+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
In the realm of civil engineering and construction, the use of innovative materials to solve traditional problems has become increasingly prevalent. Among these materials, geocomposites have emerged as a versatile and efficient solution for various applications. However, understanding the pricing of geocomposites requires a deep dive into what they are, their uses, and how they compare to similar materials like geotextiles. This article aims to shed light on geocomposite prices by exploring their differences from geotextiles, their applications, the types available, and the reasons for using geofabric, providing a comprehensive overview for professionals and enthusiasts alike.
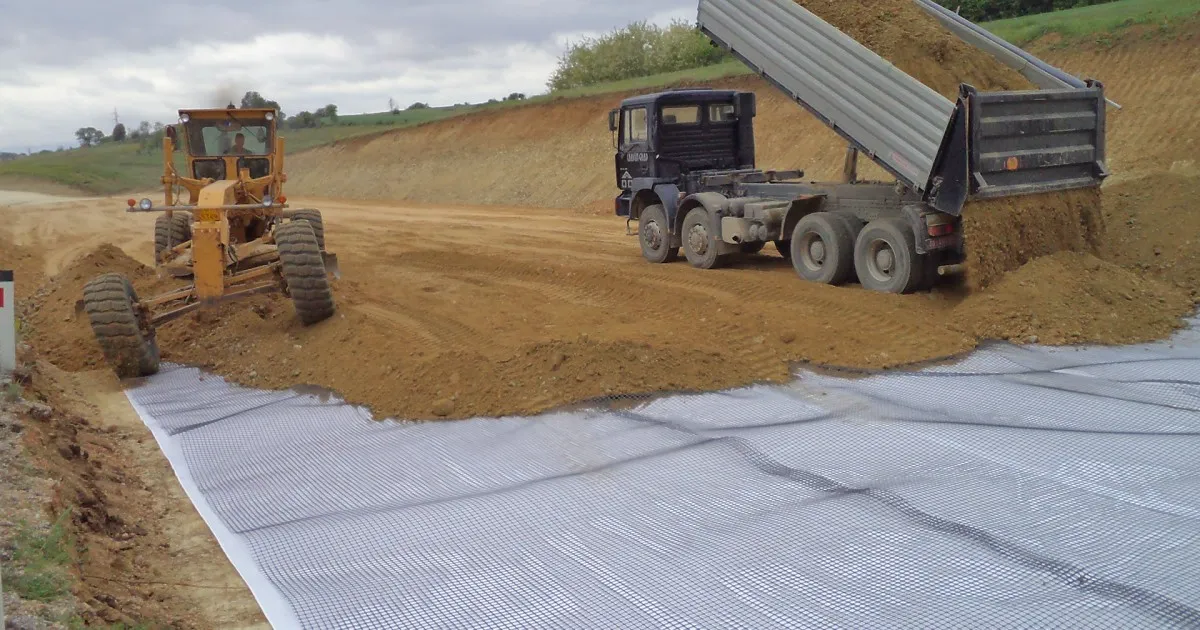

What Is the Difference Between Geotextile and Geocomposite?
- Geotextiles: Single-layer fabrics made from woven or non-woven polymers.
- Woven geotextiles: High strength for soil stabilization.
- Non-woven geotextiles: Allow better water permeability for filtration and drainage.
- Primary Functions: Separation, filtration, drainage, and reinforcement.
