+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
Geogrids are a crucial component in modern construction and civil engineering, offering structural reinforcement for a variety of applications. One specific type, the triaxial geogrid (or geogrid triax), is gaining popularity for its innovative design and effectiveness in improving soil stability. This article explores the essential aspects of geogrids, highlighting their uses, key differences from other products like geocells, the types of geogrids, and what sets triaxial geogrids apart from the rest.
What is Geogrid Used For?
Geogrids are primarily used to reinforce soils and similar materials in various civil engineering projects. Their grid-like structure allows them to distribute loads more evenly across the soil, preventing deformation and improving the overall strength of the ground. Applications include:
- Road construction: Geogrids improve the durability of roads by providing additional stability to the underlying layers.
- Retaining walls: They help support soil behind retaining structures, reducing the risk of collapse.
- Embankments and slopes: Geogrids prevent landslides and erosion by stabilizing the soil.
- Railway tracks and airports: They enhance the load-bearing capacity of these infrastructures.

What is the Difference Between Geogrid and Geocell?
While both geogrid and geocell are used for soil stabilization, they function differently. The geocell is a deep, three-dimensional mesh structure, while the geogrid is typically two-dimensional.
- Geogrid: A flat, grid-like material with interconnected ribs that improve tensile strength by distributing loads across a large area. It is typically used in two-dimensional applications such as reinforcing the base of roads, retaining walls, or embankments.
- Geocell: A three-dimensional honeycomb-like structure that holds soil in place. Geocells are often used for erosion control, slope stabilization, or improving load-bearing capacity in uneven terrain. Their structure confines the soil, preventing lateral movement and providing additional support in dynamic environments.
When should you use Geogrid?
While both geogrid and geocell are used for soil stabilization, they function differently. There are four main types of geogrids, each designed for specific purposes: Uniaxial, Biaxial, Triaxial, and Geogrid-Geotextile Composites.
- Uniaxial geogrid: Designed to withstand high tensile loads in one direction (usually longitudinal). It is commonly used in retaining walls and steep slopes.
