+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
Geogrid is a geosynthetic material, made of polymers, which is used to reinforce soil behind retaining walls. Installed in horizontal layers between wall courses and extending into the soil behind a wall, geogrid stabilizes the soil and so increases a wall system’s mass and stability.
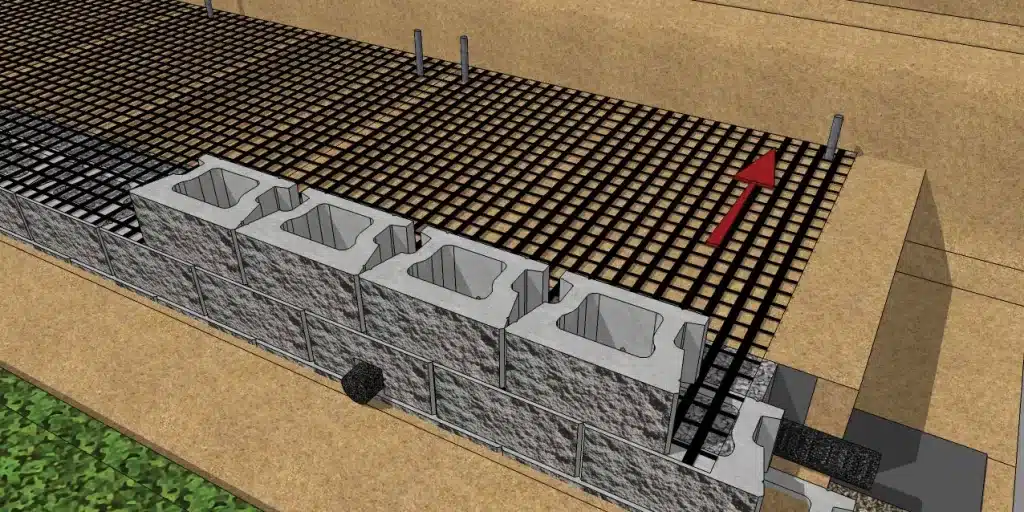
Is a geogrid needed for a retaining wall?
Factors to Consider for Geogrid’s Necessity
- Wall Height: Taller walls often require additional reinforcement. Geogrids are typically recommended for walls over 4 feet (1.2 meters) in height.
- Soil Conditions: The type and stability of the soil behind the wall. Poorly draining or loose soils often benefit from geogrid reinforcement.
- Load Considerations: Additional loads, such as vehicles, buildings, or slopes above the wall. Geogrids help distribute these loads more effectively.
- Environmental Factors: Areas prone to heavy rainfall or seismic activity. Geogrids can provide added stability in such conditions.
Role of Geogrids in Retaining Wall Construction
- Reinforcement: Geogrids are used to reinforce the soil, improving its mechanical properties and stability.
- Load Distribution: They help distribute loads more evenly, reducing pressure on the wall.
- Erosion Control: Geogrids help prevent soil erosion by maintaining the integrity of the soil structure.
Benefits of Using Geogrids
- Increased Wall Stability: Enhanced structural integrity and resistance to movement.
- Cost-Effective: Reduces the need for more expensive materials and extensive excavation.
- Longevity: Increases the lifespan of the retaining wall by preventing structural failures.
Conditions for Geogrid Recommendation
- Height: Typically recommended for walls over 4 feet (1.2 meters).
- Soil Type: Loose, sandy, or clay soils.
- Load: High load-bearing areas.
- Environmental Stress: Regions with heavy rainfall, flooding, or seismic activity.
Alternative Methods and Materials
- Reinforced Concrete: Can provide similar stability without the need for geogrids. More expensive and labor-intensive.
- Natural Stone: Suitable for smaller walls. Offers aesthetic benefits but less structural reinforcement.
- Mechanically Stabilized Earth (MSE): Uses alternating layers of soil and reinforcing materials. Similar in function to geogrids but with different materials.
- Geotextiles: Can be used in conjunction with or as an alternative to geogrids. Provides filtration, separation, and reinforcement.
How far back should Geogrid go on a retaining wall?
When designing a retaining wall with geogrid reinforcement, the length of the geogrid (how far it extends back into the soil) is critical to ensuring stability. The general rule of thumb is that the geogrid should extend back into the reinforced soil zone at least 70% to 100% of the height of the retaining wall. This means that for a 10-foot-high retaining wall, the geogrid should extend 7 to 10 feet into the soil behind the wall.
Key Factors to Consider:
- Wall Height: The higher the wall, the further the geogrid needs to extend into the soil to properly distribute the load and prevent failure.
- Soil Type: Stronger, more cohesive soils (like clay) may require less geogrid extension, while weaker soils (like loose sand) may require more.
- Wall Design: Different types of retaining walls (gravity, reinforced concrete, modular block, etc.) may have varying recommendations based on their structural requirements.
- Loading Conditions: Walls supporting heavy loads, such as slopes or other structures, might need longer geogrid reinforcement to handle the increased pressure.
