+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
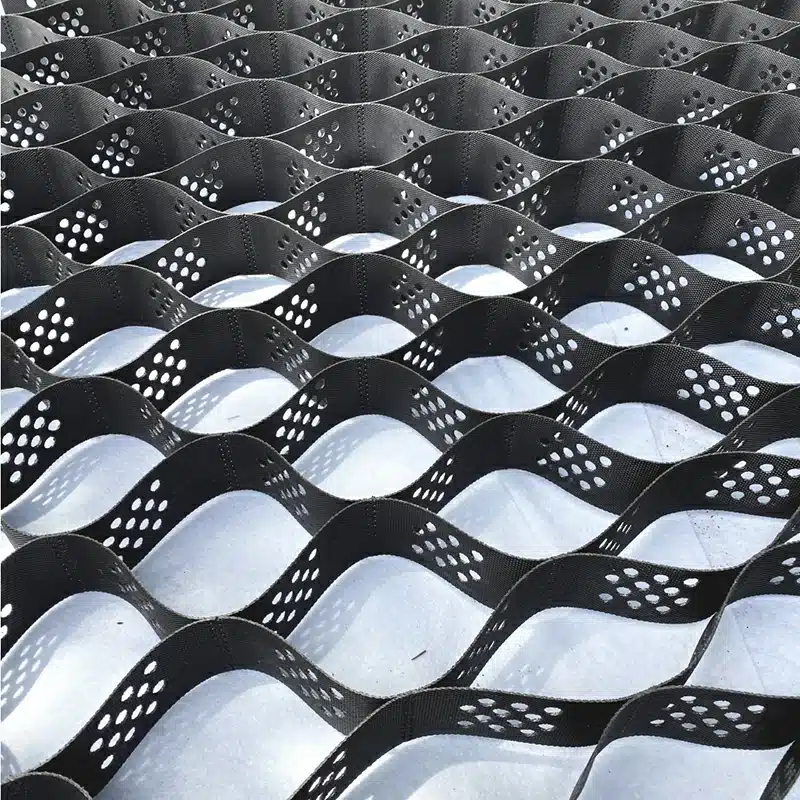
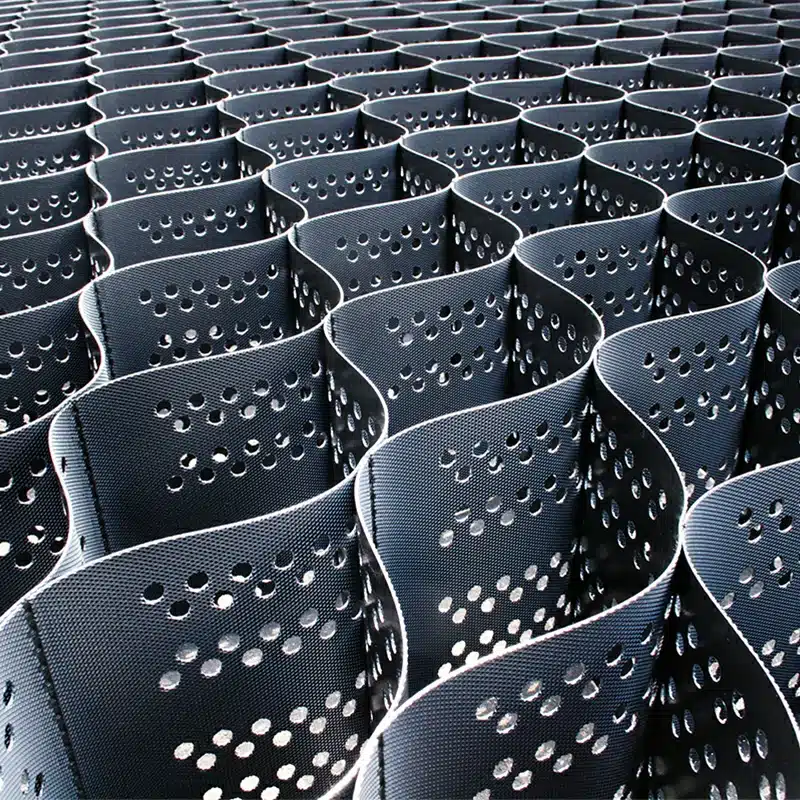
Gravel geocells revolutionize infrastructure reinforcement with their unparalleled stability and durability. These innovative cellular confinement systems excel in fortifying gravel, providing exceptional support for various applications. By securely containing and reinforcing gravel within their interconnected cells, gravel geocells enhance load-bearing capacity on flat ground and steep slopes alike. Whether for road construction, parking lots, driveways, or pathway reinforcement, the utilization of gravel geocells ensures a resilient and long-lasting solution, optimizing stability and durability in diverse projects.
