+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
The battle against slope erosion is an ongoing challenge in geotechnical engineering, a field dedicated to understanding and managing Earth’s physical properties in construction and land use. One innovative solution that has risen to prominence is the use of geocells, particularly in how Geocells Stabilize Slopes. These cellular confinement systems offer a sustainable, efficient way to protect slopes from erosion, supporting soil stability and vegetation growth. This popular science article delves into the concept of geocells, exploring their role, application, and unique characteristics in slope erosion protection.
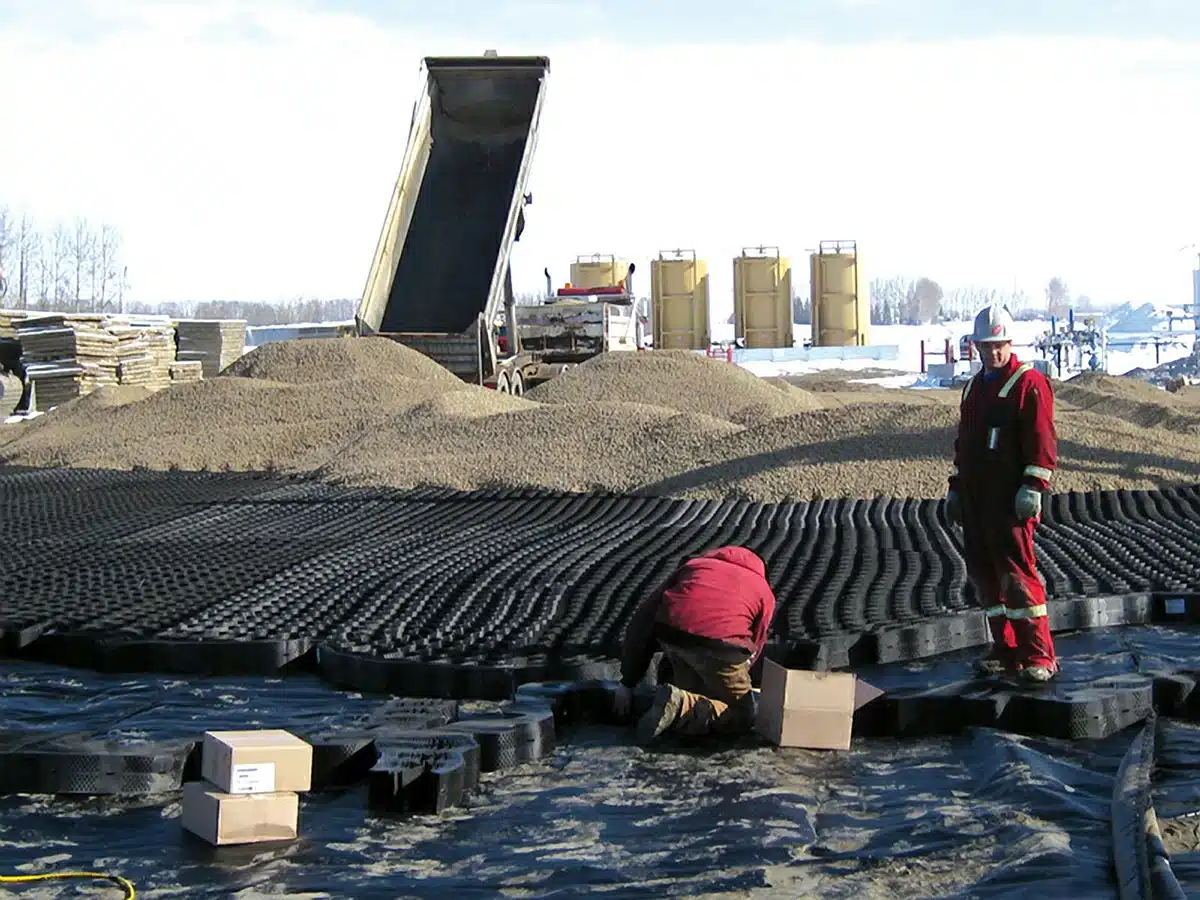

What is a Geocell for Slope Protection?
