+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
Geocomposites are versatile materials used in various engineering and construction applications. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or new to the field, understanding geocomposites is essential for successful projects.
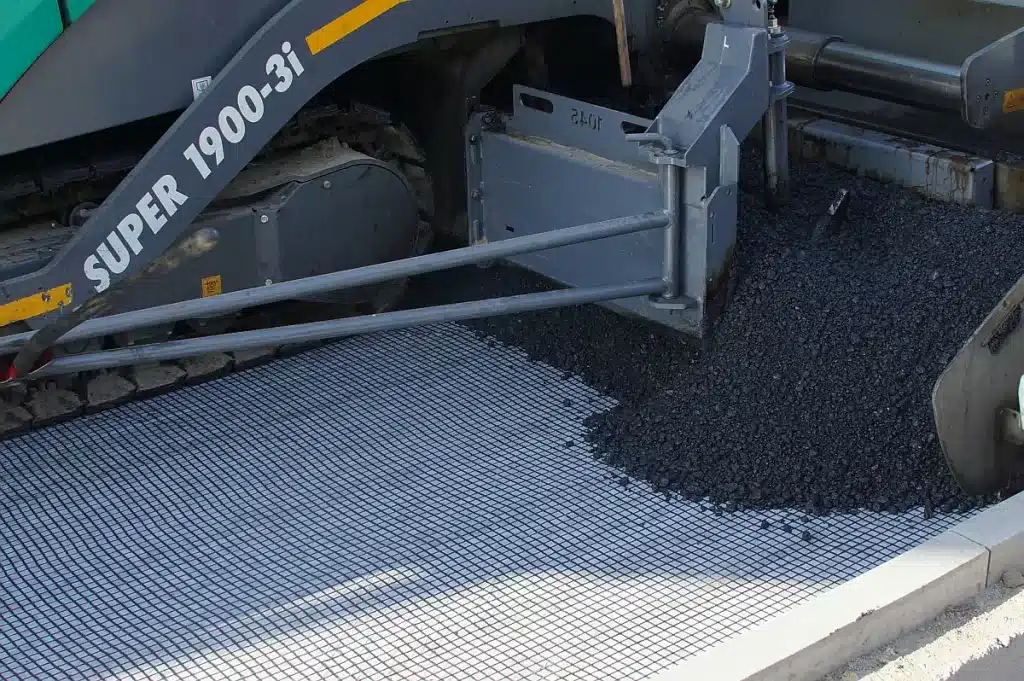

What is the Purpose of Geocomposites?
Purpose of Geocomposites in Engineering and Construction
- Drainage: Geocomposites are used to facilitate drainage in various construction projects. They help in removing excess water from soil or other construction materials, preventing waterlogging and enhancing stability.
- Filtration: Geocomposites serve as filters that allow water to pass through while retaining soil particles. This function is crucial in preventing soil erosion and maintaining the integrity of the construction site.
- Separation: In construction, geocomposites are employed to separate different layers of materials. For example, they can prevent the mixing of subgrade and sub-base materials in road construction, ensuring structural stability.
- Reinforcement: Geocomposites provide reinforcement to soil and other construction materials. They improve the load-bearing capacity and reduce the deformation of structures, enhancing overall stability and durability.
- Protection: Geocomposites offer protection to underlying materials, such as waterproofing membranes or geomembranes. They prevent damage during construction and prolong the lifespan of these critical components.
- Gas Venting: In landfill and waste management applications, geocomposites are used for gas venting. They help in safely venting gases like methane, preventing the buildup of hazardous gases, and ensuring environmental safety.
- Containment: Geocomposites are used in containment applications to control the movement of liquids or gases. They are commonly used in landfill liners and covers, as well as in mining and industrial waste containment systems.
What is Geocomposite Material?
Definition:
Geocomposite materials are engineered products made from the combination of two or more different types of geosynthetics. These materials are designed to enhance the performance characteristics of geotechnical projects by providing improved mechanical and hydraulic properties.
Composition:
Geocomposites typically consist of:
- Geotextiles: Non-woven or woven fabrics used for filtration, separation, and reinforcement.
- Geogrids: Grid-like structures used to reinforce soils and other materials.
- Geonets: Net-like materials used primarily for drainage.
- Geomembranes: Impermeable membranes used for containment and barrier applications.
- Other Components: Additional elements like geosynthetic clay liners or drainage cores may be included.
Uses:
Geocomposites are used in a variety of civil engineering and construction applications such as:
- Drainage: Enhancing water flow and drainage in structures like retaining walls, embankments, and landfills.
- Filtration: Preventing soil erosion while allowing water to pass through.
- Reinforcement: Strengthening and stabilizing soil in roadways, embankments, and slopes.
- Containment: Providing barriers in environmental applications like landfill liners and caps.
Benefits:
- Enhanced Performance: Combining materials leads to superior properties compared to using single geosynthetics.
- Cost-Effective: Reduces material costs and installation time.
- Durability: Offers long-term stability and resistance to environmental factors.
- Versatility: Applicable to a wide range of geotechnical problems.
Examples/Applications:
- Road Construction: Geocomposites are used to improve the load-bearing capacity of roads and highways.
- Landfills: They are employed to manage leachate and gas in waste containment systems.
- Retaining Walls: Used to provide effective drainage and prevent water pressure buildup.
- Erosion Control: Deployed in coastal and riverbank protection projects to control soil erosion.
What is an example of a Geocomposite?
Geocomposites combine two or more distinct materials, each with a specific role. They often include:
- Geotextile: One typical geocomposite example is the geotextile-geomembrane composite in landfill liner systems. These systems prevent leachate (contaminated water) from landfills from seeping into the environment. Geotextile provides filtration and separation, while geomembrane ensures impermeability.
- Geocomposite Drainage Systems: Another example is geocomposite drainage systems. We’ll delve into these systems shortly. These combine geotextile-geonet, geotextile-geogrid, geonet-geomembrane, or a geosynthetic clay liner (GCL), all designed for efficient water management.
What is a Geocomposite Drainage?
Geocomposite drainage systems effectively manage water in construction and civil engineering projects. They combine geotextile and drainage cores, like geonet or geospacer materials, for various functions:
- Water Collection and Conveyance: Geocomposite drainage systems efficiently collect and transport both liquids and gases away from the site, preventing soil saturation and erosion.
- Filtration: The geotextile layer acts as a filter, blocking fine particles and ensuring the core stays clear and functional.
- Protection: These systems safeguard underlying structures by preventing water damage and enhancing soil stability.
Geocomposites are versatile materials with various applications in construction and engineering. They serve purposes ranging from reinforcement to drainage and filtration. Understanding geocomposite materials and their uses is crucial for ensuring the success and longevity of construction projects. Whether you’re working on a road, landfill, or civil engineering project, geocomposites may play a vital role in its functionality and durability.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















