+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
In the evolving landscape of civil engineering and environmental management, GeoNets has emerged as a cornerstone technology, revolutionizing the way we approach sustainable construction and erosion control. This popular science article delves into the intricacies of GeoNets, exploring their definition, applications, composition, and how they differ from similar solutions like GeoGrids. Through an engaging Q&A format, we aim to unravel the complexities of GeoNets, making this cutting-edge technology accessible to all.
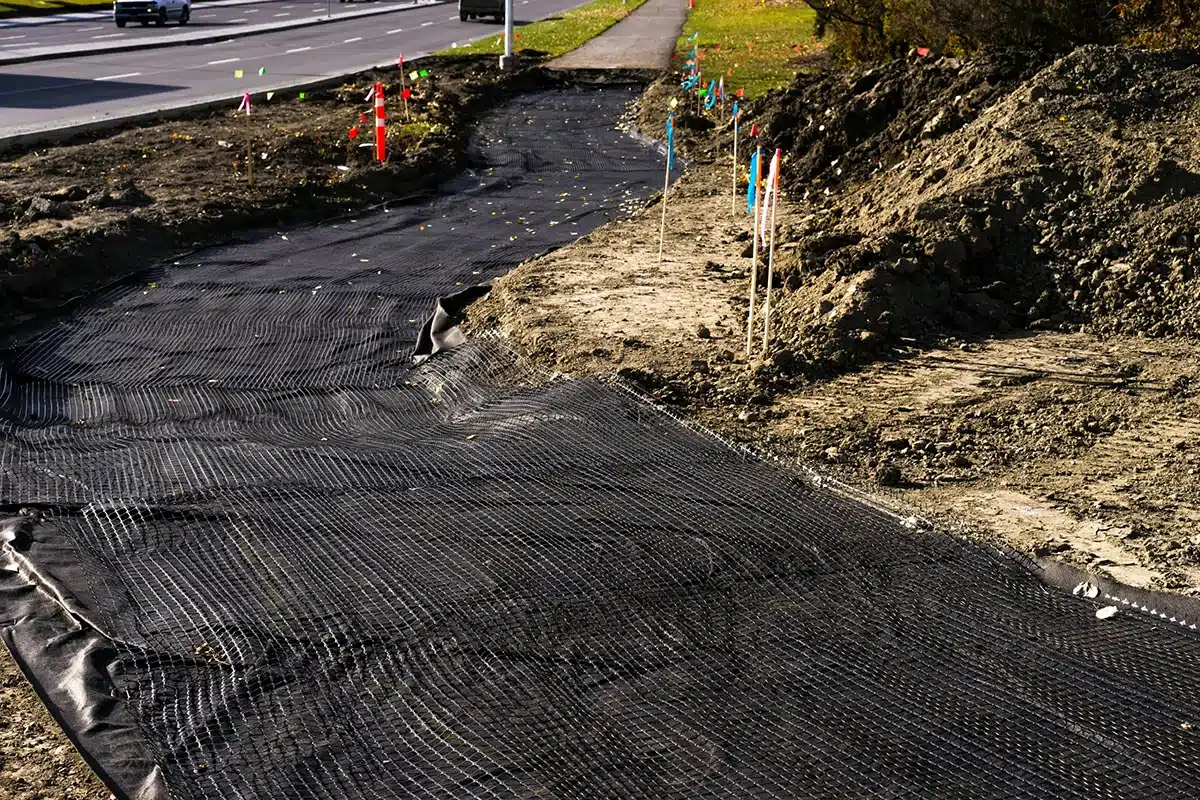

What is a GeoNet?