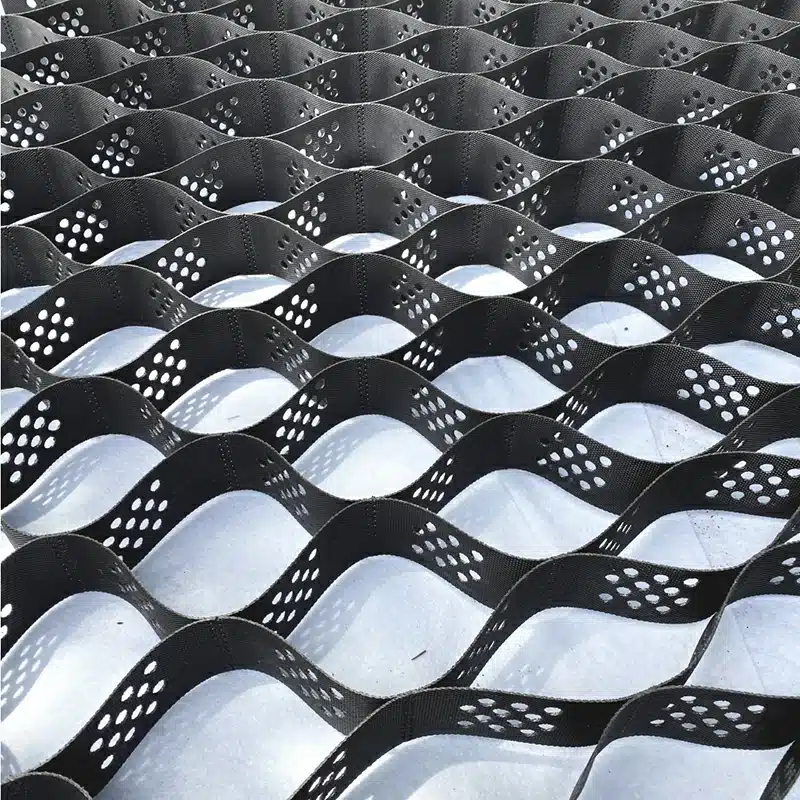
A geocell for slope protection is a three-dimensional, honeycomb-shaped cellular confinement system, typically manufactured from HDPE or PVC polymers, designed to stabilize slopes and prevent soil erosion.
- Structural confinement: The interconnected cells confine soil, sand, or gravel, reducing lateral movement and surface erosion.
- Runoff control: By slowing down water flow, geocells minimize runoff velocity and prevent soil washout.
- Vegetation support: The open-cell structure allows plant roots to grow deep and interlock with the soil, creating natural reinforcement.
- High durability: Resistant to UV exposure, chemicals, and extreme weather conditions.
- Cost-effective & sustainable: Requires less concrete or stone compared to traditional slope protection methods.
Geocells are widely used in road embankments, slope revetments, landfills, riverbanks, and flood-prone areas, providing a long-term, environmentally friendly solution for slope stabilization and erosion control.
What are the Slope Protection Measures in Geotechnical Engineering?
Slope protection in geotechnical engineering involves various techniques used to stabilize slopes and prevent erosion or failure. Key measures include:
- Geogrids: Reinforce soil and improve stability, especially for steep slopes.
- Geocells: Provide structure and prevent soil erosion on slopes.
- Retaining Walls: Hold back soil and prevent sliding, often using geotextiles for reinforcement.
- Vegetation: Planting grasses or shrubs to bind soil and reduce water erosion.
- Riprap: Large stones placed on slopes to resist water erosion.
- Drainage Systems: Redirect water to prevent saturation and instability.
These methods ensure long-term slope stability and safety in construction and natural landscapes.
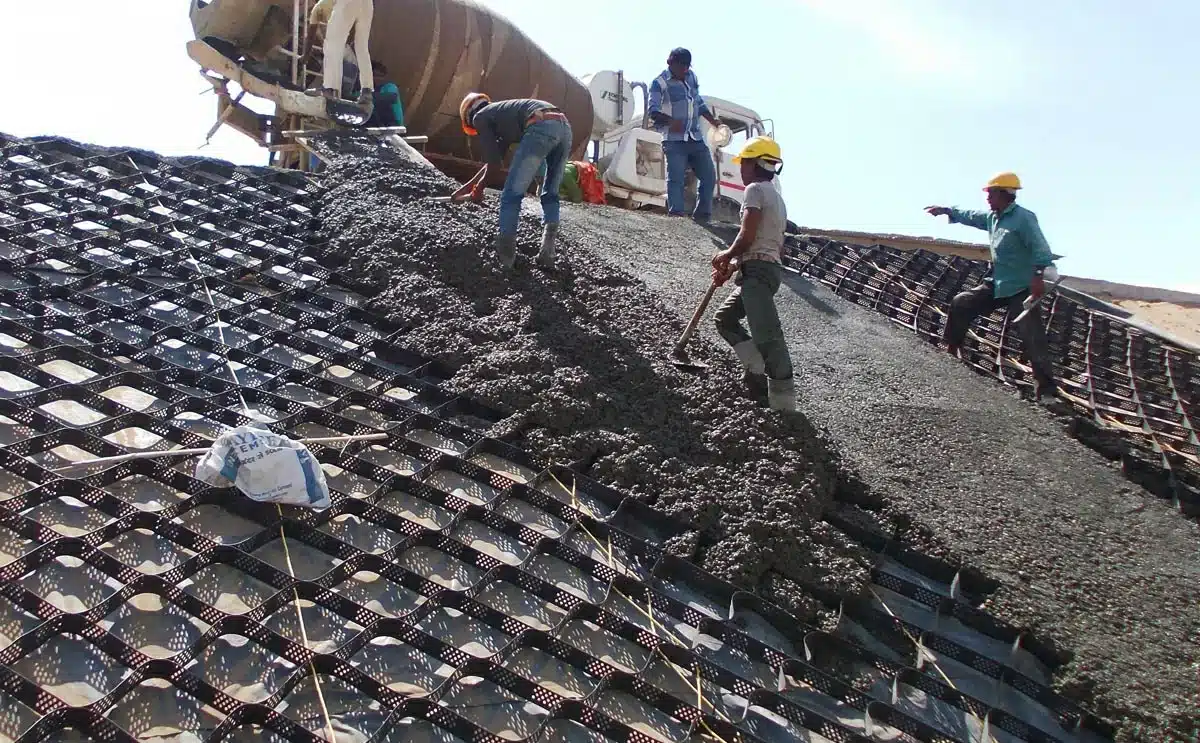

What is a Geocell?
