+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
Uniaxial Geogrids are commonly used in applications where high long-term loads are required to be mobilized. Both High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) and coated Polyester are used in the manufacture of our Uniaxial Geogrids. A wide range of Long Term Design Strengths are available depending on the application and design requirements.
GeoFanTex provides design assistance and final design for applications that use Uniaxial Geogrids.

What is uniaxial geogrid?
A uniaxial geogrid is a type of geosynthetic material made from polymers (like polyethylene or polypropylene) designed to provide high tensile strength in one primary direction (longitudinal). Its grid-like structure is optimized for applications where strength is needed in a single direction, making it ideal for:
Key Applications:
- Retaining Walls: Provides reinforcement to withstand soil pressure.
- Steep Slopes: Stabilizes slopes and prevents erosion.
- Embankments: Reinforces soil to improve stability and load-bearing capacity.
Features:
- High tensile strength in one direction.
- Resistant to corrosion, chemicals, and UV degradation.
- Lightweight and easy to install.
How It Works:
The geogrid is laid horizontally with its strong direction aligned to resist tensile forces, effectively distributing loads and reinforcing soil structures. It is commonly used in civil engineering projects requiring long-term stability and strength in a single direction.
What is the difference between uniaxial and biaxial geogrids?
However, two classes of geogrid reinforcements may be identified; uniaxial geogrids, which develop tensile stiffness and strength primarily in one direction, and biaxial geogrids which, develop tensile stiffness and strength in two orthogonal directions.
What are the three types of geogrid?
Geogrid Types and Differences
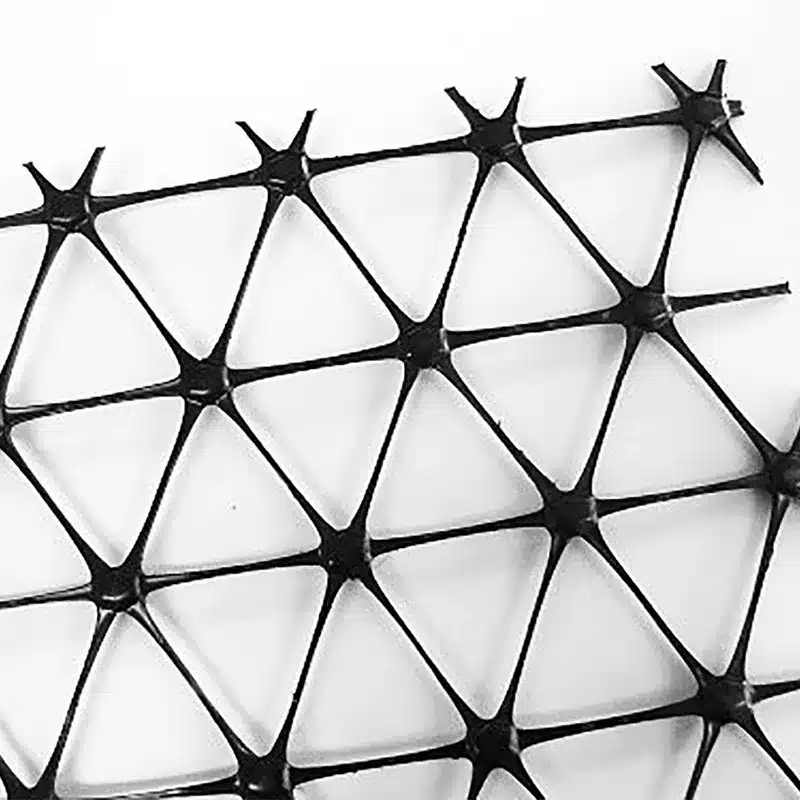
- Uniaxial Geogrid. As the name suggests, this type of geogrid is strong in the longitudinal direction. “Strength is in the length’ and it should be rolled out perpendicular to the wall or slope you are working with.
- Biaxial Geogrid. For this type, a polymer sheet is punctured and then stretched in both directions. As a result, its tensile strength is equal in the transverse and longitudinal directions. It is suitable for various applications such as embankment reinforcement, wall reinforcement, soil stabilization, slope protection, and other permanent load-bearing foundation reinforcement.
- Triaxial Geogrid. This innovative product is made from high-density polyethylene and takes advantage of the unique load-bearing properties of triangles. When arranged in a triangular grid, the geogrid is able to bear loads in all directions. This kind of geogrid can greatly enhance the load-bearing capabilities of asphalt pavement and can greatly reduce the thickness of the layer of asphalt required. This triangular structure can provide an enhanced bearing system, which can reduce the thickness of layers. For example, the application of triaxial geogrid in asphalt pavement can greatly reduce the layer of asphalt. It performs well in the reinforcement of soft soil, roadbed, subgrade, and retaining walls.
What is the difference between biaxial and triaxial geogrid?
Biaxial and triaxial geogrids are unique and distinct engineering materials, each with their own in-application performance capabilities. The presence of ribs in three directions, rather than two, is an obvious, definitive, and meaningful distinction between biaxial and triaxial geogrids.
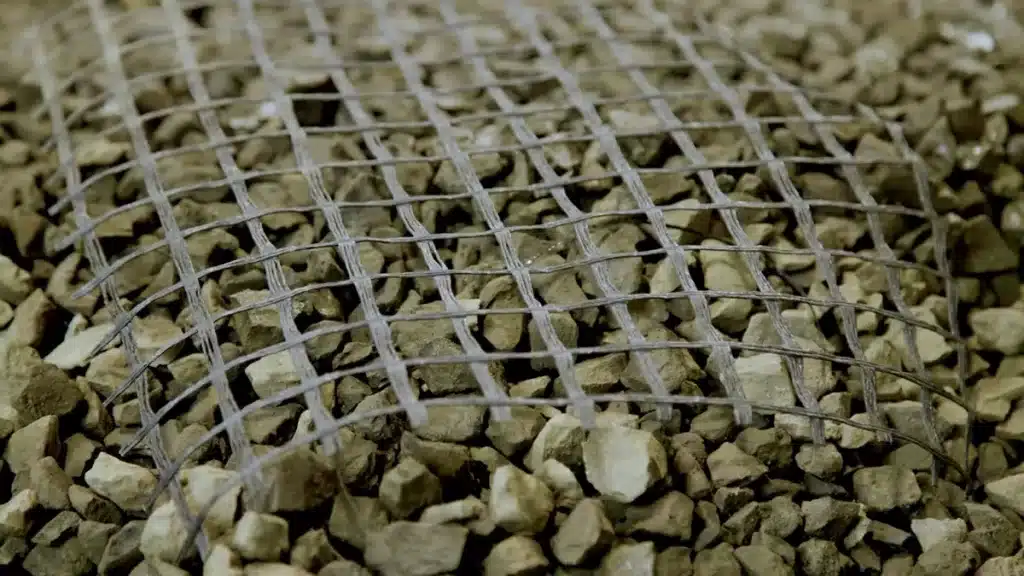