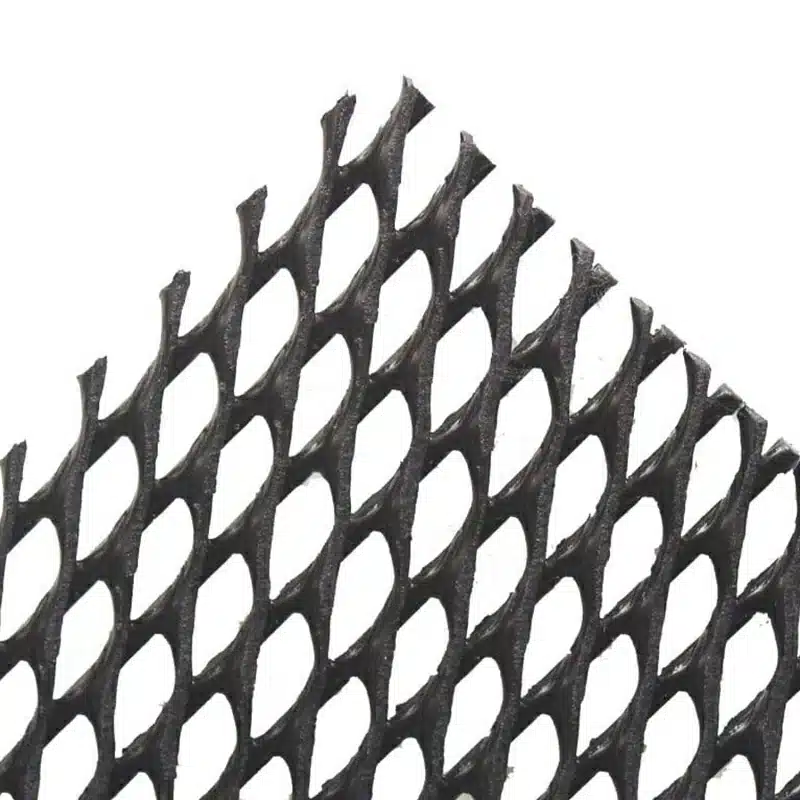
- Definition & Function: A GeoNet is a three-dimensional geosynthetic grid, usually made of high-density polyethylene (HDPE), designed to drain water or gas laterally beneath soil, geomembranes, or other layers.
- Structure: Bi-planar or tri-planar mesh forms a strong, flexible net-like core.
- Primary Uses: Acts as a drainage layer in landfills, roads, retaining walls, tunnels, foundations, and green roofs, preventing water buildup, gas accumulation, and soil instability.
- Difference from Geotextiles: While GeoNets focus on lateral drainage, geotextiles provide filtration, separation, and reinforcement; often used together to enhance performance.
What Are the Uses of GeoNets?
GeoNets are primarily used as drainage and reinforcement media in civil, geotechnical, and environmental engineering projects. Their structured polymer network enables fluid (water or gas) movement within a confined plane, making them indispensable in modern geoenvironmental systems. Key application areas include:
- Landfill Drainage & Environmental Containment: GeoNets are widely used in landfill liner and capping systems to provide lateral drainage pathways for leachate and landfill gases. This prevents hydraulic pressure buildup, improves containment efficiency, and extends landfill service life.
- Subsurface & Pavement Drainage: In highway, tunnel, and foundation works, GeoNets facilitate subsurface water removal, reducing hydrostatic pressure and mitigating soil weakening, settlement, or frost-related damage.
- Retaining Walls & Slope Systems: GeoNets support erosion control and slope stabilization by allowing controlled water movement behind retaining structures. This reduces pore pressure and enhances the mechanical stability of embankments and cut slopes.
- Environmental & Green Infrastructure: In green roofs, vegetated systems, and stormwater installations, GeoNets act as lightweight drainage layers that manage runoff, promote vegetation health, and support sustainable urban design.
- Soil Reinforcement (Complementary Use): GeoNets can improve soil’s load-bearing capacity when paired with geotextiles or geomembranes to form geocomposites, enhancing structural performance in pavements and foundations.
Across these applications, GeoNets contribute to long-term infrastructure resilience by managing water or gas flow, reducing erosion, stabilizing soil masses, and improving environmental protection outcomes.
