+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
In the intricate world of environmental engineering and hydrology, understanding the dynamics of water flow beneath our feet is crucial for sustainable development and conservation efforts. Among the myriad of technologies and materials employed to manage this flow, geonets have emerged as a silent yet powerful ally. This article delves into the properties and functions of geonets, shedding light on their role in directing water flow beneath the earth’s surface. By exploring how these synthetic drainage materials work, we can appreciate their significance in various applications, from landfill liners to erosion control in construction projects.
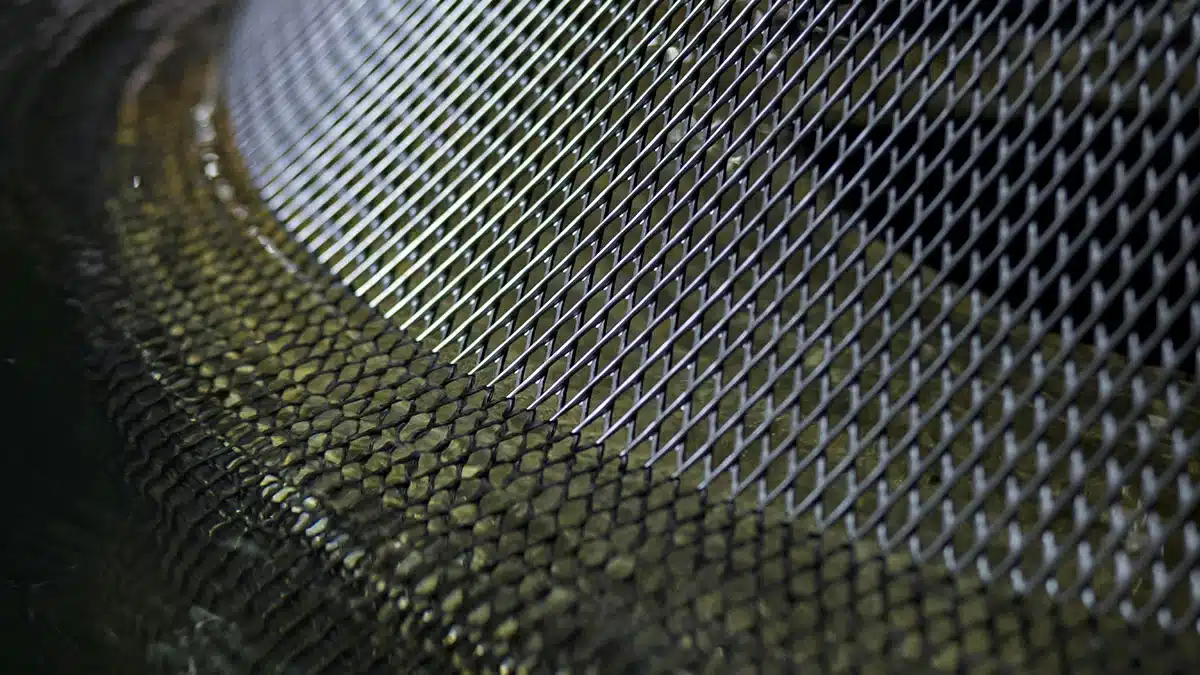
What are the properties of geonet?
Geonets are synthetic, engineered materials used primarily in civil engineering projects for drainage and filtration purposes. Here are some of their key properties:
Composition: Typically made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or polypropylene, geonets are designed to be chemically resistant and durable. This makes them suitable for use in harsh environmental conditions.
Structure: Geonets have a net-like structure that allows them to maintain flow capacity, ensuring efficient fluid drainage and filtration. Their apertures are often triangular or rectangular, and their structure is usually either biplanar (two layers) or triplanar (three layers).
Physical Attributes:
- Thickness: Usually ranges from 4 to 8 mm, offering varying drainage capacities.
- Tensile Strength: High tensile strength makes geonets suitable for withstanding pressure loads in drainage systems.
Applications:
- Landfill Drainage: Serve as drainage layers in landfill caps and liners to manage leachate and gas emissions.
- Retaining Walls: Provide drainage behind retaining walls to prevent water buildup and erosion.
- Road and Railway Projects: Ensure effective subsurface drainage to prevent soil saturation and instability.
What is the function of geonet?
GeoNet is a geological hazard monitoring system based in New Zealand. Its primary functions include:
- Earthquake Monitoring: GeoNet operates a network of seismic sensors to detect and locate earthquakes in real time. This information helps in understanding seismic activity and issuing warnings.
- Volcano Monitoring: The system includes volcano observatories and monitoring equipment to track volcanic activity. This helps in predicting eruptions and issuing alerts to minimize risk to people and infrastructure.
- Landslide Monitoring: GeoNet tracks landslide-prone areas using various sensors and techniques to provide early warnings and assess risk.
- Tsunami Monitoring: It includes a network of sea-level gauges and seismic instruments to detect and provide early warnings for tsunamis.
- Data Collection and Research: GeoNet collects and disseminates geological data, which is used for research, hazard assessment, and to inform public safety measures and policies.
- Public Information and Alerts: It provides real-time data, reports, and alerts to the public and authorities to ensure timely and informed responses to geological hazards.
