+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
In the world of geosynthetics, multi-axial geogrid stands out for its innovative design and enhanced performance. This material is widely used in civil engineering projects, especially in soil reinforcement and erosion control. Its unique structure allows it to offer superior strength and stability in various applications, making it a vital component of modern infrastructure. In this article, we’ll explore key aspects of multi-axial geogrid and its impact on geotechnical engineering.
What is a Multi-Axial Geogrid?
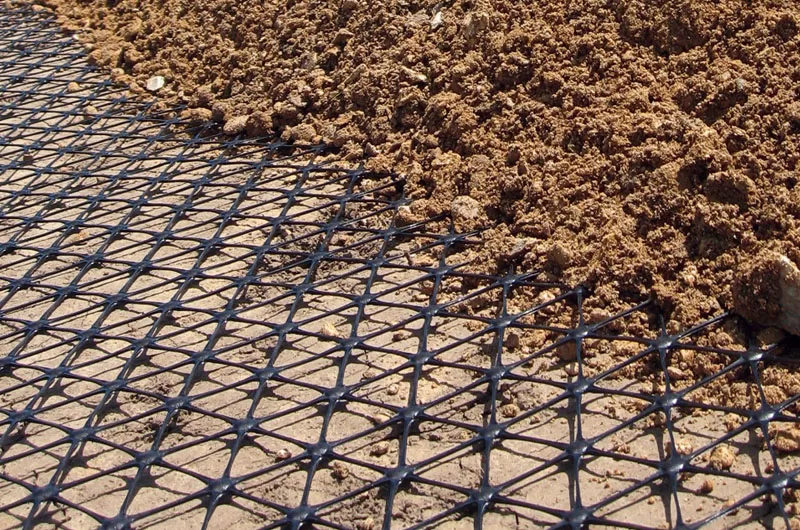

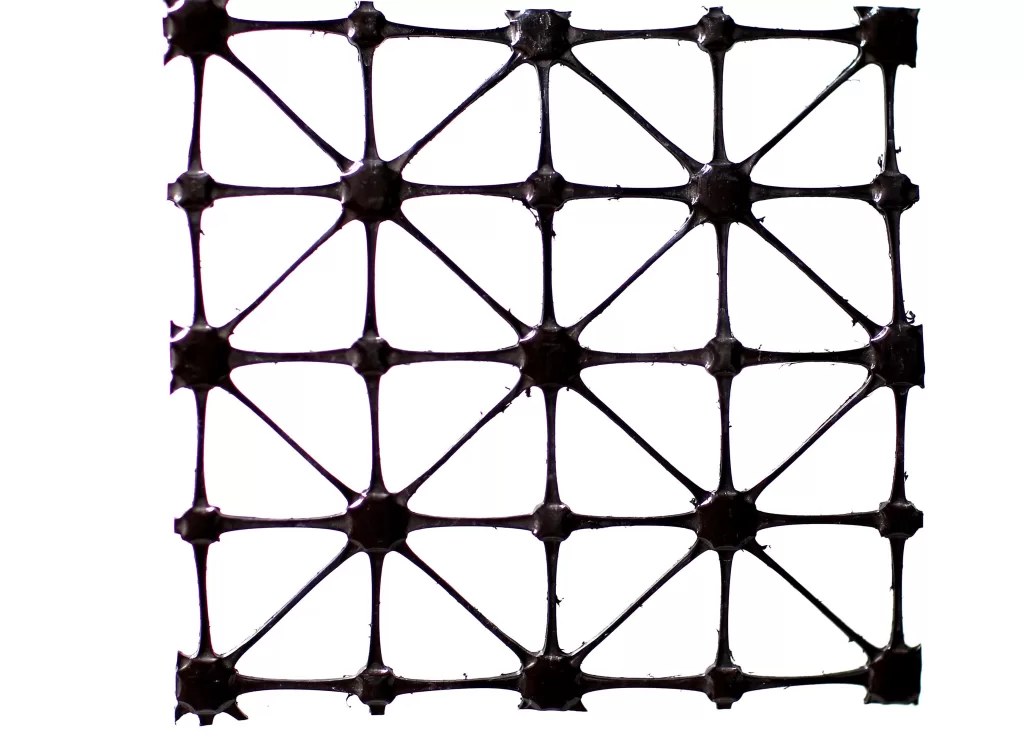
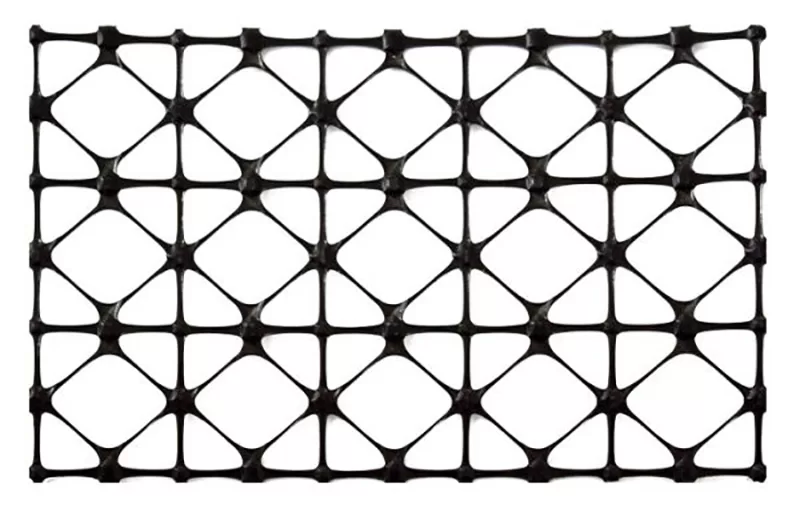
A multi-axial geogrid is a type of geosynthetic material designed to reinforce soils in multiple directions. Unlike traditional geogrids that are oriented in a single direction, multi-axial geogrids feature a network of intersecting ribs, providing strength both horizontally and vertically. This multi-directional reinforcement enhances load distribution, soil stability, and resistance to deformation under heavy loads. Multi-axial geogrids are commonly used in applications such as soil reinforcement, retaining walls, base course stabilization, and foundation support.
How Does Multi-Axial Geogrid Benefit Infrastructure Projects?
