+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
Geogrid technology plays an essential role in improving soil stabilization and reinforcement across various construction and civil engineering projects. One of the most advanced forms of this technology is the *triaxial geogrid*, commonly known as *geogrid triax*. This innovative geosynthetic material offers superior structural integrity and durability, making it an excellent choice for roadways, embankments, and retaining wall projects. In this article, we will explore what a triaxial geogrid is, its purpose, the different types of geogrids, and how it compares to biaxial geogrids.
What is a triaxial geogrid?
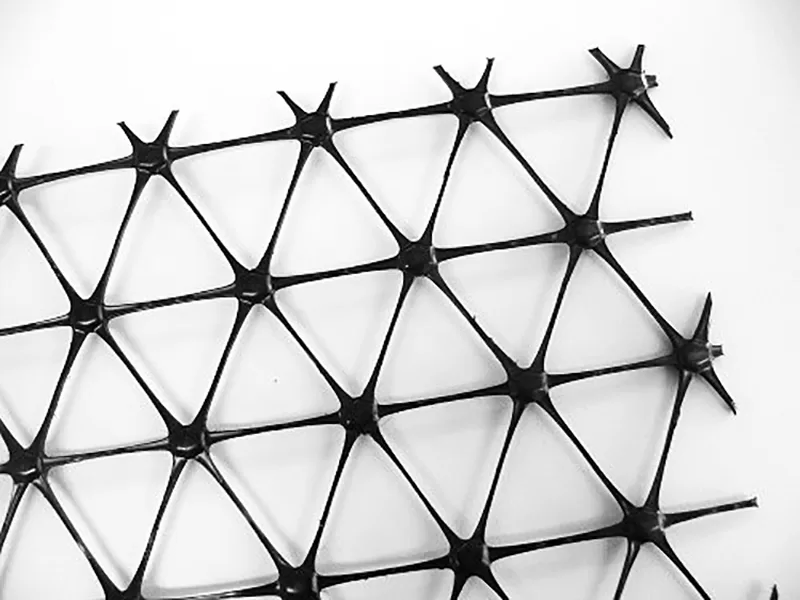
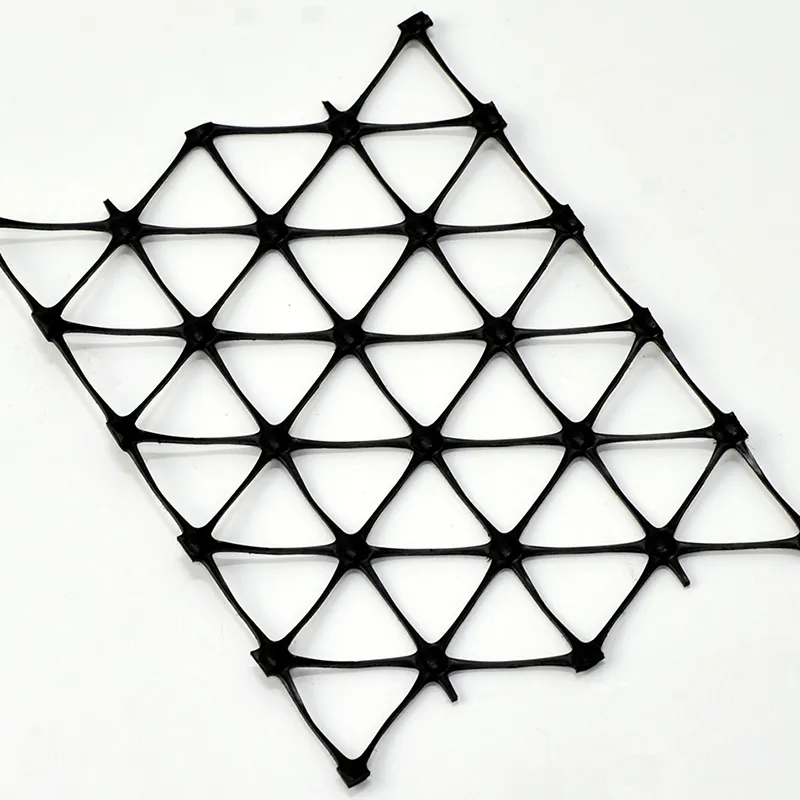
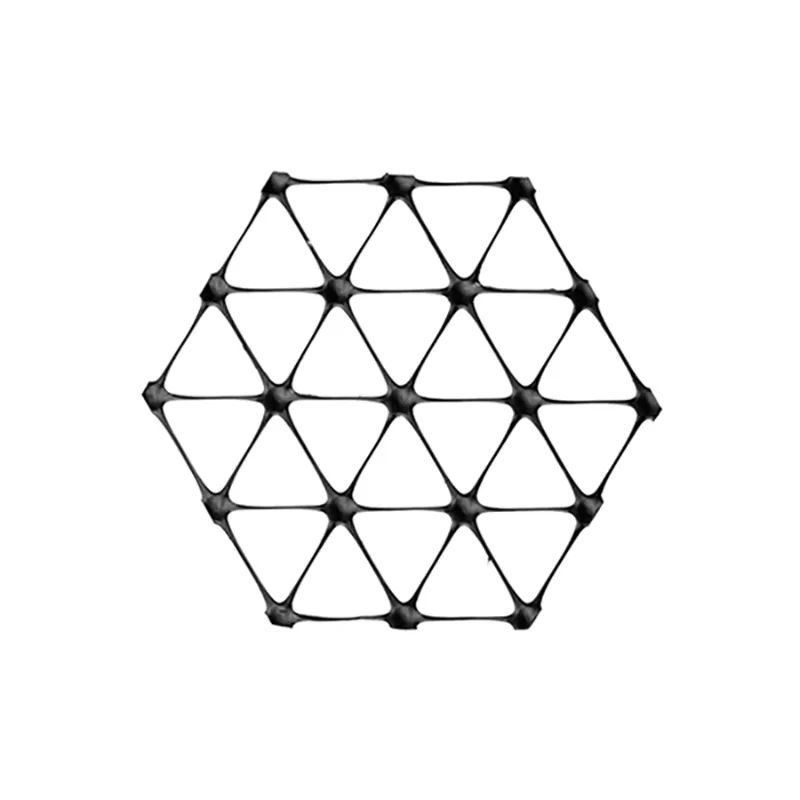
A triaxial geogrid, or triax geogrid, is a type of geosynthetic material designed with a triangular aperture structure, specifically engineered for the stabilisation of aggregates and soils. Unlike traditional biaxial geogrids that have square or rectangular patterns, the triaxial geogrid’s triangular shape distributes loads more effectively in all directions, providing greater stability and support. It is primarily used in soil reinforcement applications, where its multi-axial strength improves the overall performance of the foundation layers in construction projects.
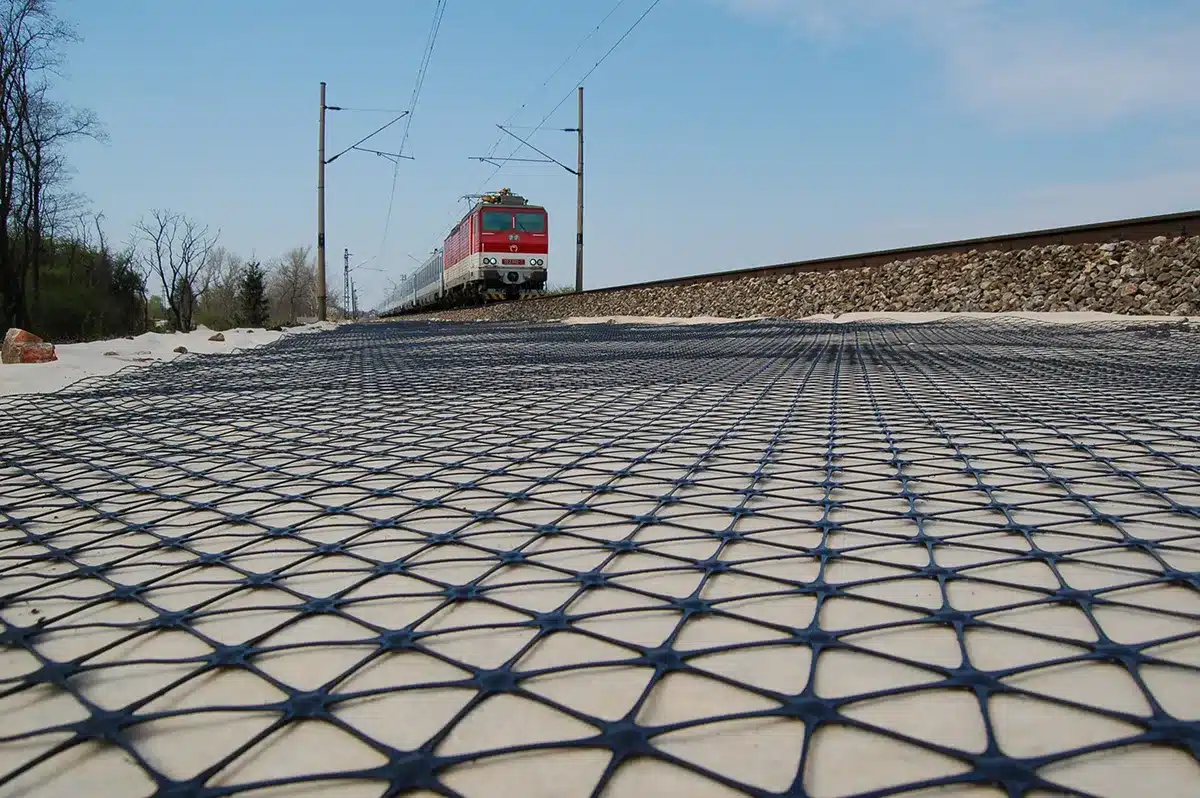

What is the purpose of a geogrid?