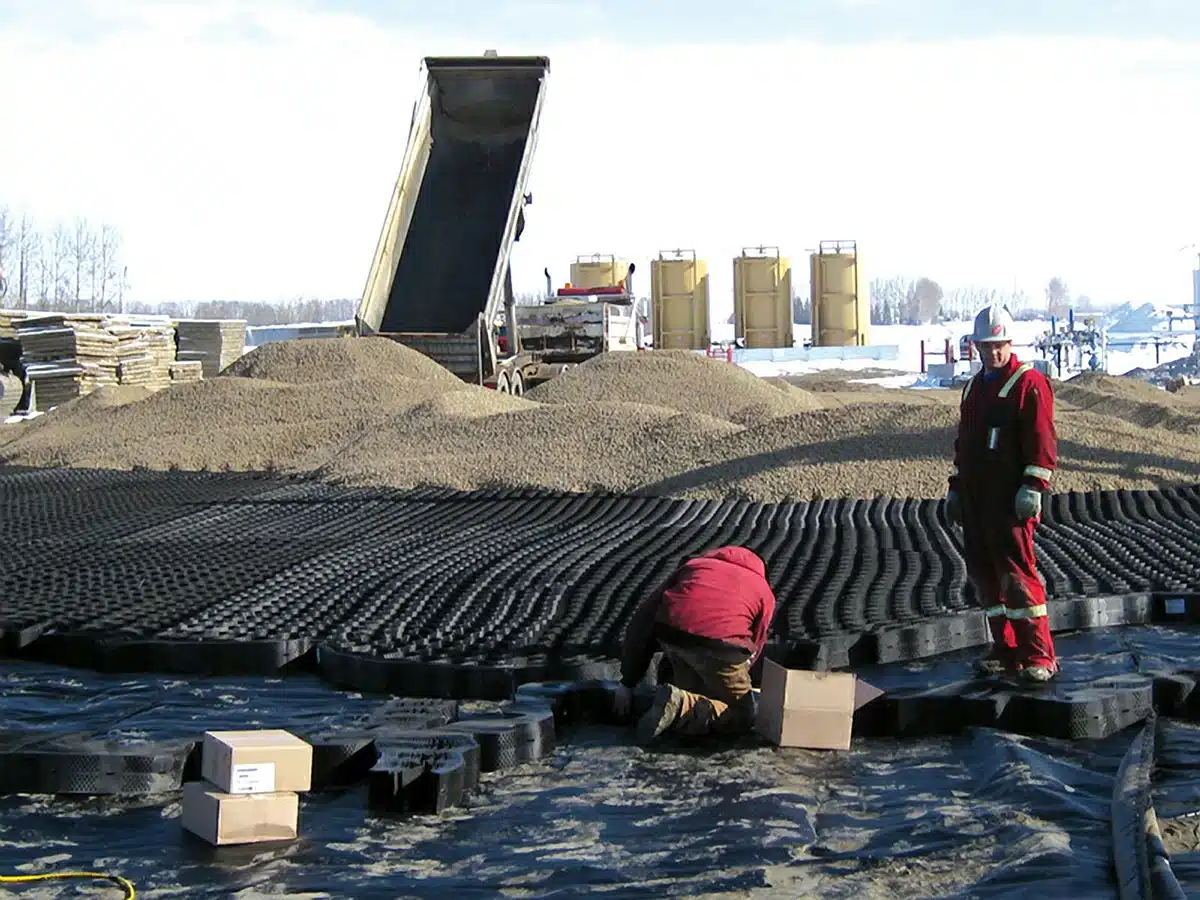

What is the best gravel for geocell?
Selecting the best gravel for geocells depends on several factors:
- Particle Size: Opt for angular gravel with uniform particle sizes between 3/8 to 3/4 inches, ensuring interlocking and stability within the geocell structure.
- Material Composition: Crushed stone or angular rock fragments are ideal choices due to their ability to interlock and distribute loads effectively.
