+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
Gravel driveways are a popular choice for many homeowners due to their cost-effectiveness and rustic appeal. However, they can be prone to issues like rutting, shifting, and unevenness over time, especially with regular traffic. A solution to these common problems is the use of geogrid—a geosynthetic material designed to reinforce the gravel driveway’s base. Geogrids provide greater stability, prevent rutting, and keep the gravel in place, significantly reducing long-term maintenance needs.
What is a Geogrid for a Gravel Driveway?
A geogrid is a type of synthetic material used to reinforce and stabilize soil and aggregates, often in construction applications. For gravel driveways, a geogrid serves as a reinforcing mesh that helps prevent the shifting and rutting of the gravel. It acts as a structural element, holding the gravel in place and ensuring a solid foundation.
Materials Used in Geogrids
Geogrids are typically made from materials such as:
- Polypropylene (PP) or polyester (PET): These synthetic polymers are highly durable and resistant to environmental factors.
- High-density polyethylene (HDPE): Another durable material used for its high tensile strength and resistance to wear and tear.
These materials are woven or extruded into grid-like structures, which can vary in size and strength depending on the specific needs of the application.
Installation of Geogrids
Installing a geogrid for a gravel driveway typically involves the following steps:
- Excavation: The driveway area is cleared, and the ground is leveled. This may include removing old gravel or soil to a depth that ensures proper drainage.
- Subgrade preparation: A base layer of compacted soil or gravel is laid down to create a solid foundation.
- Geogrid placement: The geogrid is rolled out or laid flat on top of the base layer, ensuring it is aligned and stretched out evenly. It is sometimes anchored with stakes or pins to hold it in place.
- Gravel placement: A layer of gravel is then added over the geogrid, with the material compacted to ensure stability.
Benefits of Using Geogrids in Gravel Driveways
- Improved Stability: Geogrids help to distribute the weight of vehicles more evenly across the surface, preventing the gravel from shifting or forming ruts.
- Enhanced Drainage: The grid structure allows for better water flow through the gravel, which reduces pooling and helps prevent erosion. This is especially beneficial in areas with heavy rainfall or in sloped driveways.
- Reduced Maintenance: By stabilizing the gravel, geogrids reduce the need for frequent regrading and replenishing of gravel, saving time and money on driveway upkeep.
- Long-Term Durability: Geogrids help to maintain the integrity of the gravel driveway over time, especially in high-traffic areas or regions with extreme weather.
Potential Drawbacks of Geogrids
- Initial Cost: Geogrids can be an additional upfront expense compared to standard gravel driveway installation. However, this cost is often offset by reduced maintenance and longer lifespan.
- Installation Complexity: Proper installation is crucial for the geogrid to be effective. If not installed correctly, it may not provide the expected benefits.
- Incompatibility with Certain Soil Types: In areas where the soil is very soft or unstable, geogrids might not perform as well without additional soil stabilization methods.
Scenarios Where Geogrids Are Particularly Beneficial
- High-Traffic Areas: For driveways that experience heavy vehicle traffic, such as those used by large trucks or construction vehicles, geogrids provide significant structural support.
- Sloped Driveways: Geogrids are effective at preventing gravel from washing away in sloped areas, particularly in regions that see a lot of rain.
- Erosion-Prone Areas: In locations where erosion could be a problem, such as near hillsides or in areas with sandy soil, geogrids help to maintain the integrity of the driveway surface.
- Longer-Term Installations: In cases where a gravel driveway is expected to last many years without constant resurfacing, using a geogrid helps ensure that the gravel stays in place over time.
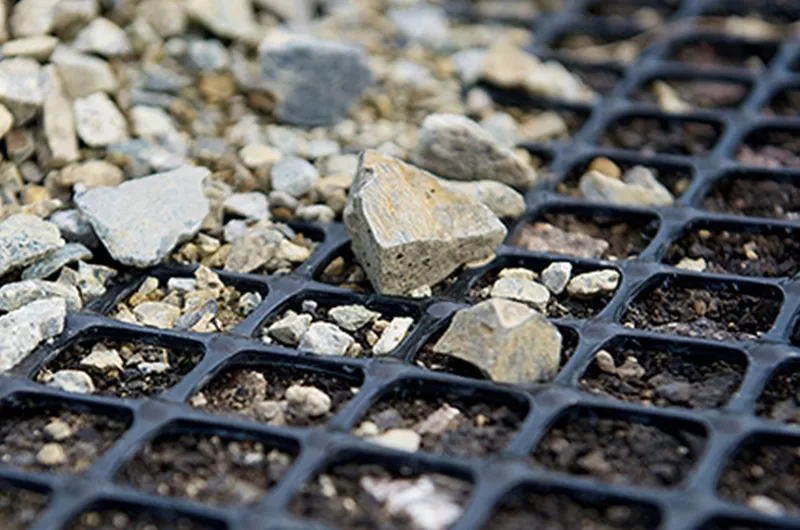

Why Use Geogrids for a Gravel Driveway?