The primary benefit of using a multi-axial geogrid in infrastructure projects is its ability to improve the stability and performance of soil structures. This is achieved by creating a reinforcing effect that helps distribute loads more evenly, reducing settlement and preventing soil movement. In road construction, for example, the inclusion of a multi-axial geogrid enhances the strength of the subgrade, allowing roads to withstand more weight without cracking or shifting. This ultimately leads to longer-lasting, more durable infrastructure.
What Are the Key Applications of Multi-Axial Geogrid?
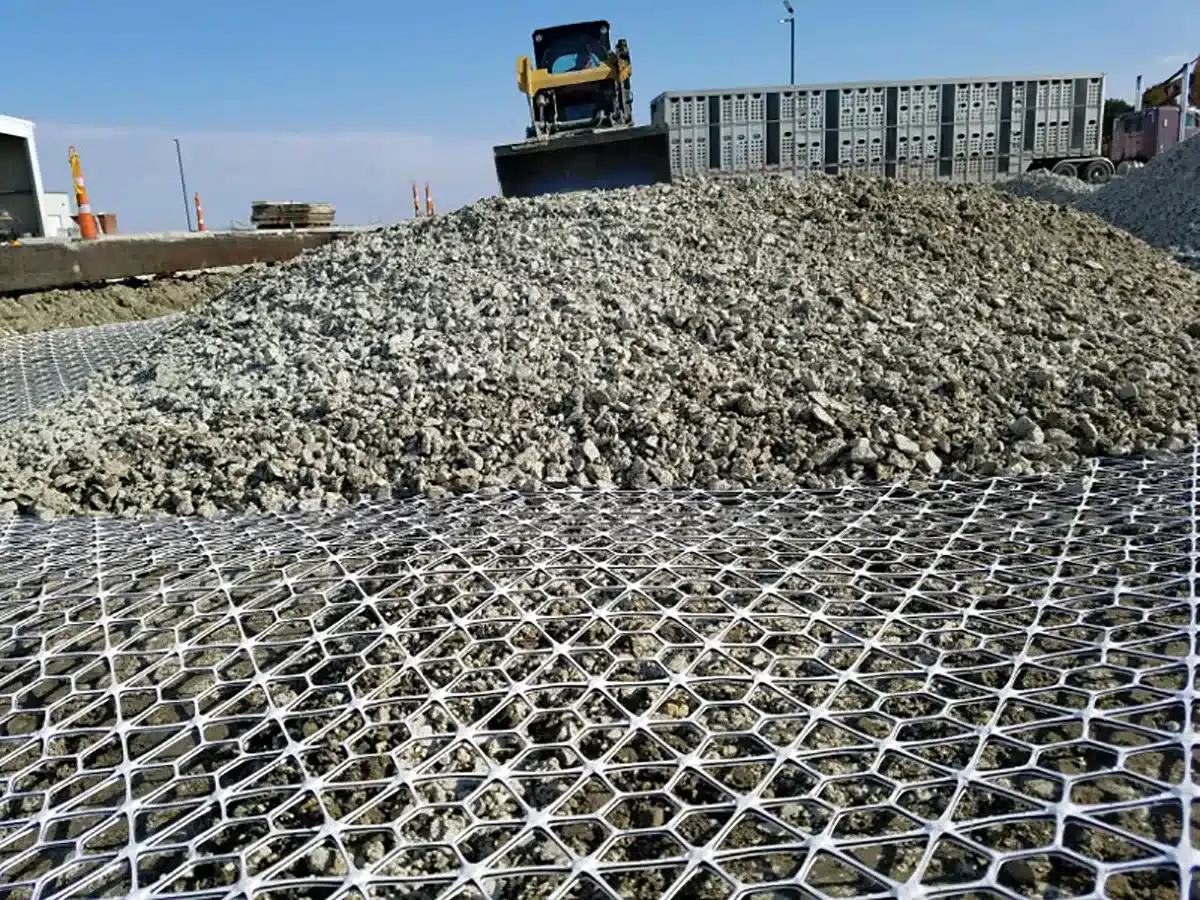

Multi-axial geogrids have a wide range of applications in the geotechnical and construction industries. Some of the most common uses include:
- Retaining walls: Multi-axial geogrids help stabilize the soil behind retaining walls, preventing the wall from shifting or collapsing under pressure.
- Roads and pavements: These geogrids are often used to reinforce base courses in roads, helping to extend the lifespan of paved surfaces.
- Slope stabilization: In areas prone to landslides or erosion, multi-axial geogrids provide additional support to prevent soil movement and erosion.
- Foundation reinforcement: By distributing the weight of structures more evenly, multi-axial geogrids can be used to reinforce foundation systems in weak or loose soils.
How Do Multi-Axial Geogrids Compare to Other Geosynthetics?
When compared to other types of geosynthetics, multi-axial geogrids offer superior load-bearing capacity and multi-directional reinforcement. Traditional geogrids, which are typically oriented in a single direction, can provide excellent tensile strength, but they may not offer the same level of stability in all directions. In contrast, multi-axial geogrids
’
multi-directional orientation ensures that they perform well even in challenging environments, where soil conditions are less predictable. Additionally, their ability to enhance the strength of the surrounding soil makes them ideal for use in applications requiring long-term performance.
In summary, multi-axial geogrids are indispensable in the world of geosynthetics for their ability to provide multidirectional reinforcement and improved soil stability. From enhancing the performance of retaining walls to reinforcing pavements and foundations, their versatile applications make them a key component in many engineering projects. Understanding their benefits can help engineers select the right materials to ensure the longevity and durability of infrastructure.

Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