- Geogrid Type: The type of geogrid used, such as uniaxial or biaxial, may affect how far it should extend into the soil.
Consulting with a geotechnical engineer is always recommended for precise calculations based on site-specific conditions.
What does Geogrid do for a retaining wall?
Geogrid plays a crucial role in the construction and stability of retaining walls. It is a type of geosynthetic material that provides reinforcement to soil structures, helping to prevent erosion, improve stability, and increase the strength of the wall. Here’s how geogrid contributes to retaining wall performance:
- Soil Reinforcement: Geogrids are placed within the soil mass behind a retaining wall to improve its overall strength. They provide tensile strength, helping to distribute loads evenly and prevent soil movement or failure under pressure.
- Increased Wall Stability: By reinforcing the soil, geogrids help maintain the stability of the retaining wall, preventing tilting or shifting due to the weight of the retained material or external forces like earthquakes or heavy rains.
- Improved Load Distribution: Geogrids effectively distribute the loads exerted on the wall across a broader area of the retained soil, reducing pressure on the base and decreasing the likelihood of failure.
- Prevention of Soil Erosion: In retaining walls, geogrids help control the movement of soil particles, reducing erosion over time. This is particularly important in areas with heavy rainfall or where there is a risk of water runoff washing away the soil behind the wall.
- Increased Wall Lifespan: The added reinforcement from geogrids can significantly extend the lifespan of retaining walls by preventing settlement, cracking, and structural degradation that can occur over time due to soil pressure and environmental factors.
Geogrids provide essential reinforcement in retaining walls by enhancing soil stability, improving load distribution, preventing erosion, and extending the lifespan of the structure. They are especially effective in situations where the soil conditions are poor or where the retaining wall is subject to heavy loads or adverse weather conditions.
What is the best option for a retaining wall?
Retaining Wall Materials Comparison Chart
| TYPE OF MATERIAL | PROS |
| Poured Concrete | Stronger than a block wall Variety of design options |
| Brick | Strong and durable |
| Wood | Accessible materials Fairly simple installation |
| Dry Stone/Boulder | The most natural solution to grade change |
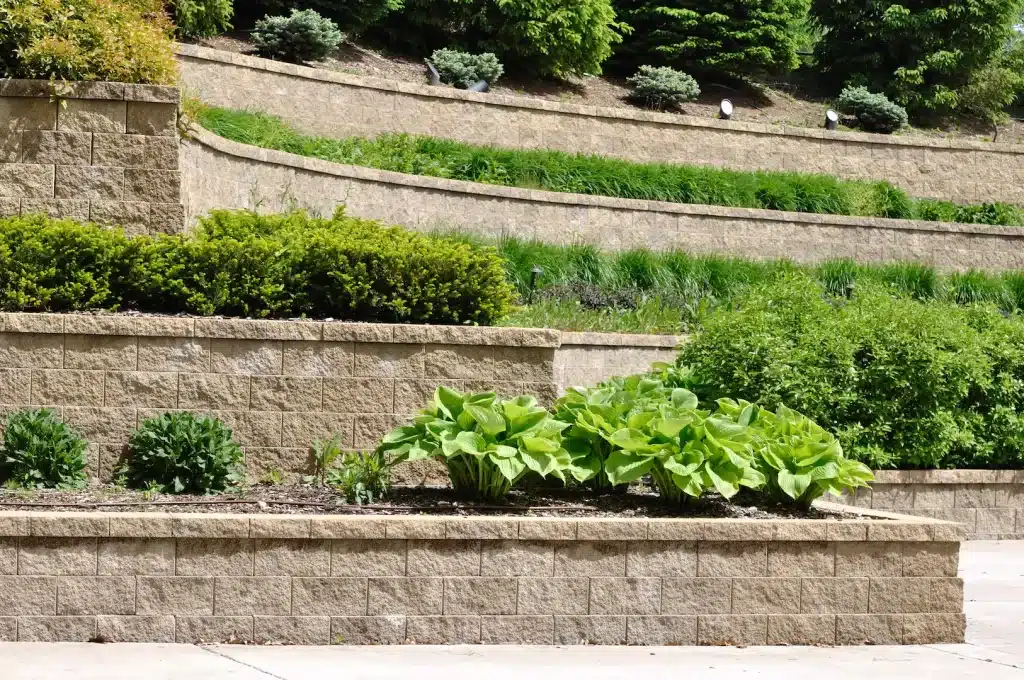

Geogrid retaining walls offer a robust and effective solution for stabilizing slopes, controlling erosion, and creating durable retaining structures. Geogrids, typically made of high-strength polymer materials, are engineered to reinforce soil and provide structural support in retaining wall construction. Whether it’s for residential landscaping or large-scale infrastructure projects, geogrid retaining walls are a reliable choice to enhance the longevity and stability of your retaining wall systems.

Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















