+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
When it comes to constructing a stable retaining wall, knowing how to install geogrid for retaining wall applications is crucial. Geogrid materials offer reinforcement to the soil, enhancing the wall’s stability and longevity. In this article, we will explore key questions related to the installation process, industry standards, and best practices for successful geogrid use in retaining walls.
What is Geogrid, and Why is it Important for Retaining Walls?
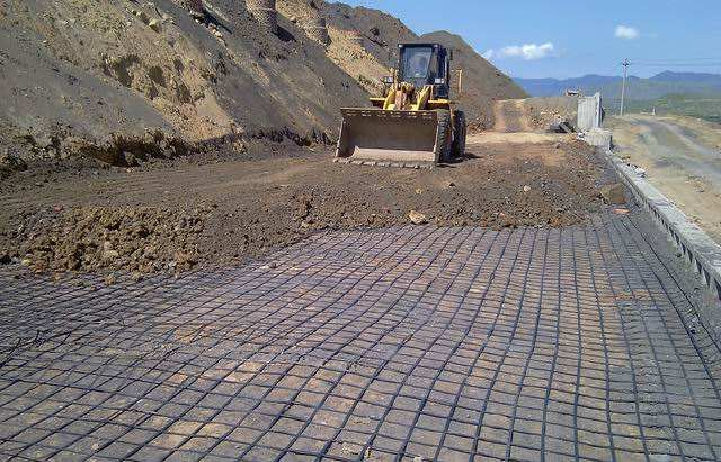

Choosing the correct geogrid type is a critical design decision that directly affects the performance, safety, and service life of a retaining wall system. Geogrids are selected based on their tensile behavior, soil interaction, and the structural demands of the project.
- Uniaxial Geogrid (UX): Uniaxial geogrids provide high tensile strength in one primary direction, making them ideal for resisting lateral earth pressures behind retaining walls. They are most commonly used in segmental retaining walls and mechanically stabilized earth (MSE) structures, especially for medium to tall walls where horizontal soil forces dominate.
- Biaxial Geogrid (BX): Biaxial geogrids offer tensile strength in two perpendicular directions. While they are not typically used as primary wall reinforcement, they are effective for base stabilization, improving load distribution, and reinforcing weak subgrade soils beneath retaining walls. Their use helps reduce differential settlement and enhances foundation performance.
- Triaxial Geogrid: Triaxial geogrids provide multi-directional strength and superior load distribution. They are well suited for complex loading conditions, poor-quality backfill, curved wall alignments, or sites subject to dynamic or seismic forces. Their geometry improves soil confinement and overall system stiffness.
- Key Selection Factors: The appropriate geogrid type should be determined based on wall height, backfill properties, anticipated surcharge loads, drainage conditions, and site-specific geotechnical data. Manufacturer design guidelines and engineered calculations should always be followed to ensure compliance with industry standards.
Selecting the right geogrid ensures effective soil reinforcement, minimizes wall deformation, and delivers long-term structural reliability for retaining wall applications.
How Do You Install Geogrid for a Retaining Wall?
Proper geogrid installation is essential for retaining wall stability and long-term performance:
- Prepare the base: Excavate a level trench and install a compacted gravel or crushed stone foundation.
- Set the first block course: Place and level the initial row of retaining wall blocks to ensure alignment.
- Install geogrid layers: Cut geogrid to the required length (typically 60–100% of wall height) and place it perpendicular to the wall, extending back into the reinforced soil zone.
- Anchor the geogrid: Lay the geogrid flat on top of the block course, ensuring firm contact at the front edge.
- Backfill and compact: Cover the geogrid with approved backfill and compact properly to lock soil and grid together.
- Repeat as required: Continue stacking blocks and installing additional geogrid layers at specified vertical intervals.
Correct placement, tension, and compaction allow the retaining wall to resist lateral earth pressure and prevent bulging or failure over time.
What Types of Geogrid are Best for Retaining Walls?
