+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
In the world of civil engineering and construction, geosynthetics play a pivotal role in enhancing the stability and performance of various projects. Among these geosynthetics, “geonet for gravel” is a versatile and crucial component. This article explores the differences between geotextile and geonet, delves into the applications of geonet, highlights the distinctions between geogrid and geonet, and explains the concept of transmissivity in geonets.
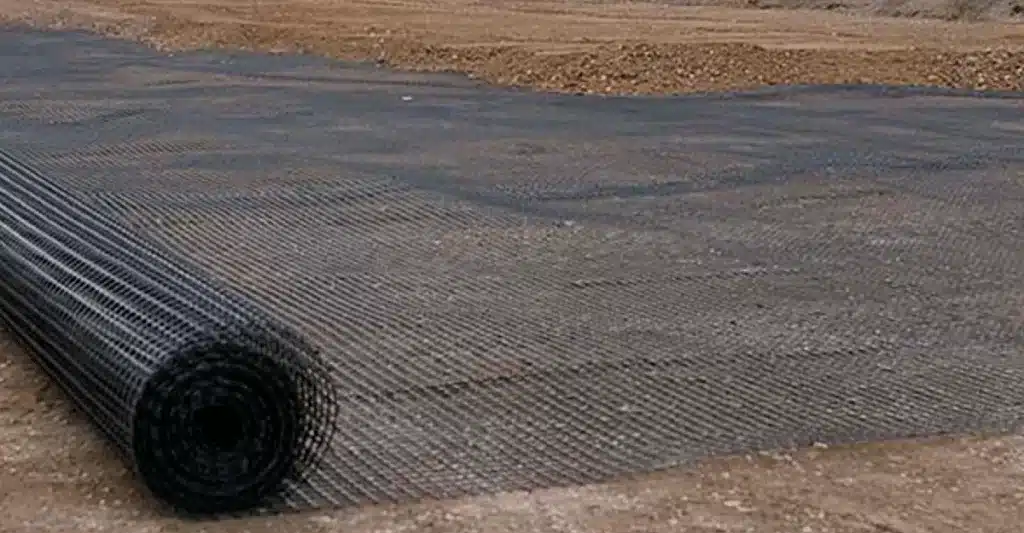

What is the difference between geotextile and geonet?
Geotextiles and geonets are both materials used in geotechnical engineering and civil engineering applications, but they serve different purposes:
- Geotextile: Geotextile is a water-permeable fabric made from synthetic materials such as polyester, polypropylene, or polyethylene. They are used for filtration, separation, reinforcement, and protection in a variety of civil engineering applications. Geotextiles are commonly used to prevent soil erosion, improve drainage, strengthen soil structure and separate different soil layers. They come in both woven and non-woven types, with varying strengths and filtering capabilities.
- Geonets: Geonets are three-dimensional structures typically made from polyethylene or other plastics.
They are used primarily for drainage and filtration purposes.
Geonets have a grid-like structure with interconnected voids, allowing for the efficient flow of water or gases.
They are often used in combination with geotextiles in drainage systems to enhance water flow and prevent soil erosion.
Geonets can also be used to provide structural support in some applications, such as beneath roadways or behind retaining walls.
What are geonets used for?
Geonets are used primarily for drainage and liquid or gas flow management in civil engineering and environmental applications. Made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or similar materials, geonets have a three-dimensional structure that provides high permeability and allows efficient fluid movement. Common uses include:
- Landfill Drainage: Placed between geomembranes to facilitate leachate collection and gas venting.
- Subsurface Drainage: Used in roadbeds, railways, and retaining walls to manage water flow and prevent waterlogging.
- Erosion Control: Helps in slope stabilization by allowing controlled water drainage.
- Foundation Drainage: Installed around structures to prevent water accumulation and hydrostatic pressure buildup.
- Tunnel and Underground Construction: Aids in water redirection and reduces seepage risks.
What is the difference between Geogrid and Geonet?
Geogrid and geonet are both materials used in geotechnical and civil engineering for various applications, particularly in soil stabilization, erosion control, drainage, and reinforcement. While they serve similar purposes, they have distinct differences in terms of structure and function:
Geogrid:
- Geogrids are typically made of polymers (such as polyester, polyethylene, or polypropylene) or occasionally metals (such as steel or fiberglass).
- They have a grid-like structure, often resembling a mesh or net, with open spaces between the grid elements.
- Geogrids are primarily used for soil reinforcement applications. They are placed within the soil or between soil layers to improve load distribution, enhance bearing capacity, and reduce deformation.
- The main function of geogrids is to provide tensile strength to soil structures, thereby preventing lateral spreading or movement.
Geonet:
- Geonets are also manufactured from polymers, usually high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or polypropylene (PP).
- They have a more complex structure consisting of closely spaced ribs or channels that create a three-dimensional network.
- Geonets are primarily used for drainage applications. They provide pathways for the flow of fluids (such as water or gases) within soil or other geotechnical materials.
- The main function of geonets is to collect and convey water away from structures or areas prone to water accumulation, thereby preventing waterlogging, soil erosion, and potential instability.
In summary, while both geogrids and geonets are used in geotechnical engineering, geogrids primarily provide reinforcement to soil structures through tensile strength, while geonets facilitate drainage by creating pathways for fluid flow within the soil or other materials.
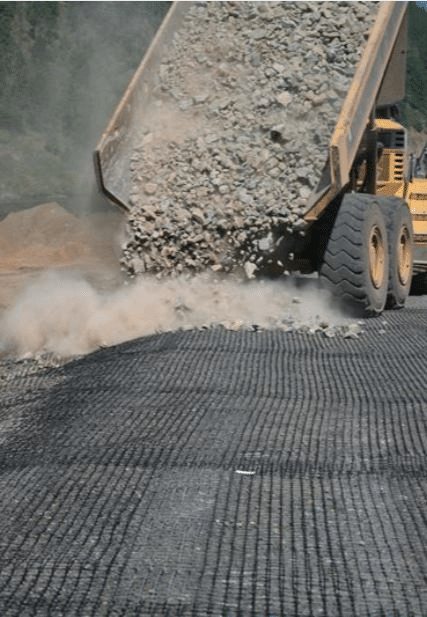

What is the transmissivity of geonet?
Transmissivity in the context of geonets refers to their ability to allow fluids to flow across their plane under a hydraulic gradient. Geonets are synthetic drainage materials commonly used in geotechnical and environmental engineering projects, such as landfills, road construction, and earth retaining structures.
- Measurement of Transmissivity: The transmissivity of a geonet is typically measured by conducting in-plane flow tests under controlled laboratory conditions. The test involves placing a section of the geonet under a hydraulic gradient and measuring the flow rate through the material. This value is expressed in terms of volume per time per width of the geonet, usually in units like liters per second per meter
- Significance in Geotechnical Engineering: Transmissivity is a critical property for geonets because it determines how effective the material will be in drainage applications. High transmissivity allows for efficient management of water and other fluids, reducing hydrostatic pressure and enhancing the stability of engineered structures. It ensures that water can be redirected or drained effectively, preventing water from pooling and potentially causing structural failures or environmental issues.
This property is crucial for designing effective drainage systems within geotechnical projects, influencing both performance and safety aspects.
In conclusion, geonet for gravel is an indispensable geosynthetic material that finds extensive use in civil engineering and construction. Understanding its differences from geotextiles and geogrids, its diverse applications, and the concept of transmissivity can help engineers and construction professionals make informed decisions when implementing geonet solutions in their projects. By harnessing the benefits of geonets, they can ensure the longevity and stability of their structures while minimizing environmental impacts.

Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















