What are geogrids?
Home » Uncategorized »+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
If you’re involved in civil engineering or construction, you’ve likely heard about geogrids and their growing role in improving project efficiency and reducing costs. But what exactly are geogrids, and how can they make a tangible difference in your project’s durability and budget? This article breaks down the essentials of geogrids — from their definition and types to their key benefits — helping you understand why they’re a game-changer in modern construction and soil stabilization.
What is a geogrid?
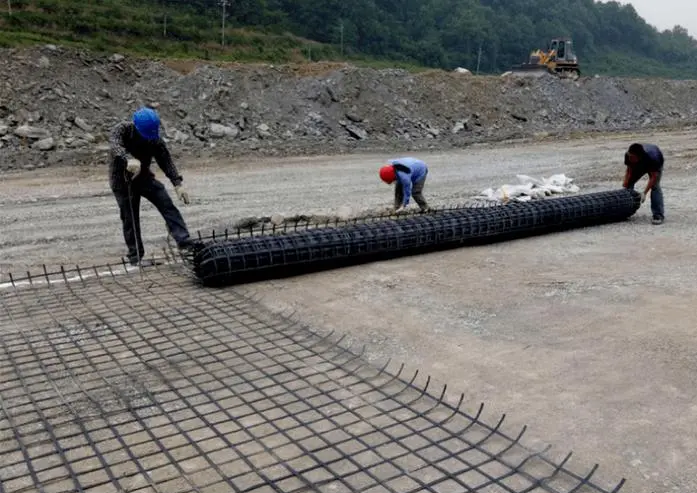

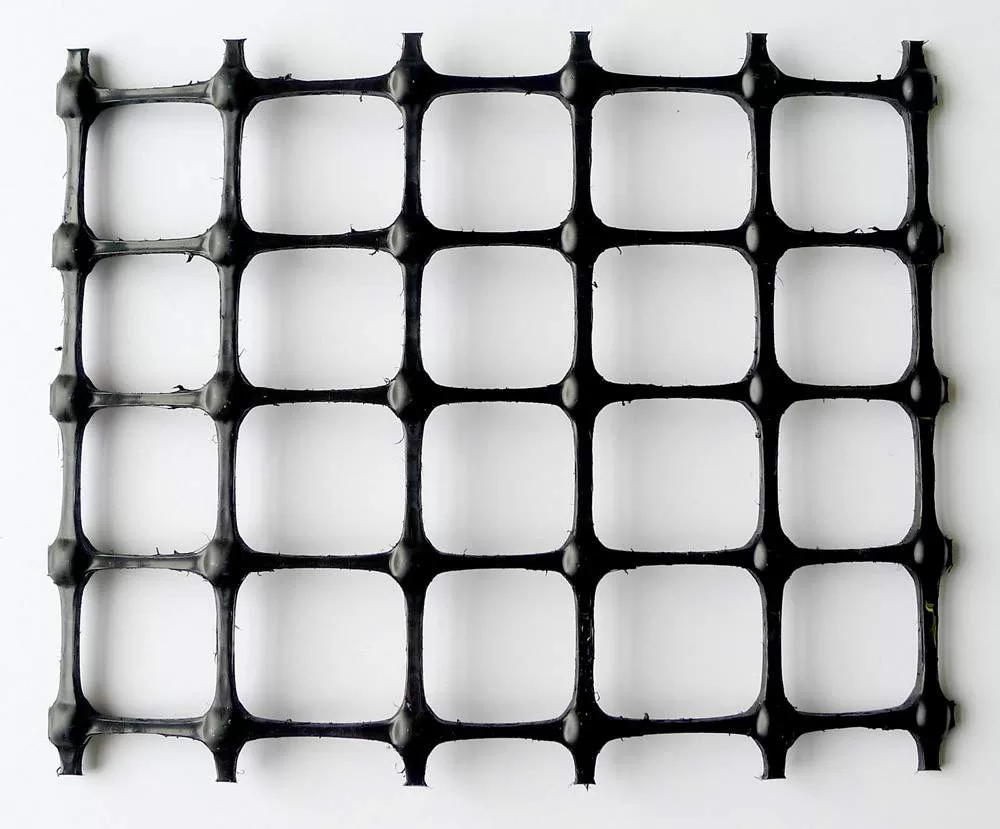
A geogrid is defined as a geosynthetic material consisting of connected parallel sets of tensile ribs with apertures of sufficient size to allow strike-through of the surrounding soil, stone, or other geotechnical material (Koerner 1998). Geogrids provide reinforcement, stabilization, and even filtration when used with properly sized aggregate fills. Made from polymers such as polypropylene, polyethylene, or polyester, they are used widely in civil engineering applications.
Geogrids are deployed for three primary applications:
- Building firm working surfaces over soft ground conditions
- Enhance a pavement’s service life
- Reduce the structural cross-section of both paved and unpaved roadways for given service life.
Geogrids have also been proven to significantly improve a pavement’s susceptibility to environmental cracking common when building over highly expansive subgrade soils. Geogrids work by interlocking with the granular or soil material placed over them. The open apertures of the geogrid allow for the confinement of material within, increasing the shear strength of overlying granular fill.