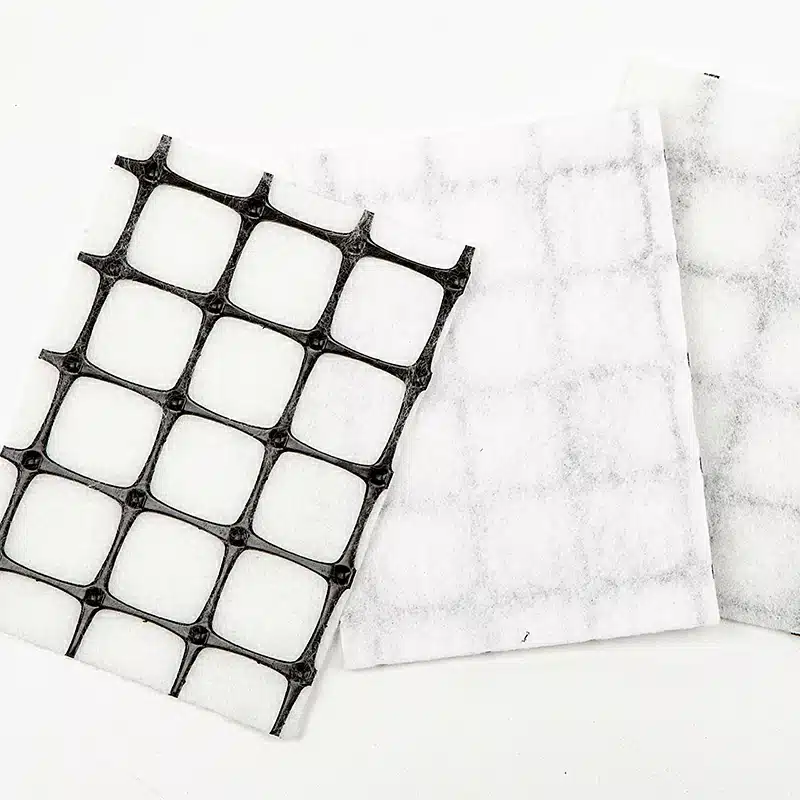
- Geocomposites: Multi-layered products combining two or more geosynthetics (e.g., geotextile + geonet, geomembrane + geogrid).
- Functions: Perform multiple roles simultaneously, such as drainage + filtration or reinforcement + containment.
- Advantages: Enhanced performance compared to single-layer geotextiles; multi-functional solutions for complex engineering projects.
Geotextiles are single-function fabrics, while geocomposites are engineered multi-layer materials offering integrated, multi-functional solutions.
What are geocomposites used for?
- Drainage:Geocomposites are commonly used to improve water flow and drainage in projects such as landfills, roadways, and retaining walls. For example, geocomposite drainage systems combine a drainage core with a geotextile fabric to filter sediments while allowing water to pass efficiently.
- Reinforcement:Geocomposites enhance the stability of soil, asphalt, and structural layers by providing additional mechanical support. By combining reinforcing elements like geogrids with geotextiles, they help distribute loads more evenly and improve long-term performance.
- Separation:In road and pavement construction, geocomposites are used to separate different material layers, such as aggregates and subgrade soils, preventing intermixing and maintaining structural integrity over time.
- Containment : In environmental protection applications, geocomposites that combine geomembranes with geotextiles are used for containment systems, such as landfill liners, to prevent the leakage of hazardous liquids and gases.
- Erosion Control : In coastal protection and slope stabilization projects, geocomposites help control erosion by reinforcing and stabilizing soil surfaces while still allowing vegetation growth and controlled water flow.
Geocomposites offer the key advantage of integrating multiple functions—such as filtration, drainage, reinforcement, and containment—into a single, efficient engineering solution.
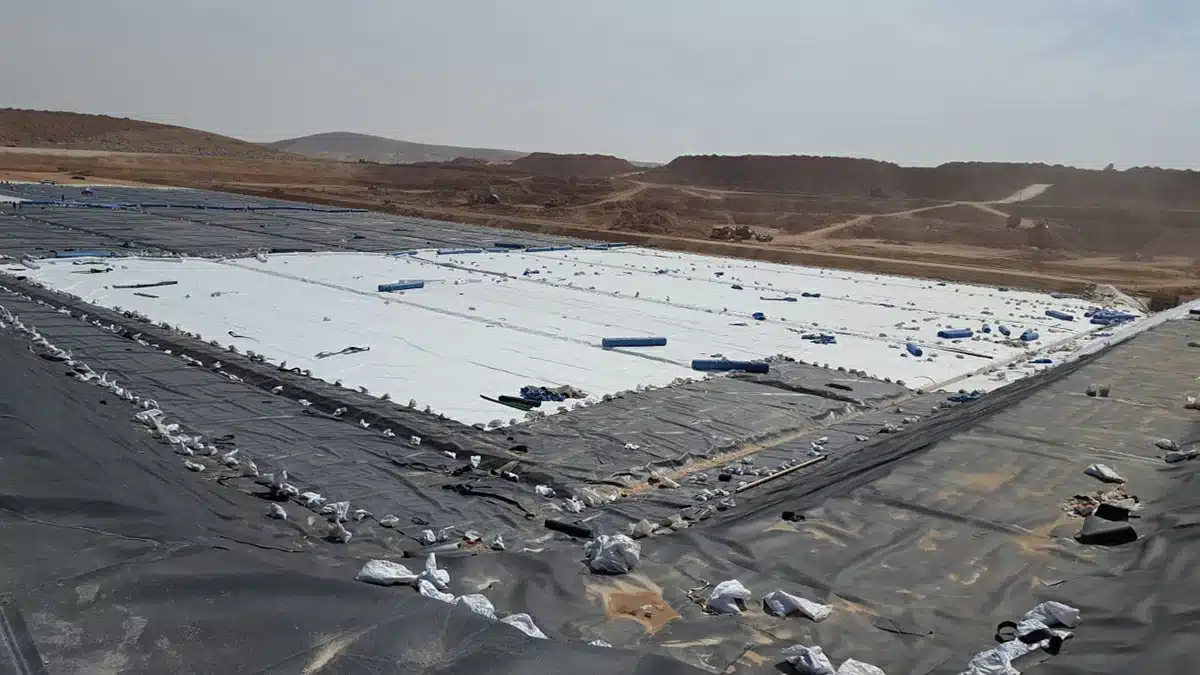

What are the different types of geocomposites?