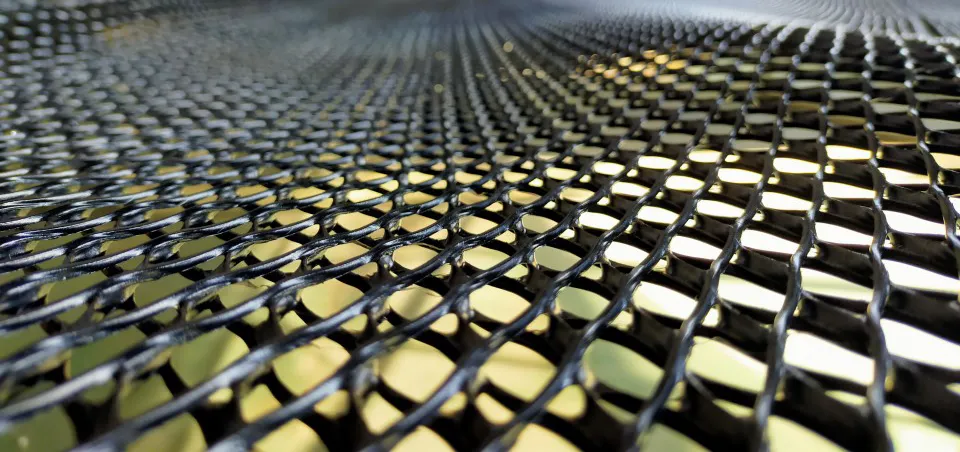
What Is a GeoNet Made Of?
A GeoNet is primarily manufactured from high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or, in some applications, polypropylene (PP). These polymer materials are selected for their durability, chemical resistance, and long-term performance in demanding civil and environmental conditions.
Key material and structural components include:
- Polymeric Core: The main body of a GeoNet consists of extruded HDPE or PP strands, forming a rigid yet flexible drainage core capable of withstanding sustained loads.
- Bi-planar or Tri-planar Structure: The intersecting ribs are arranged in two or three layers, creating continuous flow channels that enable efficient lateral movement of water or gas.
- Nodes and Intersections: Fusion-bonded intersections provide structural integrity, maintain channel geometry, and ensure consistent drainage capacity under pressure.
- Optional Geotextile Layer (Geocomposite): In many applications, a nonwoven geotextile is thermally bonded to one or both sides of the GeoNet to provide filtration and prevent soil intrusion into the drainage core.
Material Advantages: HDPE and polypropylene GeoNets resist chemical attack, biological degradation, UV exposure (when protected), and temperature fluctuations, ensuring reliable performance over long service lives.
How do GeoNets Enhance Soil Stability Compared to Traditional Solutions?
- Drainage-Driven Stability Improvement: Unlike traditional gravel drains or sand layers, GeoNets provide engineered, high-capacity lateral drainage within a thin profile. By rapidly removing excess water and gases, they reduce hydrostatic and pore water pressure buildup—one of the primary causes of slope instability and structural distress.
- Consistent Hydraulic Performance: Natural drainage materials can clog, shift, or lose permeability over time. GeoNets maintain uniform flow channels due to their structured polymer core, ensuring predictable long-term drainage performance under sustained loads.
- Reduced Structural Thickness: Traditional drainage systems often require thick aggregate layers, increasing excavation depth and material costs. GeoNets achieve equivalent or superior drainage capacity with significantly thinner sections, reducing dead load and conserving space.
- Improved System Integration: GeoNets can be combined with geotextiles and geomembranes to form geocomposite drainage systems that simultaneously provide filtration, separation, containment protection, and drainage. Conventional systems typically require multiple independent material layers to achieve similar functionality.
- Enhanced Durability and Chemical Resistance: Constructed from HDPE or polypropylene, GeoNets resist corrosion, biological degradation, and chemical exposure commonly found in landfills and contaminated sites—where traditional materials such as metal drains or untreated aggregates may deteriorate.
- Construction Efficiency and Cost Control: GeoNets are lightweight, easy to transport, and faster to install than bulk drainage aggregates. This reduces labor requirements, accelerates project timelines, and lowers overall lifecycle costs.
By delivering controlled drainage, long-term hydraulic stability, structural efficiency, and material durability, GeoNets provide a more reliable and sustainable alternative to many conventional soil stabilization and drainage methods used in civil and environmental engineering.
GeoNets represent a pivotal innovation in geosynthetic engineering, offering versatile solutions for drainage, erosion control, and soil reinforcement. Made from durable materials like HDPE and polypropylene, GeoNets are designed to withstand harsh environmental conditions, providing a sustainable option for modern construction and environmental protection. Understanding the differences between GeoNets and similar products like GeoGrids is crucial for selecting the right material for each specific application. As we continue to embrace these advanced technologies, the potential for sustainable development and environmental preservation becomes increasingly attainable.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