A Geocell is a three-dimensional, honeycomb-like structure made from polymers or other materials, designed to reinforce and stabilize soils in various civil engineering applications. It is typically used in construction, erosion control, and road construction projects.
Geocells are often filled with gravel, sand, or other aggregates, which help to distribute loads evenly, prevent soil erosion, and improve the strength and durability of the ground. These structures are particularly useful for stabilizing soft soils, reinforcing slopes, and enhancing drainage systems in areas prone to erosion or instability.
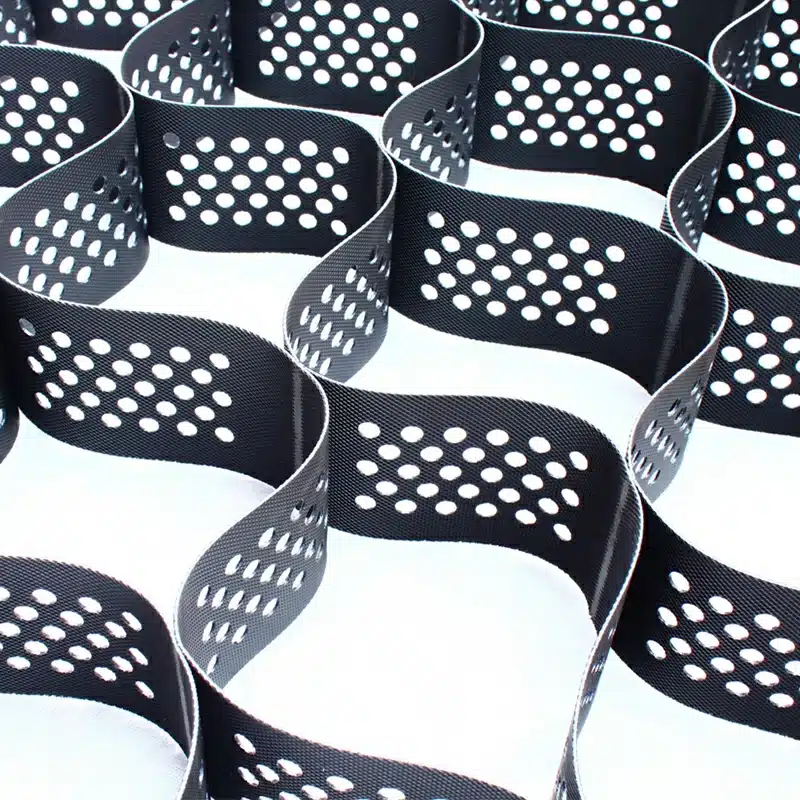
What are the Characteristics of a Geocell?
A geocell is a three-dimensional, honeycomb-like structure made from polymer materials, typically used for soil stabilization and erosion control. Key characteristics include:
- Flexibility: Easily conforms to different terrains.
- Strength: Enhances soil stability by distributing loads evenly.
- Durability: Resistant to UV rays, chemicals, and weathering.
- Permeability: Allows water flow while preventing erosion.
- Eco-friendly: Supports vegetation growth by allowing root penetration.
Geocells have emerged as a highly effective and sustainable solution for slope erosion control in modern geotechnical engineering. By confining soil within a three-dimensional structure, they significantly improve slope stability, reduce surface runoff, and promote vegetation growth. Compared with traditional slope protection methods, geocells offer advantages in flexibility, durability, cost efficiency, and environmental compatibility. As infrastructure development expands into more challenging terrains and sustainability becomes a core engineering priority, geocell systems will continue to play a vital role in long-term slope stabilization, erosion protection, and resilient landscape design.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