Geocomposites are engineered materials that combine two or more geosynthetic products, typically geotextiles, geomembranes, or geogrids, to provide enhanced performance for specific applications. Here are the common types of geocomposites:
- Geocomposite Drainage Systems (Geocomposite Drains): These combine a geotextile (typically a nonwoven fabric) with a drainage core, such as a perforated pipe or a geonet. They are primarily used for water drainage and help prevent soil erosion, commonly in landfills, road construction, and retaining wall applications.
- Geocomposite Clay Liners (GCLs): These are typically made of a layer of sodium bentonite clay sandwiched between geotextiles or geomembranes. They are used as liners for landfills, ponds, or other containment systems, offering impermeability to liquids.
- Geogrid-Geotextile Geocomposites: A geogrid (a reinforcing grid) combined with a geotextile fabric provides both strength and filtration. These geocomposites are used for soil reinforcement, slope stabilization, and in pavements or embankments.
- Geotextile-Geomembrane Geocomposites: These combine a geomembrane (usually a plastic layer) with a geotextile fabric to provide both impermeability and filtration. They are commonly used in applications like landfill liners, pond liners, or other containment systems.
- Geocomposite Filters: These geocomposites combine a geotextile with a drainage or filtration material to allow the free flow of water while preventing soil migration. They are used in construction projects like road drainage or in the protection of pipelines.
- Geosynthetic Reinforced Soil (GRS) Geocomposites: These typically combine geotextiles or geogrids with soil to form a composite material that reinforces soil structure, often used for slope stability or retaining walls.
Each type of geocomposite is designed to address specific engineering needs, such as drainage, filtration, reinforcement, or containment, making them vital for a wide range of civil engineering and environmental applications.
Why use Geofabric?
Geofabric, often referring to geotextiles, is widely used because of its durability, multifunctionality, and environmental benefits. Here are the main reasons for its use:
- Erosion Control: Geofabric helps protect soil from water and wind erosion, particularly in embankments and coastal areas.
- Drainage Solutions: It allows water to pass while filtering out sediments, making it crucial for subsurface drainage systems.
- Soil Stabilization: Geofabric improves load-bearing capacity by separating and reinforcing different soil layers in construction projects.
- Cost and Environmental Benefits: According to Allied Market Research (2023), geotextiles reduce maintenance costs by up to 25% in road construction and contribute to sustainable practices by preventing soil loss.
Geofabric is essential in civil engineering, agriculture, and landscaping projects, as it combines strength, longevity, and eco-friendliness.
Understanding geocomposite prices involves more than just looking at numbers; it requires an appreciation of the material’s composition, types, applications, and benefits over similar products like geotextiles. Geocomposites offer a multifunctional solution that can be tailored to meet the specific needs of a wide range of engineering projects. Their cost is reflective of their versatility, advanced functionality, and the value they bring to construction and environmental applications. As the industry continues to evolve, the role of geocomposites and their cost-benefit analysis will undoubtedly remain a topic of interest for professionals seeking innovative and efficient solutions.

Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















