+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
Geosynthetics, including geogrids and geonets, play a crucial role in civil engineering, environmental protection, and construction. Geogrids provide strength and durability for large-scale projects, whereas geonets offer excellent drainage capabilities for retaining walls and soil separation. Although they may sound similar, geogrids and geonets serve different functions and are applied in distinct ways. This article explores the fundamental differences between these two materials, highlights their unique applications, and discusses their advantages.
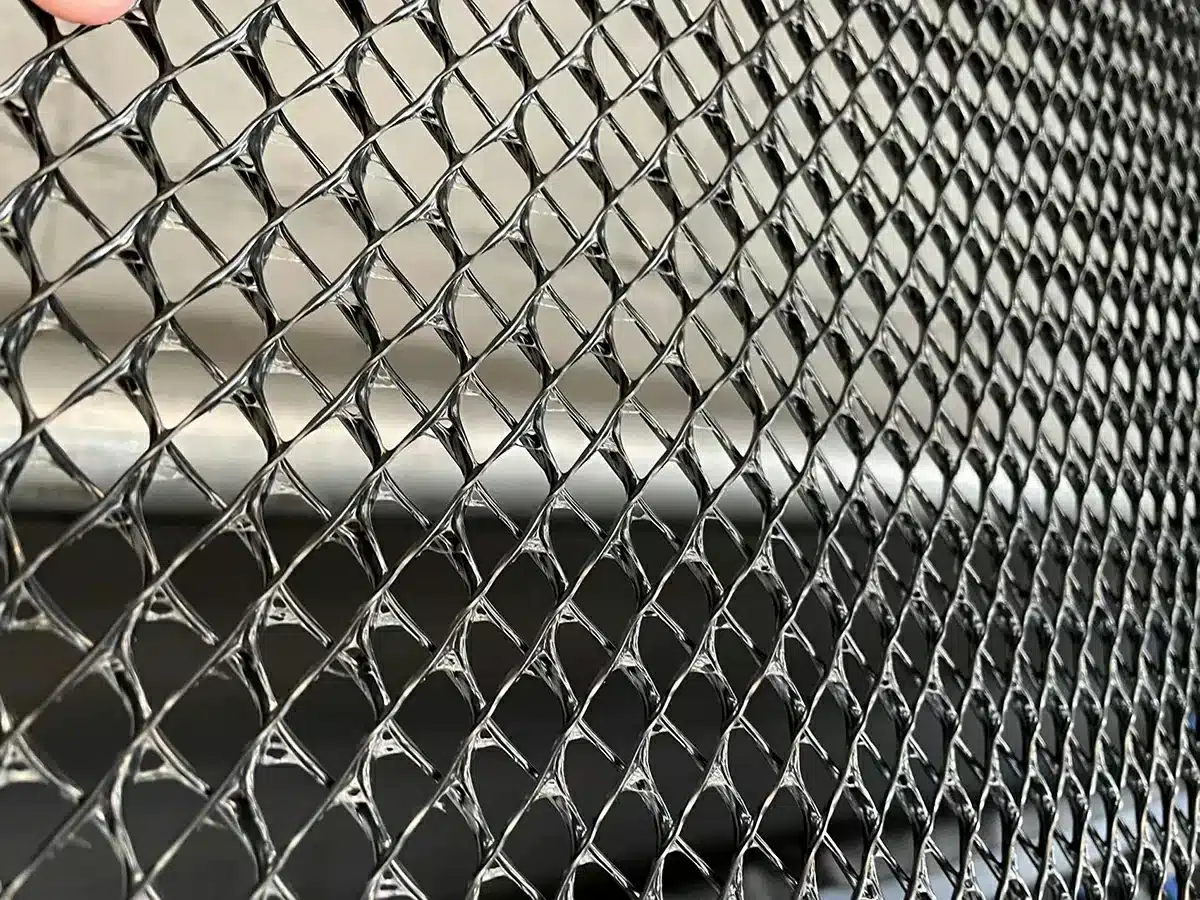
What is a Geonet and Its Applications?
A geonet is a type of synthetic, net-like material primarily used for drainage, filtration, and erosion control in civil engineering and environmental projects. Made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or similar durable polymers, geonets feature an open, three-dimensional grid structure that efficiently channels liquids and gases. This makes them ideal for applications where water or gas needs to be drained away quickly to prevent soil instability or moisture buildup.
Common uses of geonets include:
- Landfills: To manage leachate and prevent contamination.
- Retaining walls and slopes: To control water accumulation and reduce hydrostatic pressure.
- Roadways and highway systems: To improve drainage, stabilize embankments, and prevent erosion.
- Composite geosynthetic systems: Geonets are often combined with geotextiles to form geocomposites that offer both filtration and drainage, ensuring soil stability while controlling fluid flow.
By facilitating effective drainage and moisture management, geonets help prevent erosion, reduce maintenance costs, and extend the lifespan of infrastructure projects.