The different types of geogrids?
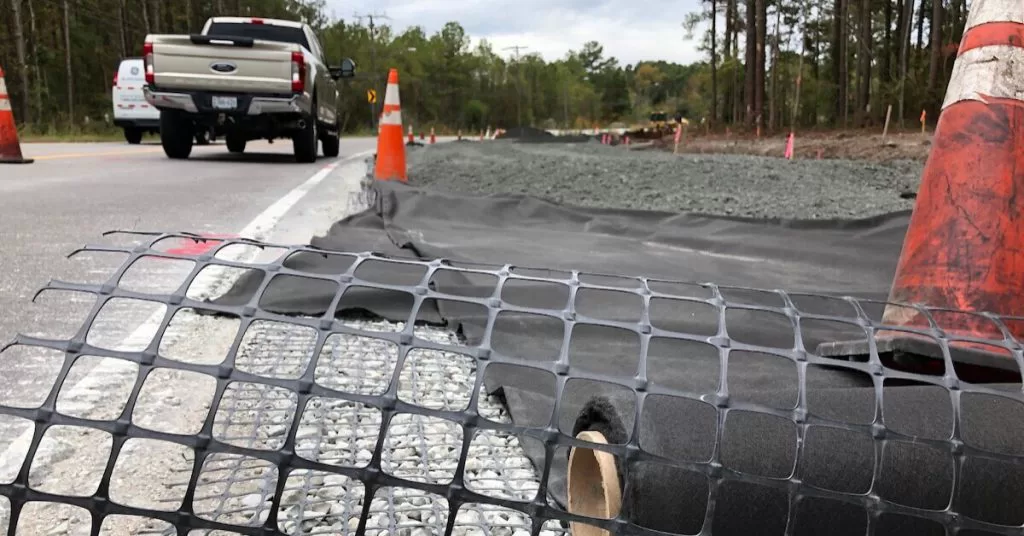

There are four types of geogrids Uniaxial, Biaxial, Triaxial (Triax®) and Geogrid-Geotextile Composites. Each designed and manufactured for specific construction applications with various geometric and structural index properties.
- Uniaxial Geogrid Certain Uniaxial (UX) geogrids are oriented along the longitudinal, “machine direction” of an extruded sheet of polymer, thus yielding a grid structure consisting of long narrow ribs. Other products utilize polyester yarns to render extremely high allowable strengths at deficient strains. Given their unique properties, Uniaxial geogrids are ideal for both wall and slope applications such as retaining walls, landfill liner systems, embankments over soft soils, and very steep earthen slopes.
- Biaxial Geogrid Biaxial (BX) geogrids are stretched in two directions, the longitudinal and transverse, equally distributing stress along both directions. While woven geogrids are still commercially available, extruded punched-and-drawn geogrids made of polypropylene are the most deployed among biaxial geogrids. Providing the geogrid with the ability to distribute loads over a wider area than usual while increasing its capacity in base stabilization applications. Biaxial geogrids are best for applications such as foundations for roadbeds, railroad truck beds, permanent unpaved roads, airport runways, construction haul roads, working platforms on weak subgrades, and parking lots.
- Triaxial Geogrid TriAx® (TX) geogrids, a next-generation enhancement to biaxial geogrids, have additional diagonal ribs that increase the product’s in-plane stiffness. The triangular pattern is formed into a hexagon to improve how the product absorbs traffic loading forces. TriAx® creates a more efficient effect that delivers optimal in-service stress transfer from the aggregate to the geogrid. Triaxial geogrids have undergone extensive full-scale and field testing and have been calibrated within the more common pavement design methodologies, both for paved and unpaved roads.
- Geogrid-Geotextile Composites Geogrid-Geotextile Composites are comprised of both material types that are heat or sonically welded together to yield an effective reinforcement and separation element for very challenging subgrade soil conditions. When subgrade filtration-separation criteria cannot be met with adequately graded fill materials, Geogrid-Geotextile Composites are ideal for deploying. Such that underlying subgrade soils may be appropriately filtered, thus preventing contamination of the overlying granular fill.
What is a Geogrid?
- Definition: A geogrid is a synthetic material made from high-strength polymers (polypropylene, polyethylene, or polyester). It consists of parallel tensile ribs that are designed to interlock with soil and aggregate, providing reinforcement and stabilization.
- Primary Applications: Geogrids are used to:
- Stabilize soft ground, allowing for the creation of firm working surfaces.
- Extend the service life of pavements by reducing maintenance costs.
- Reduce the structural cross-section required for both paved and unpaved roadways.
Choosing the right geogrid can significantly enhance your project’s performance, longevity, and cost-effectiveness. Whether you are stabilizing weak soils, reinforcing pavements, or building robust retaining walls, understanding the different types of geogrids and their specific applications is essential. With advancements like Triaxial geogrids and geogrid-geotextile composites, modern engineering offers tailored solutions for even the most challenging site conditions. When planning your next project, consider the advantages geogrids bring — and consult experts to select the ideal product that aligns with your goals, ensuring success from ground level up.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