- Durability: Choose gravel resistant to degradation and erosion, ensuring longevity and sustained performance within the geocell system.
- Compatibility: Consider gravel that complements the environmental conditions and load-bearing requirements of the intended project.
What is Geocell used for?
Geocells are versatile in their applications across different sectors, catering to:
- Soil Stabilization on Flat Ground and Steep Slopes: These cells effectively reinforce weak soils, offering solutions for erosion control and enhancing load-bearing capacities crucial for roads, embankments, and sloped areas.
- Gravel Stabilization: Geocells play a pivotal role in confining and supporting gravel, particularly in parking lots, driveways, and pathways. By doing so, they minimize surface rutting and bolster structural integrity.
- Erosion Control, Channel Protection, and Structural Reinforcement: In slope applications, geocells serve to mitigate erosion, ensuring stability, soil retention, and safeguarding the landscape’s integrity. Furthermore, they provide structural reinforcement for load support and earth retention, offering comprehensive solutions for erosion control and channel protection.
What is the difference between a geocell and a geogrid?
Definitions and Design:
Geocells:
- Design: Geocells are three-dimensional, honeycomb-like structures made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or other polymeric materials. They form a cellular confinement system when expanded.
- Function: Geocells are designed to confine and stabilize granular materials, reducing lateral movement and increasing load-bearing capacity.
- Geogrids:
- Design: Geogrids are two-dimensional, grid-like structures made from polymers such as polyethylene, polypropylene, or polyester. They have an open mesh design with integrally connected tensile ribs.
- Function: Geogrids are used to reinforce soils and other materials by providing tensile strength and distributing loads over a wider area.
Construction:
Geocells:
- Installation: Geocells are expanded on-site and filled with soil, gravel, or concrete. The cells are then compacted to create a solid, stable structure.
- Configuration: They are often used in slope stabilization, erosion control, load support, and retaining walls.
- Geogrids:
- Installation: Geogrids are laid out in layers within soil or aggregate materials. They are typically used in conjunction with other geosynthetics.
- Configuration: Common applications include roadways, retaining walls, embankments, and foundation reinforcement.
Applications:
Geocells:
- Primary Uses: Geocells are primarily used for soil stabilization on slopes and embankments, erosion control, and load support in pavements and roads.
- Advantages: They provide excellent load distribution, reduce material displacement, and enhance the overall stability of structures.
- Geogrids:
- Primary Uses: Geogrids are widely used in road and railway construction, retaining walls, embankments, and foundation reinforcement.
- Advantages: They improve soil stability, increase the bearing capacity, and extend the lifespan of infrastructure projects.
Key Differences:
- Structural Design: Geocells are three-dimensional and confine materials within their cells, while geogrids are two-dimensional and provide reinforcement through their grid structure.
- Applications: Geocells are often used for slope and load support applications, whereas geogrids are more commonly used for soil reinforcement and stabilization in various construction projects.
What do you put under gravel grids?
To ensure proper installation and functionality of gravel grids, several layers and components are typically used. Here is a detailed explanation:
Sub-Base Layer:
- Material: Crushed stone or compacted aggregate.
- Purpose: Provides a stable foundation for the gravel grid system, distributes weight evenly, and prevents sinking or shifting.
- Depth: Usually 4-6 inches, depending on soil conditions and load requirements.
Geotextile Fabric:
- Material: Permeable fabric.
- Purpose: Separates the sub-base from the soil, preventing mixing and maintaining the integrity of the sub-base. It also aids in drainage and prevents weed growth.
- Installation: Laid directly on top of the soil before adding the sub-base layer.
Gravel Grid System:
- Material: Interlocking plastic grids.
- Purpose: Provides a stable structure for the gravel, preventing movement and rutting. It also helps distribute loads and allows for proper drainage.
- Installation: Placed on top of the compacted sub-base layer.
Gravel Fill:
- Material: Angular gravel.
- Purpose: Fills the cells of the gravel grid, providing a durable and stable surface. The angular shape helps lock the gravel in place.
- Depth: Filled to the top of the gravel grid cells.
In conclusion, the synergy between geocells and the choice of gravel significantly impacts the efficiency and durability of infrastructure projects. By understanding the ideal gravel characteristics, coupled with the diverse applications of geocells, engineers and project managers can maximize the performance and longevity of their construction endeavors.

Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