GeoNet is crucial for mitigating the impact of natural hazards in New Zealand by providing timely and accurate information and facilitating research and preparedness efforts.
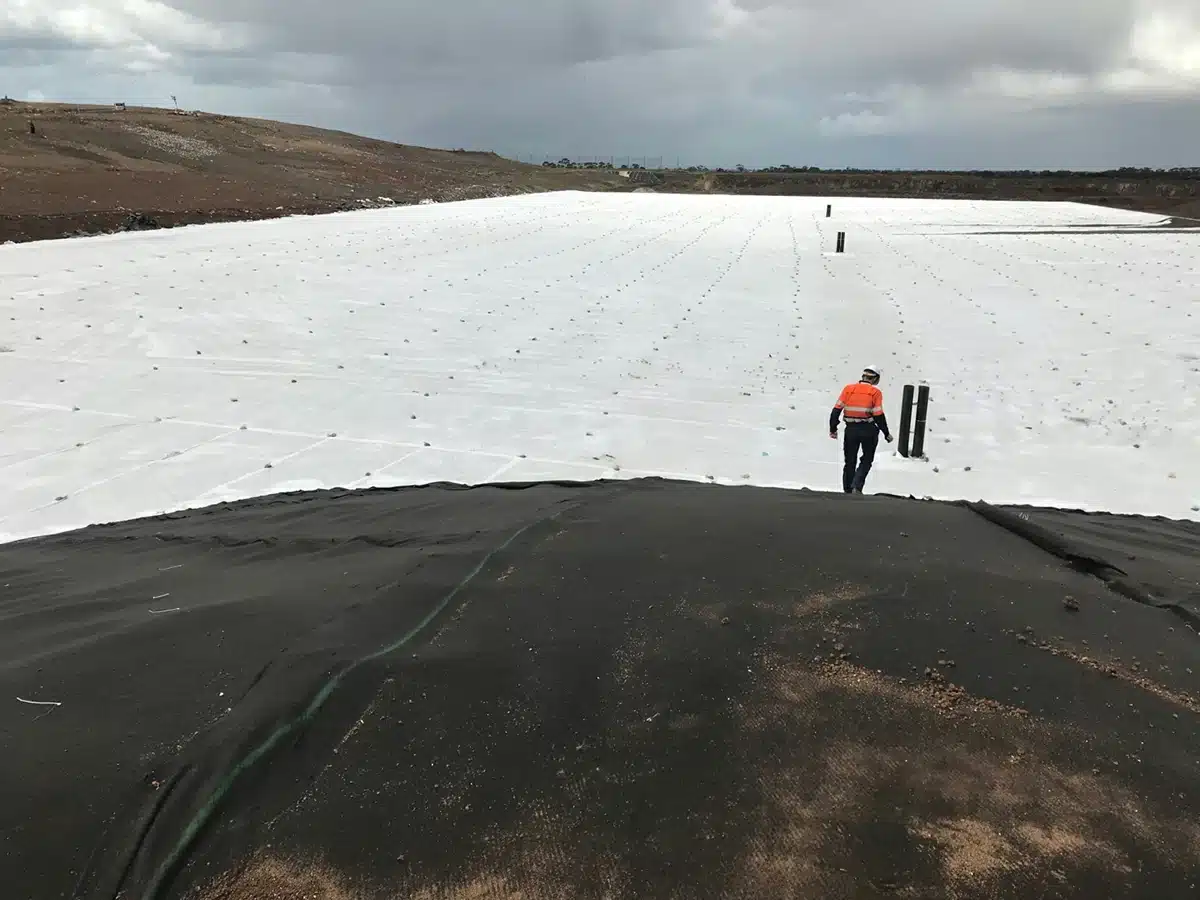

How does geonet water flow direction influence environmental and construction projects?
GeoNet water flow direction significantly influences both environmental and construction projects in various ways. Here’s a detailed breakdown of its impact on each:
Environmental Impact
Water Quality Management:
- Pollutant Transport: Understanding water flow direction helps in predicting the movement of pollutants. This is crucial for protecting water bodies from contamination.
- Erosion and Sedimentation: Flow direction affects erosion rates and sediment transport, impacting aquatic habitats and water quality.
- Wetland Hydrology: Proper management of wetlands depends on the knowledge of water flow patterns to maintain their ecological functions.
Habitat Conservation:
- Aquatic Ecosystems: Flow direction influences the distribution of nutrients and oxygen in rivers and streams, affecting fish and other aquatic life.
- Floodplain Management: Identifying flow directions helps in designing floodplains that support biodiversity while mitigating flood risks.
Groundwater Recharge:
- Sustainable Water Use: Understanding surface water flow can aid in identifying areas suitable for groundwater recharge, ensuring sustainable water resources.
Soil Moisture and Vegetation:
- Vegetation Patterns: Flow direction affects soil moisture distribution, which in turn influences plant growth and ecosystem health.
- Agricultural Planning: Effective irrigation planning requires knowledge of natural water flow to optimize water use and prevent waterlogging or drought stress.