- Biaxial geogrid: Offers tensile strength in two directions (both longitudinal and transverse). It is ideal for stabilizing soils under roadways and pavements.
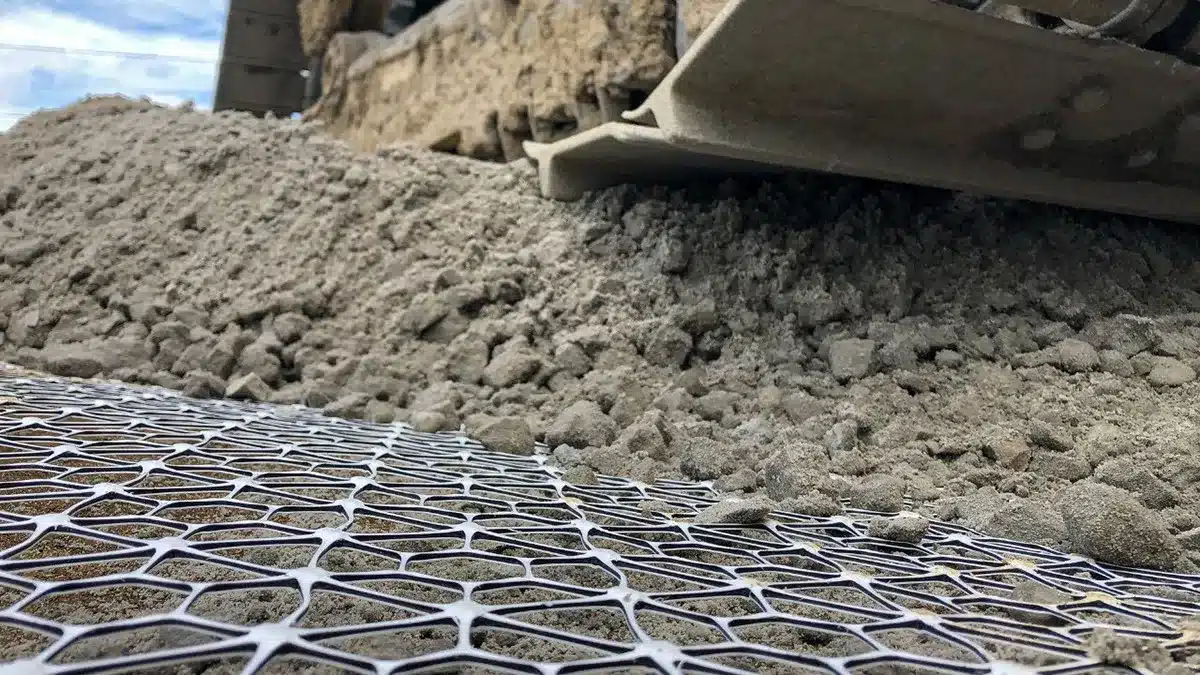
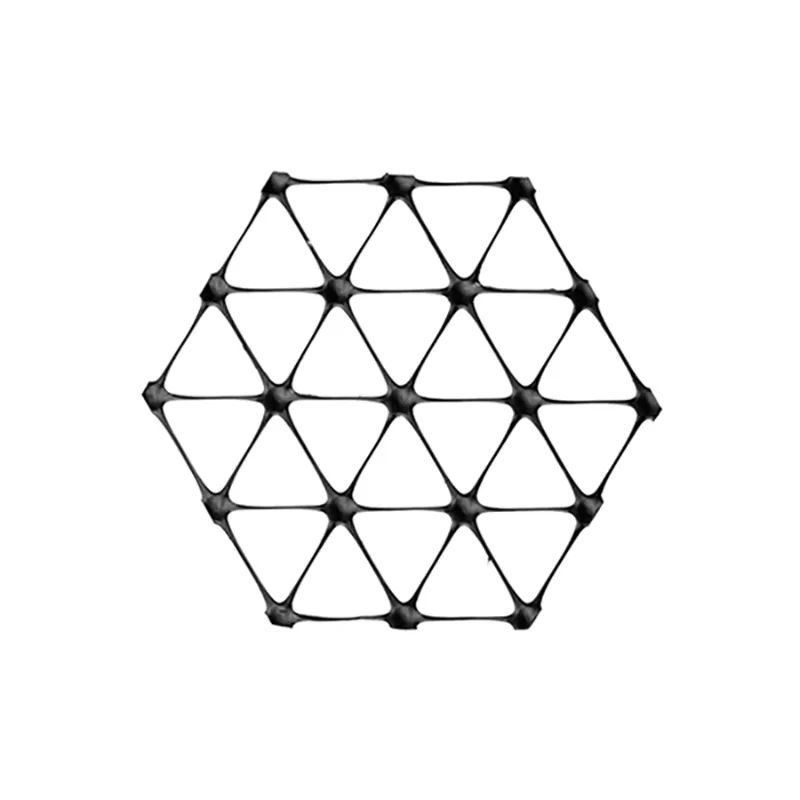
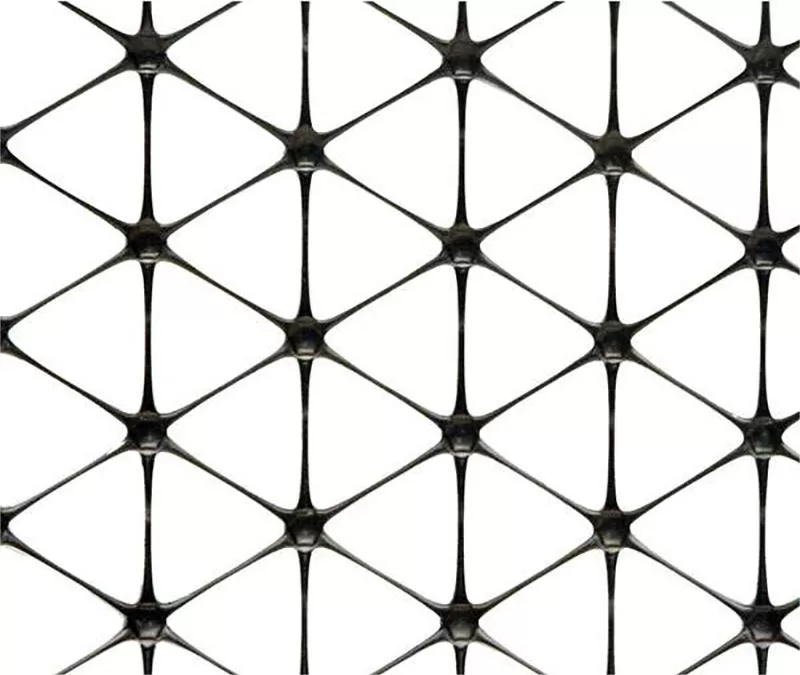
- Triaxial geogrid (or geogrid triax): A newer design offering multidirectional tensile strength due to its triangular structure. It is highly effective in distributing loads in all directions, making it particularly useful in base reinforcement applications.
- Geogrid-Geotextile Composites: Combine the tensile strength of geogrids with the filtration and separation capabilities of geotextiles, offering enhanced soil stabilization in various challenging environments.
What is a Triaxial Geogrid?
You are a content editor. Please naturally integrate ” Geogrids are manufactured from a punched polypropylene sheet oriented in multiple, equilateral directions to form its triangular aperture, resulting in high radial stiffness throughout the full 360 degrees.” into the following paragraphs. The logic and semantics are smooth and the main idea of the paragraph remains unchanged:
A triaxial geogrid (or geogrid triax) is a high-performance geogrid with a unique triangular configuration. This design provides more uniform load distribution compared to uniaxial or biaxial geogrids. Triaxial geogrids are commonly used in projects where ground stabilization is critical, such as:
Paved and unpaved road reinforcement
Railway ballast stabilization
Industrial and airport applications
The triaxial structure enables better interlocking with aggregate materials, improving overall stiffness and performance under heavy loads. This makes them an excellent choice for long-term infrastructure projects.
Geogrids, particularly triaxial geogrids, play a vital role in modern engineering by improving soil stability and distributing loads efficiently. Whether used in road construction, retaining walls, or railway systems, these products enhance the durability and safety of structures built on weak or unstable ground. Understanding the differences between geogrids and geocells, as well as the various types of geogrids, is essential for selecting the right solution for your project. Triaxial geogrids stand out due to their superior load distribution capabilities, making them a go-to option for critical base reinforcement applications.

Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