The primary purpose of a geogrid is to **reinforce soils and similar materials**, providing stability and strength. Geogrids help distribute applied loads over a larger area, which minimizes deformation and prevents soil movement, erosion, or sinking. In construction projects such as roads, embankments, and retaining walls, geogrids are used to strengthen the soil foundation, reduce the risk of structural failure, and extend the lifespan of the infrastructure. They are particularly effective in improving load-bearing capacity and reducing the thickness of aggregate layers.
What are the different types of geogrids?
There are three main types of geogrids, classified based on their structure and application: Uniaxial, Biaxial, Triaxial (Triax®), and Geogrid-Geotextile Composites.
- Uniaxial Geogrids: These are designed to resist tension in one direction (longitudinal), and are commonly used in retaining walls and embankment reinforcement where loads are applied in a single direction.
- Biaxial Geogrids: These geogrids are designed to resist tension in two directions (longitudinal and transverse). They are ideal for general soil reinforcement applications such as roadways, parking lots, and railways.
- Triaxial Geogrids (Triax®): The most advanced form, triaxial geogrids provide multi-directional support. Their triangular structure distributes loads evenly, making them highly effective in applications requiring superior stabilization and durability, such as roads and heavy-duty construction.
Additionally, Geogrid-Geotextile Composites combine the reinforcement capabilities of geogrids with the separation and filtration functions of geotextiles, offering enhanced performance in complex geotechnical projects.
What is the difference between a biaxial and triaxial geogrid?
The main difference between a biaxial and triaxial geogrid lies in their structure and load distribution capabilities. Biaxial geogrids have a square or rectangular aperture pattern, offering strength primarily in two directions—longitudinal and transverse. They are effective for projects that require support in two axes, such as simple soil stabilization.
On the other hand, triaxial geogrids feature triangular apertures and ribs with a higher aspect ratio, which distribute loads more uniformly across three axes. This results in enhanced stability and durability, making triax geogrids ideal for more complex and heavy-load applications like highways or areas with high traffic volumes.
Geogrid triaxial technology is an innovative solution in the realm of soil reinforcement, providing superior load distribution and durability compared to its uniaxial and biaxial counterparts. With its multi-directional support system, the triaxial geogrid excels in challenging construction projects where soil stabilization and long-lasting infrastructure are essential. Whether used in roadways, embankments, or retaining walls, this advanced material ensures optimal performance and sustainability for modern engineering demands.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