Construction Projects Impact
Site Selection and Design:
- Flood Risk Assessment: Knowing the flow direction helps in selecting sites less prone to flooding, reducing risk and costs associated with flood damage.
- Foundation Design: Water flow can affect soil stability; understanding it helps in designing stable foundations for buildings and infrastructure.
Drainage Systems:
- Efficient Drainage: Proper drainage system design relies on understanding the natural flow direction to prevent waterlogging and soil erosion.
- Stormwater Management: Effective stormwater management systems are designed based on flow direction to minimize flooding and pollution.
Construction Materials and Methods:
- Material Durability: Knowledge of water flow helps in selecting materials that can withstand water-related wear and erosion.
- Construction Techniques: Techniques can be adapted to manage water flow, such as using retaining walls or other structures to redirect water away from construction sites.
Environmental Compliance:
- Regulatory Adherence: Construction projects must comply with environmental regulations that often require assessments of water flow direction to mitigate adverse impacts.
Infrastructure Longevity:
- Roads and Bridges: Ensuring these structures are designed with consideration of water flow direction prevents water damage and prolongs their lifespan.
- Utility Lines: Water flow direction affects the placement and protection of underground utilities to avoid water intrusion and damage.
GeoNet water flow direction is a critical factor in both environmental and construction contexts. It informs water quality management, habitat conservation, sustainable resource use, and the planning and execution of construction projects. Understanding and accurately mapping water flow directions leads to better decision-making, cost savings, and the minimization of environmental impacts, ensuring the sustainability and resilience of both natural and built environments.
What are the challenges and considerations in implementing geonet systems?
Implementing geonet systems, which typically involve a network of sensors for monitoring environmental and geospatial data, presents several challenges and considerations. These can be broadly categorized into technical, logistical, and operational domains:
Technical Challenges
- Data Accuracy and Precision: Ensuring the sensors provide accurate and precise measurements is crucial. This often requires high-quality sensors, which can be expensive and require regular calibration and maintenance.
- Sensor Integration: Integrating various types of sensors (e.g., temperature, humidity, seismic, GPS) into a cohesive network can be complex due to different data formats, communication protocols, and power requirements.
- Communication Infrastructure: Establishing reliable communication links, especially in remote or difficult-to-access areas, can be challenging. This may involve choosing between wired, wireless, or satellite communication, each with its own set of trade-offs.
- Data Management and Storage: Handling the vast amount of data generated by a geonet system requires robust data management strategies, including storage solutions, real-time data processing, and backup systems.
- Power Supply: Ensuring a reliable power supply for sensors, especially in remote areas, can be difficult. Options include solar power, battery power, or energy harvesting, each with limitations regarding lifespan and environmental conditions.
Logistical Challenges
- Deployment and Maintenance: Deploying sensors in challenging terrains (e.g., mountains, underwater, or urban environments) requires careful planning and often specialized equipment and personnel. Regular maintenance and calibration of sensors are necessary to ensure ongoing accuracy and reliability, which can be logistically complex.
- Scalability: Scaling up the network to cover larger areas or to include more sensors can be difficult in terms of both infrastructure and cost.
Operational Challenges
- Security: Ensuring the security of the network and the data it collects is crucial. This involves protecting against physical tampering, and cyber-attacks, and ensuring data privacy.
- Interoperability: Achieving interoperability between different sensor types and data systems is necessary for cohesive data analysis and utilization. Standards and protocols need to be established and adhered to.
- Environmental and Physical Challenges: Sensors must be designed to withstand harsh environmental conditions (e.g., extreme temperatures, humidity, physical shocks), which can vary widely depending on the deployment location.
Considerations
- Cost: Balancing the initial setup costs, ongoing operational costs, and the potential benefits of the geonet system is critical. This includes costs for hardware, software, personnel, and maintenance.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring compliance with local, national, and international regulations regarding environmental monitoring, data collection, and transmission can be complex.
- Data Analysis and Utilization: Developing robust methods for analyzing the collected data and converting it into actionable insights is essential. This may involve machine learning, statistical analysis, and visualization techniques.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Engaging with stakeholders, including government agencies, local communities, and researchers, to ensure the system meets their needs and to foster collaboration and data sharing.
- Redundancy and Reliability: Building redundancy into the system to ensure continued operation in the event of sensor or communication failures is crucial for reliability.
- Ethical Considerations: Addressing ethical issues related to data privacy, especially when monitoring human activities or private properties, is important to maintain trust and legal compliance.
Implementing a geonet system requires careful planning, technical expertise, and ongoing management to address these challenges and considerations effectively.
Geonets play a crucial role in managing water flow direction beneath the earth’s surface, offering a robust solution to drainage and gas venting challenges in environmental and construction projects. Their unique properties, such as high durability, chemical resistance, and efficient water conductivity, make them indispensable in modern engineering applications. However, the successful implementation of geonet systems requires careful planning, design, and maintenance to overcome challenges and ensure their long-term effectiveness. As we continue to harness the power of geonets, their contribution to sustainable development and environmental conservation becomes increasingly evident, marking them as a key component in the world’s subsurface water management strategies.



Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















