+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
In the realm of civil engineering and environmental applications, the terms ‘geomembrane‘ and ‘geosynthetic’ are often used interchangeably, yet they hold distinct meanings and applications. This article aims to demystify these terms, offering a clear understanding of their differences, types, and classifications. By exploring the nuances between geomembranes, geosynthetics, and related materials like geotextiles, we can appreciate the innovative solutions they provide in contemporary engineering challenges.
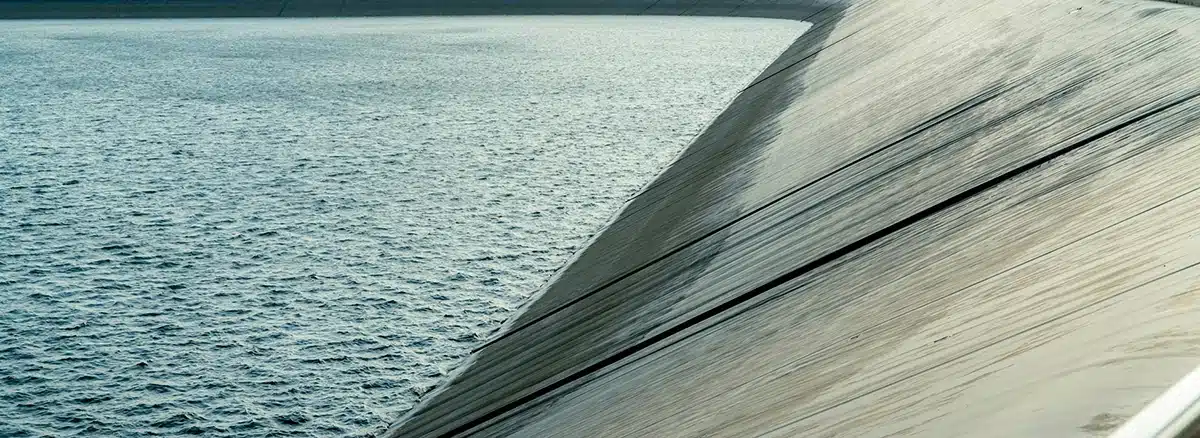

What is the difference between geomembrane and geosynthetic?
In civil engineering, the distinction between geomembranes and geosynthetics is important, though they are often mistakenly used interchangeably. A geomembrane is a specific type of geosynthetic—an impermeable polymeric sheet primarily used as a barrier to prevent the movement of fluids or gases. Common materials include HDPE, LLDPE, PVC, and EPDM, and typical applications involve landfill liners, water reservoirs, and containment ponds. Geosynthetics, on the other hand, refer to a broader category that includes geomembranes as well as geotextiles, geogrids, geonets, geocomposites, geocells, and more. These materials are engineered for various functions such as separation, filtration, reinforcement, drainage, and containment across infrastructure, environmental, and geotechnical projects. In summary, while all geomembranes are geosynthetics, not all geosynthetics are geomembranes. Understanding their roles and differences is essential for selecting the right material for a given project.
What is the difference between geosynthetic and geotextile materials?
- Geosynthetics are a broad category of synthetic materials used in geotechnical engineering. They include various types like geotextiles, geomembranes, geogrids, and geocomposites. Their primary purpose is to provide solutions for civil engineering challenges involving soil stabilization, reinforcement, filtration, drainage, and erosion control.
- Geotextiles are a subset of geosynthetics. They are permeable fabrics, either woven or non-woven, used primarily for separation, filtration, and reinforcement. Their applications include road construction, soil stabilization, drainage systems, and erosion control.
Key Differences:
- Scope: Geosynthetics include geotextiles and other materials, while geotextiles specifically refer to fabric-like materials.
- Functions: Geosynthetics encompass a broader range of functions due to the inclusion of other materials like geomembranes for waterproofing, geogrids for reinforcement, and so forth. Geotextiles, however, focus on filtration, separation, and reinforcement functions.
- Applications: Both are used in similar civil engineering contexts, but geosynthetics offer a more comprehensive set of solutions.
