+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
In the vast and ever-evolving field of civil engineering, the quest for materials that offer durability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness has led to the innovation of geogrids. Geogrid rolls, in particular, have emerged as a cornerstone in the construction of roads, retaining walls, and various soil stabilization projects. This popular science article aims to demystify geogrids, exploring their applications, operational principles, optimal usage conditions, and inherent advantages. By weaving through these aspects, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of geogrid rolls and their significant impact on modern engineering practices.
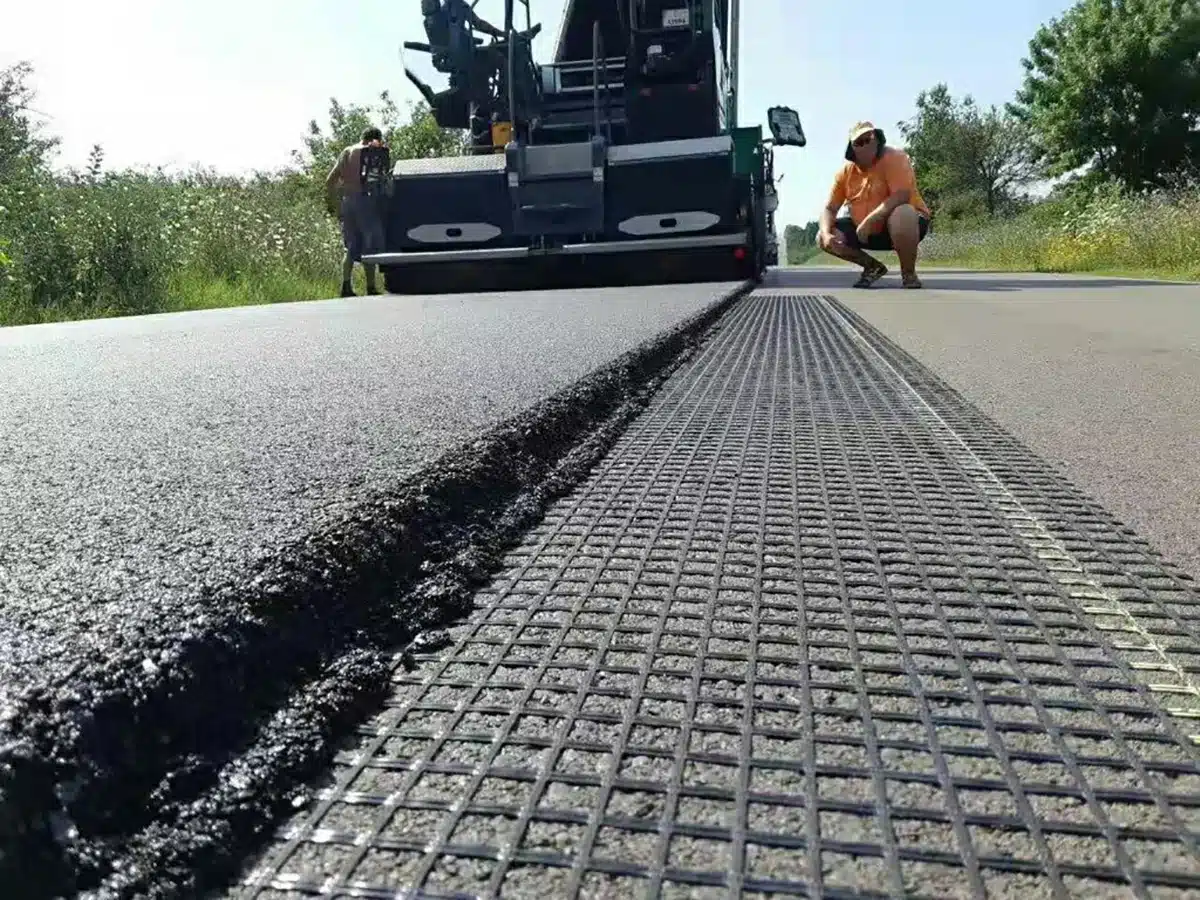

What is Geogrid Used For?
Geogrid is a geosynthetic material used extensively in construction and civil engineering projects. Here are the primary applications and uses:
Soil Reinforcement
- Road Construction: Geogrids are used to reinforce subgrades and subbases, improving load-bearing capacity and preventing road failure.
- Railway Construction: They help in stabilizing tracks and reducing maintenance costs by reinforcing the ballast layer.
