundations: Keeping basements and foundations dry by directing water away.
Advantages
- Efficiency: High drainage capacity reduces the risk of water-related issues.
- Durability: Resistant to environmental factors and mechanical stress.
- Cost-Effective: Reduces the need for traditional drainage materials and systems.
- Easy Installation: Lightweight and flexible, making it easier to handle and install.
A Geocomposite Drainage Layer is a versatile and efficient solution for managing water in various construction and engineering projects. Its multi-component structure ensures effective drainage, filtration, protection, and stabilization, making it a critical material for maintaining the longevity and safety of infrastructure.
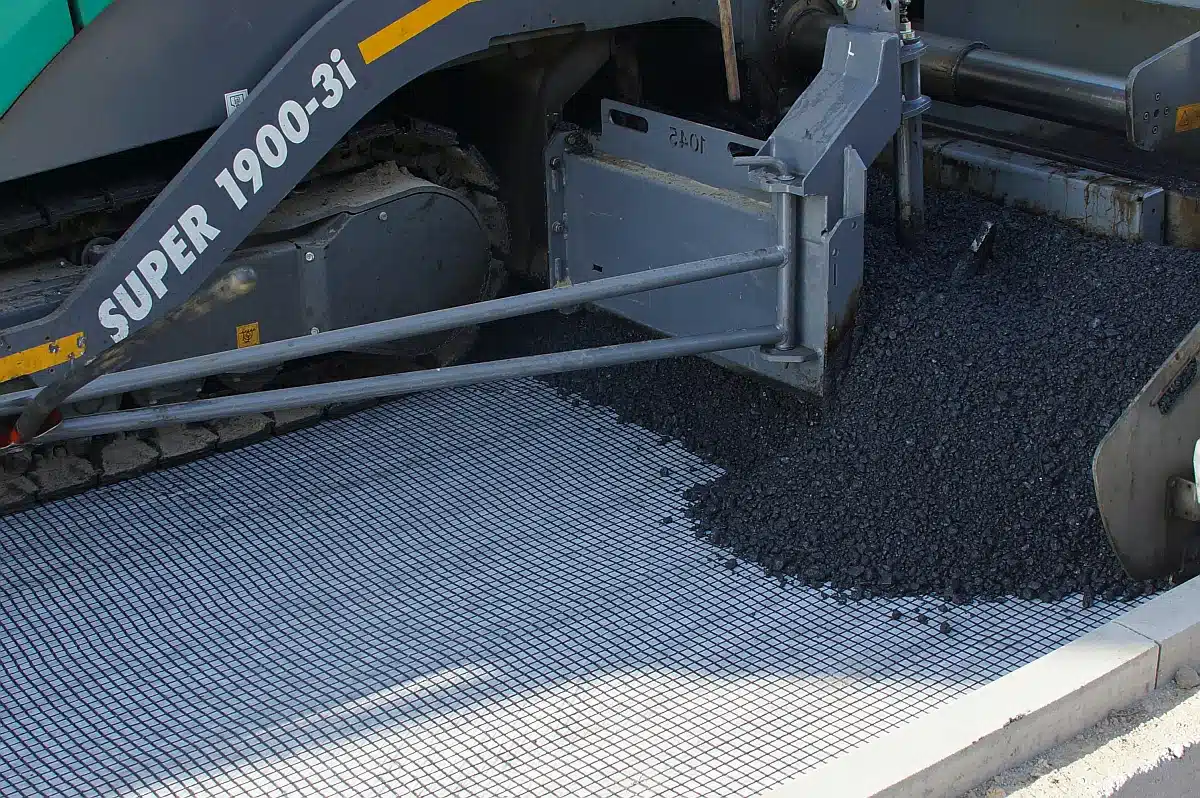

What is the Purpose of Geocomposites?
The primary purpose of geocomposites is to offer a multifaceted solution encompassing separation, reinforcement, filtration, drainage, and containment within various civil engineering and environmental applications, including landfills. By skillfully integrating different materials with complementary properties, geocomposites are designed to deliver superior performance across all these functions. They excel in water management, soil stabilization, and erosion control, thanks to their ability to separate distinct layers, reinforce structural stability, filter particulates, efficiently drain fluids, and securely contain waste materials. Specifically, in the context of landfills, geocomposites play a pivotal role in ensuring effective leachate management, safeguarding groundwater resources, and reinforcing the structural integrity of waste containment systems, thereby addressing the comprehensive needs of modern waste management practices.
What are the Properties of Geocomposite?
Geocomposites exhibit a wide range of properties tailored to meet the specific requirements of the applications they are designed for. Key properties include:
- High permeability with vertical and horizontal permeable capacity: This allows for the rapid drainage of fluids in both vertical and horizontal directions, which is crucial for managing leachate in landfills and adapting to varied landfill configurations.
- Filtration capability: Prevents the passage of fine particles, thus maintaining the integrity of drainage systems by ensuring that only clear fluids pass through, while solid particles are filtered out.
- Mechanical strength: Provides significant resistance to physical stresses, supporting the structure of waste containment systems and ensuring long-term stability.
- Chemical resistance: Ensures durability and functionality in the harsh chemical environment of landfills, withstanding the effects of a wide range of chemical substances found in waste materials.
This comprehensive set of properties, including the enhanced vertical and horizontal permeable capacity, makes geocomposites an indispensable component in the design and operation of modern landfills, contributing to their efficiency and environmental safety.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















