+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
Geogrids are a vital material used in modern engineering and construction, playing a significant role in improving the strength and stability of various structures. They are synthetic materials made of polymers, designed to reinforce soil and aggregate, ensuring better load distribution and preventing shifting or deformation. In this article, we will explore the purpose, usage, and applications of geogrids to help you understand how this technology enhances infrastructure projects worldwide.
What is the purpose of a geogrid?
The main purpose of a geogrid is to reinforce the ground and soil, to reinforce soils and similar materials, providing structural support where conditions might otherwise lead to instability. By distributing loads more evenly, geogrids help prevent soil displacement and erosion. They are commonly used in road construction, retaining walls, and other civil engineering projects, ensuring that surfaces remain stable under heavy loads and challenging environmental conditions.
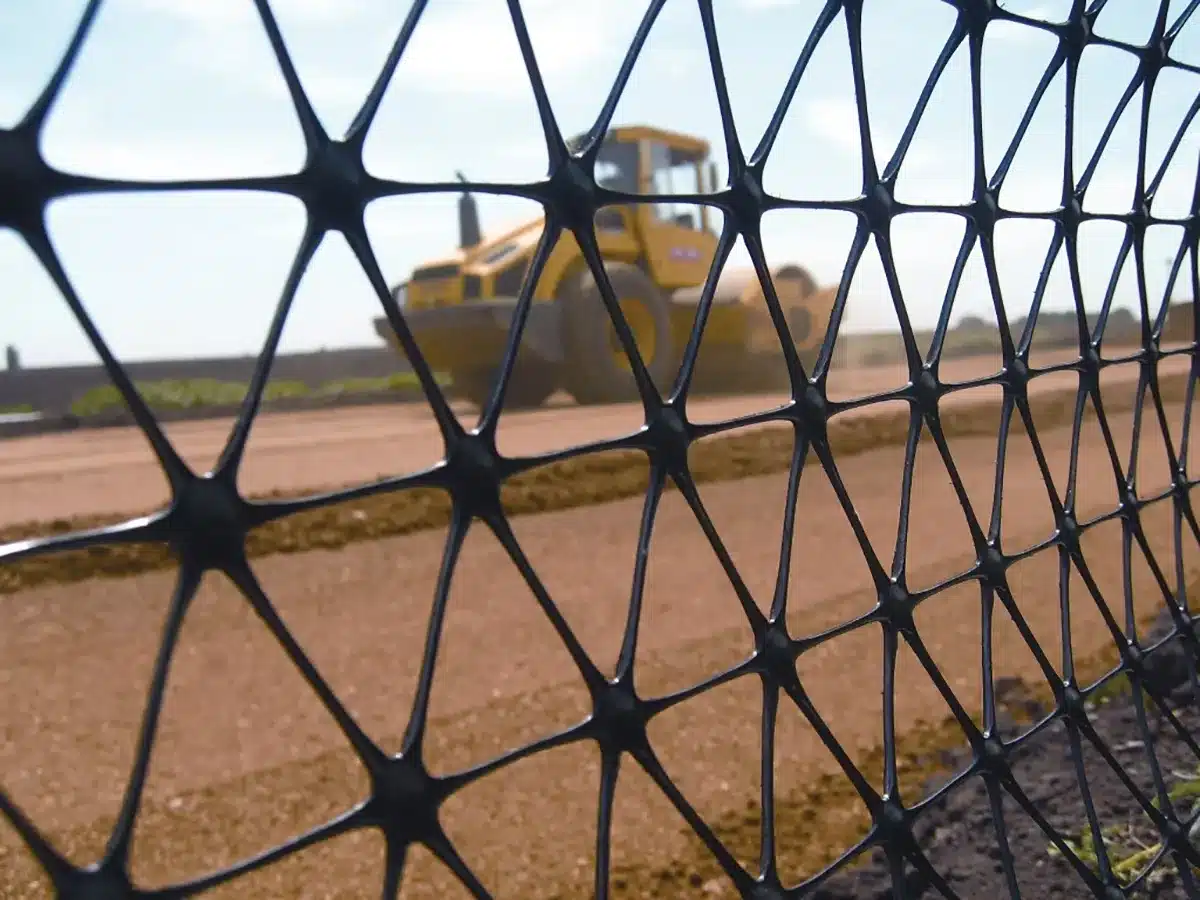

When should you use Geogrid?
Geogrids should be used in situations where soil reinforcement is necessary to ensure long-term durability, particularly for walls taller than three to four feet. They are especially beneficial in areas with weak or unstable soil, where traditional foundations may fail. If a project involves the construction of roads, railways, or embankments in areas prone to shifting soil or erosion, geogrids provide the added strength and stability needed to support these structures safely.
Where do you put a geogrid?
Geogrids are typically placed between layers of soil or aggregates to maximize their reinforcing effect, on the subgrade, either parallel to a road centerline or at right angles. In road construction, for instance, they are positioned beneath the surface layer to stabilize the ground beneath. Similarly, in retaining walls or embankments, geogrids are embedded within the soil to prevent lateral movement and ensure the structure remains intact.
Where are geogrids used?
Geogrids are used in a variety of construction projects, including roadbeds, parking lots, or airport runways:
- Roads and highways: Enhancing the stability of the foundation to support heavy traffic loads.
- Railroad construction: Reinforcing soil under tracks to ensure a smooth and stable surface.
- Retaining walls: Prevent soil erosion and support vertical soil structures.
- Landfills and waste management: Providing stability in waste containment areas and preventing settling.
- Pavement and flooring: Improving the durability and longevity of paved surfaces.
Geogrids are a crucial component in modern civil engineering, offering essential reinforcement for soil and structures that need to endure significant stress. By enhancing stability, preventing erosion, and ensuring proper load distribution, geogrids make it possible to build durable infrastructure in areas with challenging soil conditions. Understanding their applications and benefits is key for anyone involved in construction or design.

Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