Retaining Walls and Slopes
- Retaining Walls: Geogrids provide tensile strength to retaining wall systems, allowing for steeper and more stable wall designs.
- Slope Stabilization: They are used to reinforce slopes and embankments, preventing soil erosion and landslides.
Embankment Construction
- Over Soft Soils: Geogrids distribute loads over soft and compressible soils, allowing for the construction of embankments and other structures.
Pavement Systems
- Asphalt Reinforcement: Geogrids are used to reinforce asphalt layers, reducing rutting and extending the lifespan of pavements.
Erosion Control
- Coastal Protection: They help in stabilizing coastal and riverbank areas, preventing erosion due to water flow.
Load Transfer Platforms
- Bridges and Overpasses: Geogrids are used in load transfer platforms to distribute loads evenly and reduce settlement issues.
Geogrids are versatile materials crucial for enhancing the performance and longevity of various construction and civil engineering projects. Their primary functions include soil reinforcement, erosion control, and load distribution.
What is the Principle of Geogrid?
Principle of Geogrid
Definition: Geogrids are geosynthetic materials used to reinforce soils and similar materials. They are typically made from polymers such as polypropylene or polyester and are characterized by their grid-like structure.
Function
- Reinforcement: Geogrids provide tensile strength to soil, which inherently has low tensile strength. This reinforcement improves the stability and load-bearing capacity of the soil.
- Separation: By preventing the intermixing of different soil layers, geogrids help maintain the integrity of the construction foundation.
- Confinement: Geogrids confine the soil particles, which reduces lateral displacement and enhances the overall stability of the soil structure.
Applications
- Road Construction: Used to stabilize the subgrade and subbase layers, geogrids improve the longevity and load-bearing capacity of roadways.
- Retaining Walls: In retaining wall construction, geogrids are used to reinforce the soil behind the wall, increasing its stability and preventing collapse.
- Slope Stabilization: Geogrids help in stabilizing slopes and embankments, preventing soil erosion and landslides.
- Railway Construction: They reinforce the track bed, providing better load distribution and reducing maintenance costs.
Geogrids are essential in modern civil engineering for their ability to reinforce and stabilize various soil structures. Their applications in road construction, retaining walls, slope stabilization, and railways highlight their versatility and importance in creating durable and reliable infrastructure.

When Should You Use Geogrid?
The use of geogrid is recommended when constructing over soft soils that need reinforcement, in areas prone to erosion, or where the longevity of the structure is paramount, including for walls taller than three to four feet. It’s particularly effective in projects requiring high load-bearing capacity, such as roadways, commercial parking lots, or retaining walls exceeding the specified height. Additionally, geogrids are ideal for environmentally sensitive areas where minimal impact on the natural landscape is desired, as they can help stabilize soil without extensive excavation or fill materials. This makes geogrids a versatile solution in both urban and natural settings, ensuring structural stability and longevity across a wide range of engineering projects.
What are the Advantages of Geogrids?
Geogrids offer a multitude of advantages, including their remarkable resistance against chemicals and bacteria, alongside providing high tensile strength. These properties significantly increase the structural integrity of projects, ensuring long-term stability and durability. Furthermore, their flexibility allows for accommodation to ground movements, effectively preventing cracks and damage. Geogrids are also cost-effective, reducing the need for expensive traditional materials like concrete. Additionally, their use contributes to environmental conservation by utilizing recycled materials and preserving natural topography, making them a preferred choice in sustainable construction practices.
Geogrid rolls represent a remarkable fusion of engineering ingenuity and environmental stewardship. As a versatile and efficient solution for soil stabilization and structural reinforcement, geogrids play a pivotal role in the success of contemporary construction projects. Their ability to distribute loads, reinforce soft soils, and integrate seamlessly with the environment underscores the value they bring to the field of civil engineering. As we continue to explore and understand the capabilities of geogrids, their role in shaping the landscapes of tomorrow becomes increasingly evident, promising a future where sustainability and stability go hand in hand.