Biaxial geogrids and uniaxial geogrids are the most common types of geogrids. A geogrid is defined as a geosynthetic material consisting of connected parallel sets of tensile ribs with apertures of sufficient size to allow strike-through of the surrounding soil, stone, or other geotechnical material (Koerner 1998). More simply described as plastic lattice structures with different technical properties and functions.
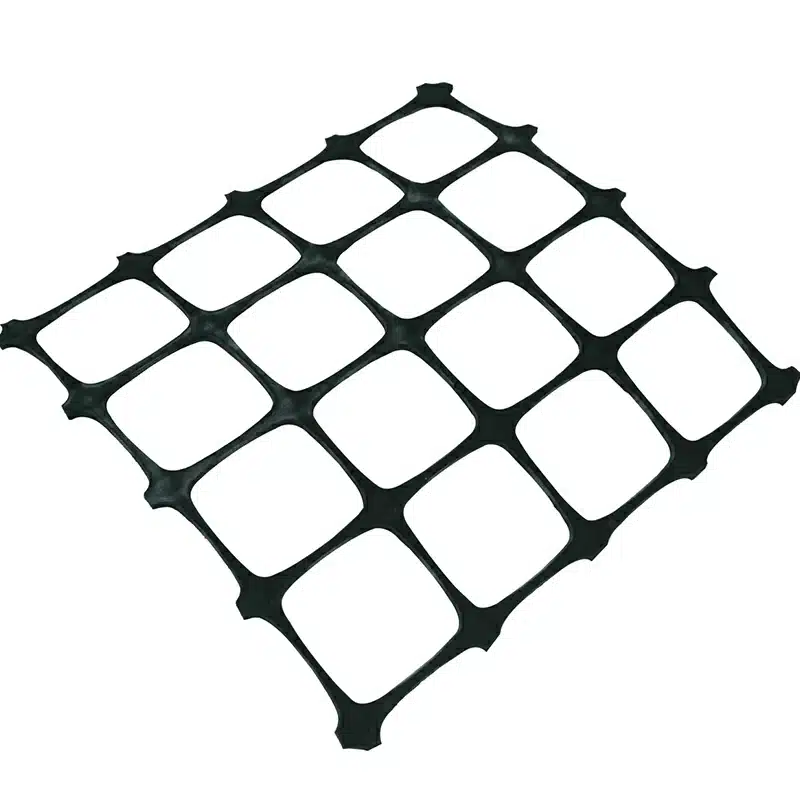
A biaxial geogrid is a bi-directional structure with a two-way stretch that provides the same mechanical properties in two directions, both longitudinal and transverse. A uniaxial geogrid is a unidirectional structure with a one-way stretch that provides stabilization in one direction only, mainly longitudinal.
Each is used in specific civil engineering applications depending on the desired reinforcement and stabilization outcomes. Biaxial geogrids allow for wider load distribution making them ideal for the construction of roads, working platforms, or preparation of site subgrades where base stabilization is needed in two directions; while uniaxial geogrids are best used in the construction of structures with a vertical component like earth retaining walls and steep soil slopes. This geogrid provides reinforcement in one direction.
GeoFanTex both biaxial and uniaxial geogrids suited to different applications and civil engineering designs.

Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