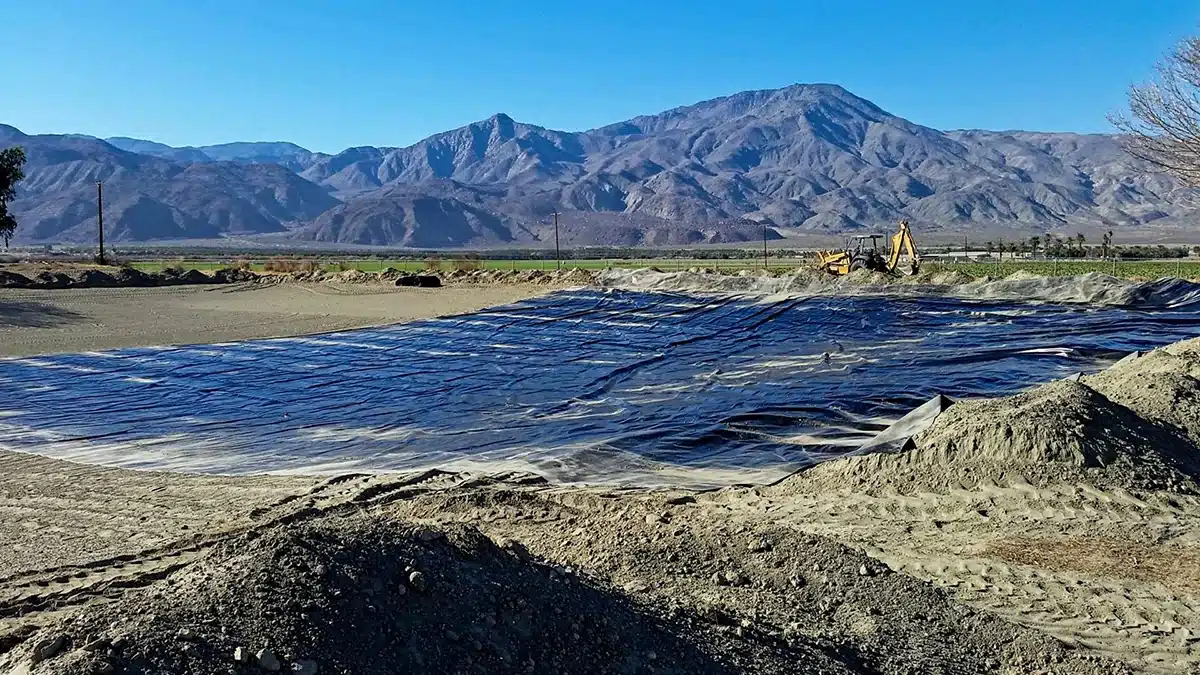

What are the major types of geosynthetics?
Main Categories of Geosynthetics:
Geotextiles:
- Description: Fabrics made from synthetic fibers.
- Types: Woven, non-woven, and knitted.
- Functions: Separation, filtration, drainage, reinforcement, and protection.
Geomembranes:
- Description: Impermeable sheets made from polymeric materials.
- Materials: HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene), PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride), EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer).
- Functions: Containment, barrier, and lining systems for water, waste, and other liquids.
Geogrids:
- Description: Grid-like structures made from polymers.
- Types: Uniaxial, biaxial, and triaxial.
- Functions: Soil reinforcement, stabilization, and load distribution.
Geonets:
- Description: Net-like structures formed by intersecting ribs.
- Functions: Drainage systems to manage fluid flow in various engineering projects.
Geocomposites:
- Description: Combinations of geosynthetics, such as geotextiles and geomembranes.
- Functions: Integrate multiple functions like drainage, reinforcement, and barrier in a single product.
Geocells:
- Description: Honeycomb-like structures made from polymers.
- Functions: Soil stabilization, erosion control, and load support.
Geofoam:
- Description: Lightweight blocks or panels made from expanded polystyrene.
- Functions: Lightweight fill, thermal insulation, and ground stabilization.
Geosynthetic Clay Liners (GCLs):
- Description: Layers of bentonite clay sandwiched between geotextiles or geomembranes.
- Functions: Impermeable barriers for containment applications.
What are the classifications of geomembranes?
Geomembranes are classified based on various factors such as materials, properties, and applications. Here is a detailed breakdown:
Materials
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE):
- Properties: High chemical resistance, durable, UV resistant.
- Applications: Landfill liners, mining applications, water reservoirs.
Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE):
- Properties: More flexible than HDPE, lower chemical resistance.
- Applications: Canal linings, decorative ponds, water storage.
Linear Low-Density Polyethylene (LLDPE):
- Properties: Greater flexibility than HDPE, moderate chemical resistance.
- Applications: Waste containment, lining for containment ponds.
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC):
- Properties: Flexible, easy to weld, good puncture resistance.
- Applications: Water and waste containment, tunnel liners.
Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM):
- Properties: High flexibility, excellent UV and weather resistance.
- Applications: Roofing, decorative ponds, irrigation ponds.
Properties
- Permeability: Low permeability geomembranes are used to prevent liquid migration (e.g., HDPE, PVC).
- Tensile Strength: High tensile strength geomembranes are used in applications requiring durability (e.g., HDPE).
- Chemical Resistance: Geomembranes with high chemical resistance are used in hazardous waste containment (e.g., HDPE).
- UV Resistance: UV-resistant geomembranes are suitable for applications exposed to sunlight (e.g., EPDM).
Applications
- Environmental Protection: Landfill liners, caps, hazardous waste containment.
- Water Management: Reservoirs, canals, irrigation ponds, decorative ponds.
- Mining: Heap leach pads, tailings dams, process ponds.
- Construction: Waterproofing of tunnels, basements, and roofs.
- Agriculture: Lining of irrigation canals, water storage.
This article has explored the intricate world of geosynthetics, focusing on the differences and classifications of geomembranes and related materials. Understanding these differences is crucial in the field of civil engineering and environmental applications, where the correct selection of materials can significantly impact the success and sustainability of a project. Geomembranes and geosynthetics, with their diverse types and applications, continue to play a pivotal role in shaping modern engineering solutions, offering both versatility and reliability in managing environmental challenges.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