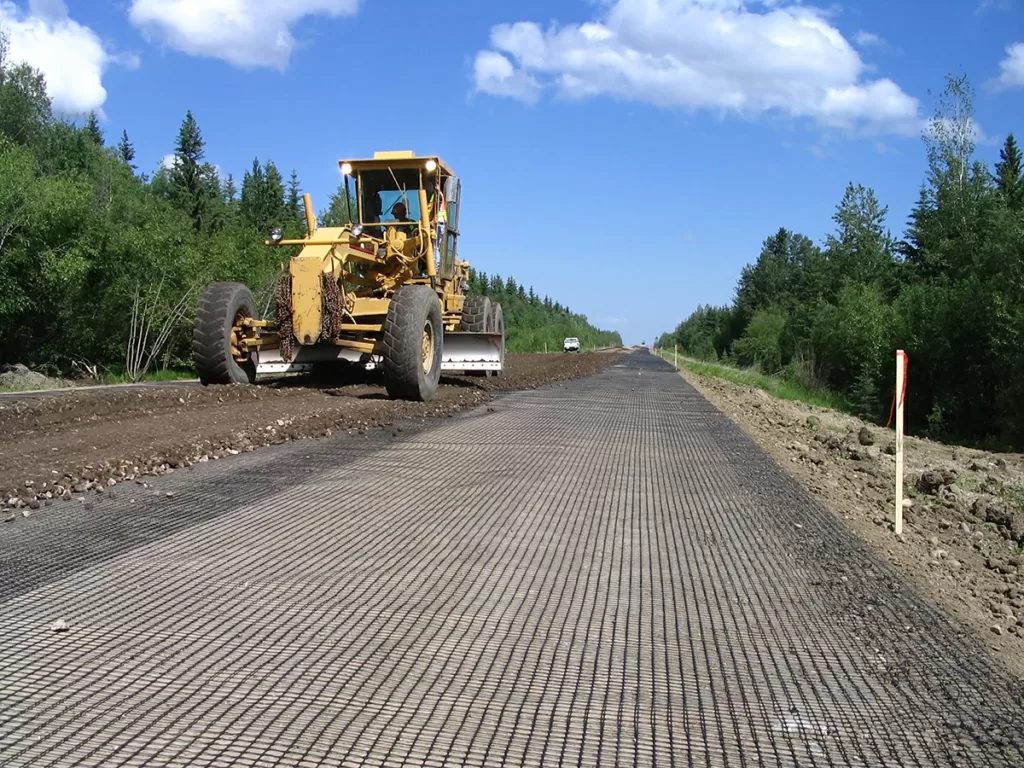
What Are Geogrids Used For?
Geogrids are primarily designed for soil reinforcement and stabilization, making them essential in construction projects where the ground must support heavy loads or maintain structural integrity. These materials consist of rigid or flexible grid patterns that interlock with soil and aggregate, creating a reinforced layer that distributes loads and improves stability.
Common applications of geogrids include:
- Retaining Walls: Reinforce the backfill soil to prevent collapse and maintain wall stability.
- Embankments and Slopes: Provide additional strength to soil layers, reducing the risk of landslides or erosion.
- Roadways and Pavement Foundations: Enhance load-bearing capacity, prevent rutting, and extend the lifespan of roads, highways, and parking lots.
- Railway Tracks: Support ballast and subgrade layers, improving track stability and reducing maintenance.
- Landfills and Containment Areas: Reinforce soil layers to improve settlement control and structural durability.
By integrating geogrids into soil systems, engineers can increase load-bearing capacity, enhance slope stability, and prolong infrastructure lifespan, particularly in areas with weak or unstable soils.

What Is the Difference Between Geogrids and Geonets?
The key difference between geogrids and geonets lies in their function, structure, and engineering purpose.
- Primary Function: Geogrids are designed for soil reinforcement and load distribution, while geonets focus on drainage and fluid or gas flow management.
- Structural Design: Geogrids feature a rigid or semi-rigid open grid with large apertures that interlock with soil and aggregate to improve strength and bearing capacity; geonets have a thinner, three-dimensional net-like structure that creates continuous flow channels.
- Engineering Role: Geogrids enhance stability in retaining walls, embankments, pavements, and slopes, whereas geonets reduce hydrostatic pressure and moisture buildup in landfills, retaining walls, and roadway drainage systems.
- Load vs. Flow Performance: Geogrids resist tensile forces and control deformation, while geonets prioritize efficient liquid and gas transmission rather than structural reinforcement.
- Application Focus: Geogrids are used where mechanical strength is critical; geonets are selected where drainage and moisture control determine long-term performance.
What are the Advantages of Geonet?
Geonets offer several unique advantages in construction and environmental projects:
- Effective Drainage: Geonets are excellent for managing water and gas flow, which is essential in applications like landfills and retaining walls. Acting as liquid or gas collectors, they prevent moisture buildup that can destabilize soil structures.
- Erosion Prevention and Road Improvement: By providing controlled drainage, geonets help maintain soil stability and prevent erosion, making them valuable in slope protection and road segment restoration. Their use can stop cracking during road extensions, improve the quality of the road, and strengthen fill materials in geotechnical applications.
- Compatibility with Other Geosynthetics: Geonets can be combined with geotextiles to form geocomposites that provide both filtration and drainage, enhancing their functionality in complex projects, especially in drainage applications.
- High Chemical Resistance and Cost Efficiency: Made from materials like HDPE, geonets are highly resistant to chemicals and environmental stress, ensuring durability under harsh conditions, including exposure to contaminants. Their application in road construction also leads to significant cost reduction in road repair and increases the lifespan of the road, making them a cost-effective solution in long-term infrastructure projects.
Geogrids and geonets serve distinct roles in construction and environmental engineering. While geogrids are primarily used for soil reinforcement, geonets focus on effective drainage management. Understanding the differences between these materials allows for better selection based on project requirements, leading to safer, more stable, and long-lasting structures.
Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