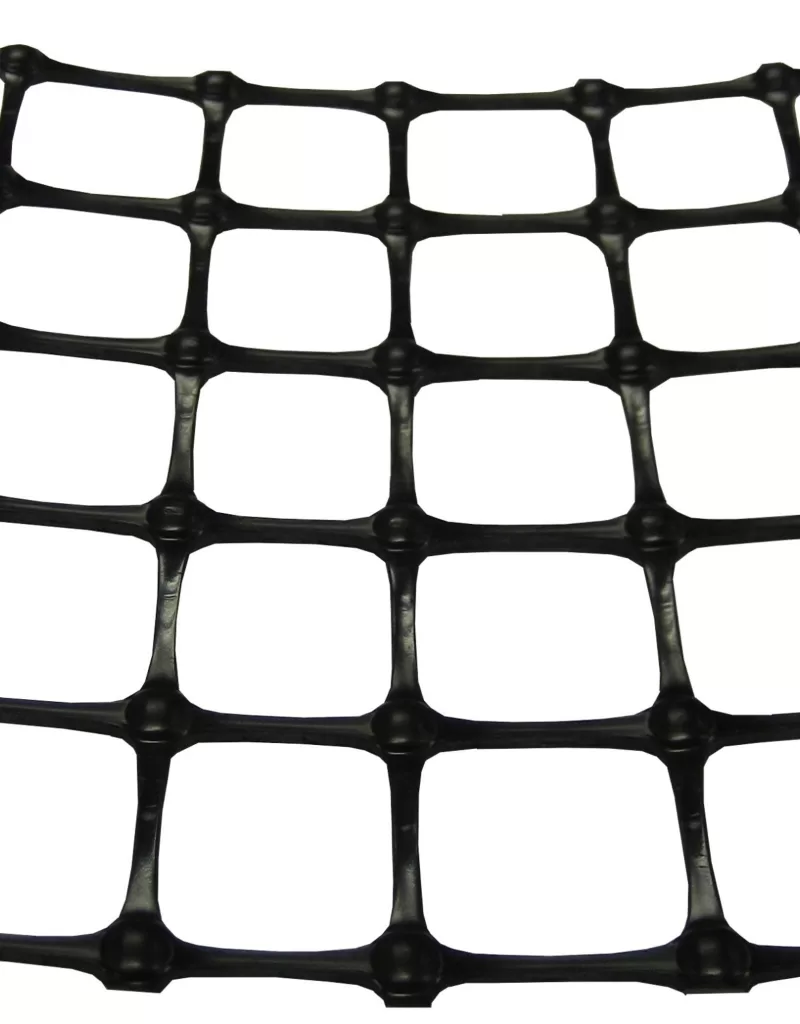
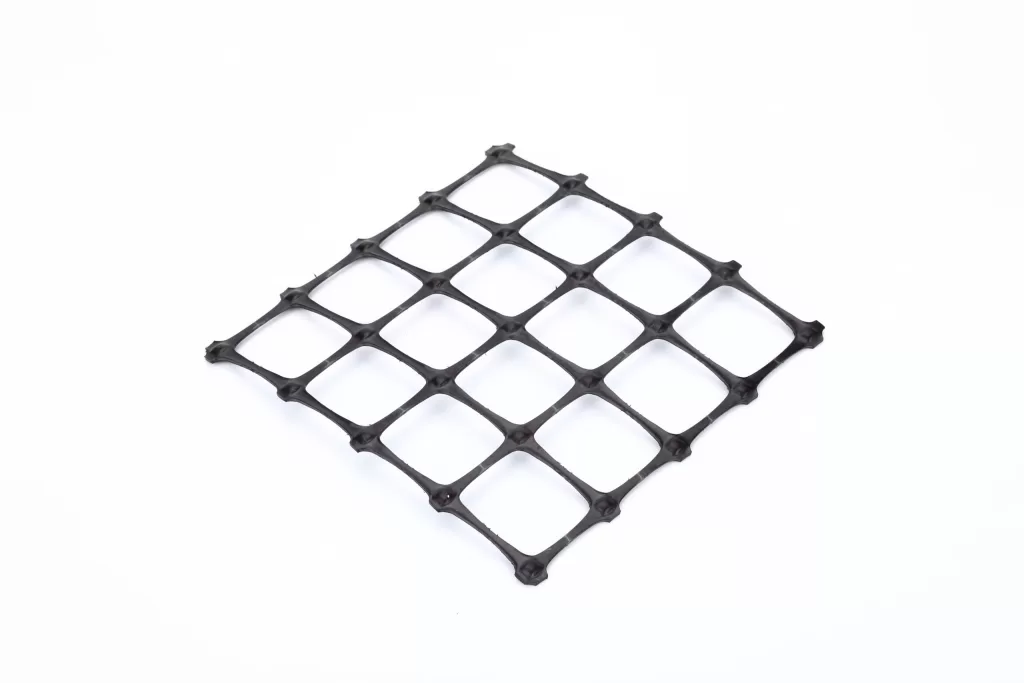


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