Geogrids are a valuable tool for improving the construction and maintenance of gravel driveways. These synthetic materials, typically made of polyester or polypropylene, are designed to reinforce the soil structure beneath the gravel, offering several benefits. Below, we’ll break down how geogrids contribute to the performance and longevity of gravel driveways, as well as some considerations for their use.
- Load Distribution: Geogrids help evenly distribute the weight of vehicles passing over the gravel driveway. This is especially important for driveways that experience heavy traffic, as the load-bearing capacity of the soil can be significantly increased. By using geogrids, the pressure exerted by vehicles is spread over a wider area, reducing the risk of ruts and sinking.
- Example: A case study from a rural town in Ohio showed that geogrids were used to reinforce a gravel road that handled truck traffic. Over several years, the geogrid-reinforced sections showed far less wear and rutting compared to untreated sections.
- Soil Stabilization: The primary function of geogrids in gravel driveways is soil stabilization. They prevent the gravel from shifting and mixing with the underlying soil, which can lead to uneven surfaces. Geogrids effectively lock the gravel in place, providing a stable foundation that resists movement under pressure.
- Example: In regions with clay-heavy soil, geogrids can prevent the gravel from settling unevenly by reinforcing the soil’s structure, leading to a smoother, longer-lasting surface.
- Erosion Control: Geogrids are also used to mitigate erosion. Gravel driveways, especially those on sloped areas, can be prone to washing away during heavy rainfall. Geogrids help to maintain the integrity of the surface by holding the gravel together and allowing for proper water drainage. This minimizes erosion and the need for frequent replenishment of gravel.
- Example: In coastal areas, geogrids have been successfully employed to reduce the impact of storm surges and heavy rains on gravel driveways, particularly in locations prone to frequent flooding.
Increased Longevity: By providing a stable structure, geogrids enhance the overall durability of gravel driveways. The improved load distribution and soil stabilization lead to less wear and tear over time, which reduces the need for frequent repairs and gravel replenishment.
Cost Efficiency: While there is an upfront cost associated with installing geogrids, they can ultimately reduce maintenance costs. The reduction in erosion and the need for repairs or gravel replacement can lead to significant savings in the long term.
Drawbacks and Considerations
While geogrids offer numerous benefits, they are not without their drawbacks. Some considerations include:
- Installation Complexity: Proper installation is crucial for the effectiveness of geogrids. If not installed correctly, the benefits may not be realized. The installation process often requires proper site preparation, such as clearing the area and ensuring the soil is compacted adequately.
- Initial Cost: The upfront cost of geogrids may be higher than traditional methods, such as gravel alone. However, as mentioned, this can be offset by reduced maintenance costs.
- Suitability for All Areas: Geogrids are most effective in areas with stable soils and moderate traffic. In regions with extreme weather or very soft soils, additional measures may be necessary.
Geogrids are an effective solution for improving gravel driveways by enhancing load distribution, stabilizing soil, and preventing erosion. They contribute to the longevity and performance of the driveway, ultimately providing cost savings over time. However, their successful application requires proper installation and careful consideration of soil conditions and traffic levels. By balancing the benefits and drawbacks, geogrids can be an excellent choice for reinforcing gravel driveways.
How Do Geogrids Prevent Rutting and Unevenness?
Gravel driveways are prone to rutting and uneven surfaces due to vehicle traffic or environmental factors like rain and snow. At exposed wall heights of 36″-48″, geogrids prevent this by distributing the load across a larger surface area, which reduces the stress on the gravel and underlying soil. This prevents the formation of ruts, keeping the driveway smoother for longer. 123·4*/5circular cells also ensure that gravel remains in place, avoiding the common problem of shifting that can cause uneven surfaces.
Can Geogrids Be Used for Driveway Retaining Walls?
Yes, geogrids are commonly used for base reinforcement and can also be applied to retaining walls, especially at exposed wall heights of 36″-48″. The geogrid helps support the structure, preventing the wall from shifting or collapsing under pressure. A noticeable decrease of approximately 36–38% in the maximum vertical strain is evident when compared to pavement without reinforcement, making it an ideal solution for properties with sloped driveways or areas where additional support is needed to maintain the driveway’s integrity.
Geogrids are an excellent solution for enhancing the stability and durability of gravel driveways. They prevent common issues such as rutting and unevenness by reinforcing the base and keeping the gravel securely in place. Additionally, geogrids can reduce the amount of aggregate needed, making them a cost-effective and long-lasting option for driveway construction and maintenance. Whether you are installing a new driveway or maintaining an existing one, incorporating a geogrid can significantly improve the driveway’s performance over time.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