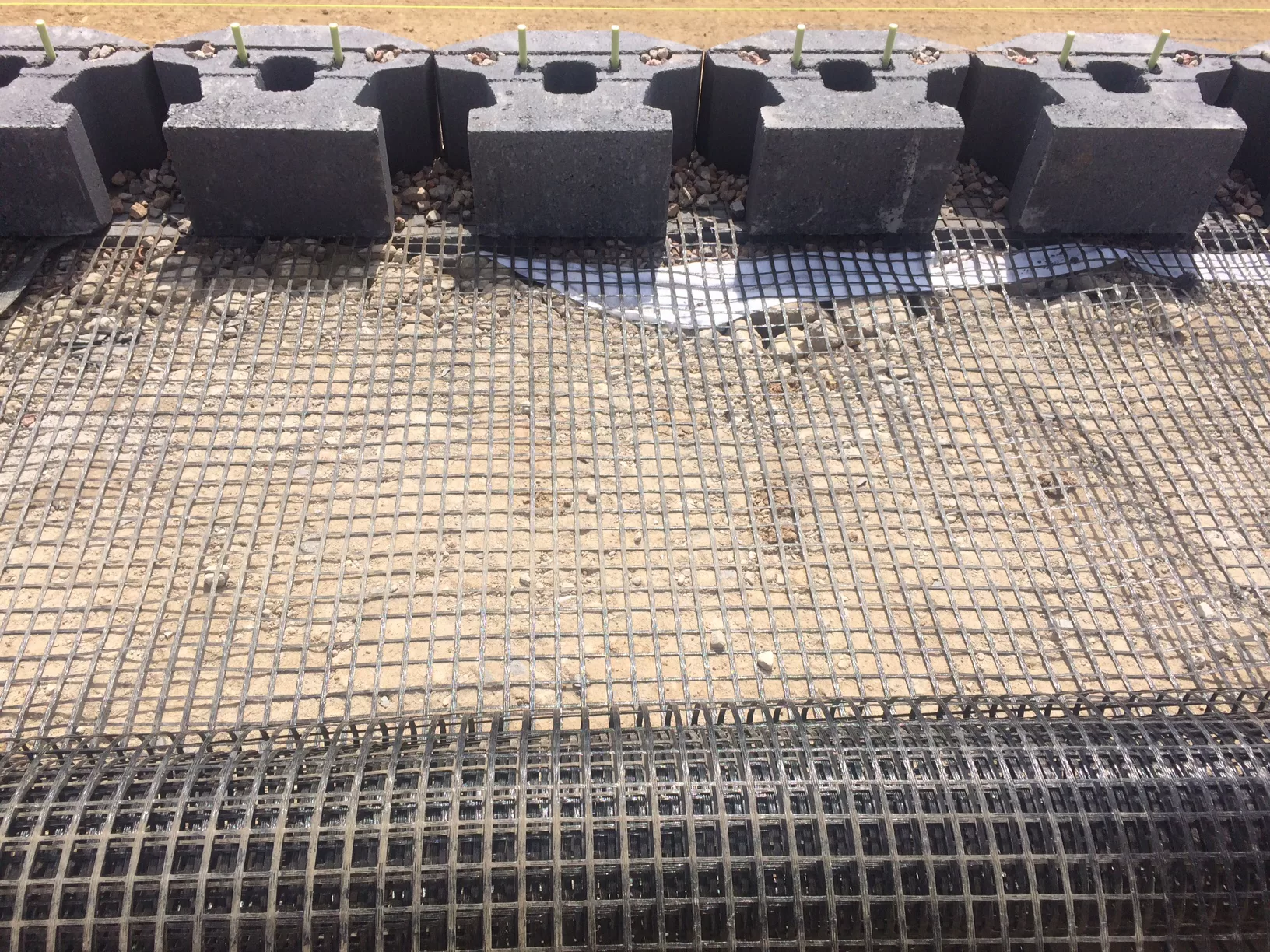

Selecting the right geogrid type is essential for building stable and durable retaining walls. Key options include:
- Uniaxial Geogrid (UX): Provides high tensile strength in one direction, ideal for resisting horizontal pressure behind tall walls. Commonly used in segmental retaining walls and mechanically stabilized earth (MSE) systems.
- Biaxial Geogrid (BX): Offers strength in both directions, suitable for base reinforcement and distributing loads on weaker soils. Helps reduce settlement and improve foundation stability.
- Triaxial Geogrid: Provides multi-directional strength, useful for complex sites, poor subgrades, or seismic-prone areas. Ensures even load distribution across angles.
Considerations for choosing geogrid: wall height, backfill soil type, expected loads (traffic, structures), drainage conditions, and adherence to manufacturer or engineering guidelines.
Using the proper geogrid type ensures effective soil reinforcement, prevents wall deformation, and enhances long-term performance of the retaining structure.
How do you install geogrid for a retaining wall?
Installing geogrid for a retaining wall involves several critical steps to ensure stability and durability:
- Prepare the base: Excavate a stable trench and add compacted gravel or crushed stone.
- Lay first course of blocks: Ensure they are level and aligned properly.
- Place geogrid layers: Cut the geogrid to the required length (usually 60–100% of wall height) and lay it perpendicular to the wall, anchoring the front edge.
- Backfill: Cover the geogrid with compacted soil or gravel, then continue building additional block courses, repeating geogrid placement at specified intervals.
- Choose the right type: Use uniaxial geogrid for high tensile strength along the slope, biaxial for foundation stabilization, or triaxial for multi-directional reinforcement.
- Ensure proper embedment and compaction: Maintain correct tension, layering, and compaction to maximize reinforcing effect.
Proper installation distributes loads evenly, prevents bulging or settlement, and significantly extends the retaining wall’s lifespan.
By understanding how to install geogrid for retaining wall applications, engineers and construction professionals can ensure long-lasting, stable, and effective retaining walls. Implementing proper installation techniques, selecting the right type of geogrid, and following industry guidelines are all key to achieving optimal results.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















