+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
In civil and geotechnical engineering, understanding the differences between geogrid vs geotextile is crucial for selecting the right soil reinforcement solution. Both materials serve important purposes, but their performance, cost, and suitability vary depending on the project requirements. This article explores real-world cases to illustrate how geogrids and geotextiles are applied effectively in infrastructure projects.
Understanding Geogrid vs Geotextile
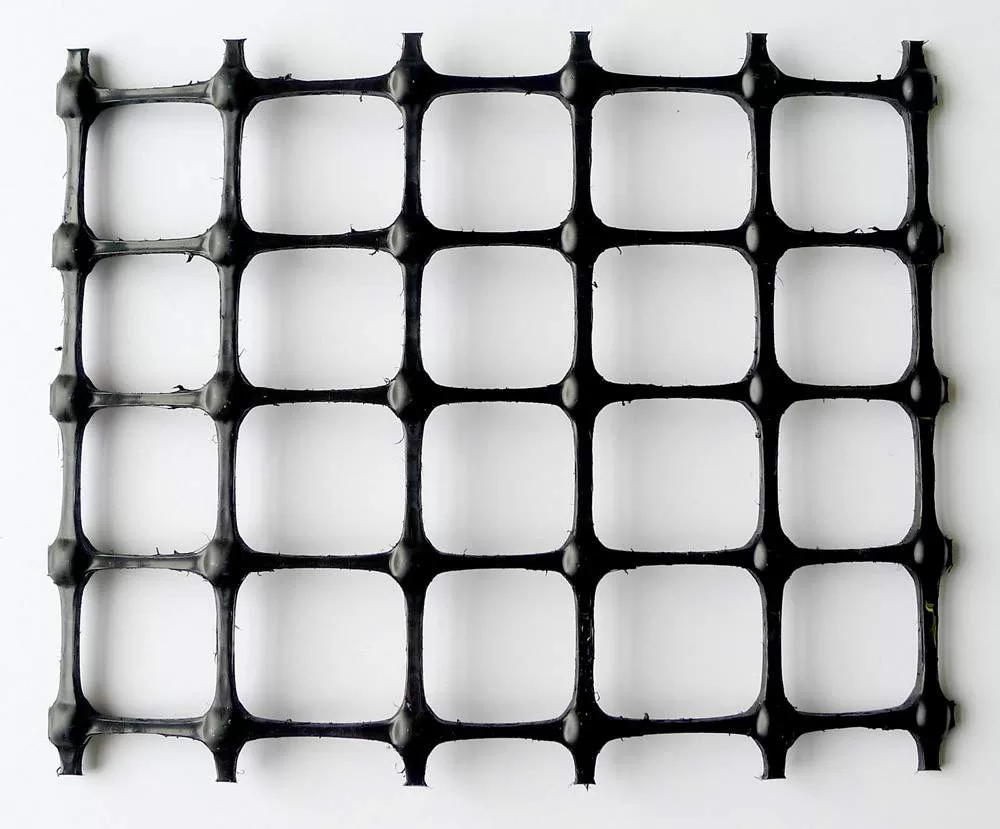
- Geogrid: A polymeric material with an open grid structure designed to interlock with soil or aggregate, providing tensile reinforcement and load distribution. Geogrids are widely used in road bases, embankments, retaining walls, and slope stabilization.
- Geotextile: A permeable fabric made from polypropylene or polyester fibers that primarily functions as separation, filtration, or drainage material. Geotextiles are often applied under pavements, drainage layers, and erosion control projects.
- Key difference: Geogrids are stronger in tension and primarily reinforce soil structure, while geotextiles focus on separation, filtration, and drainage, though some geotextiles also provide light reinforcement.
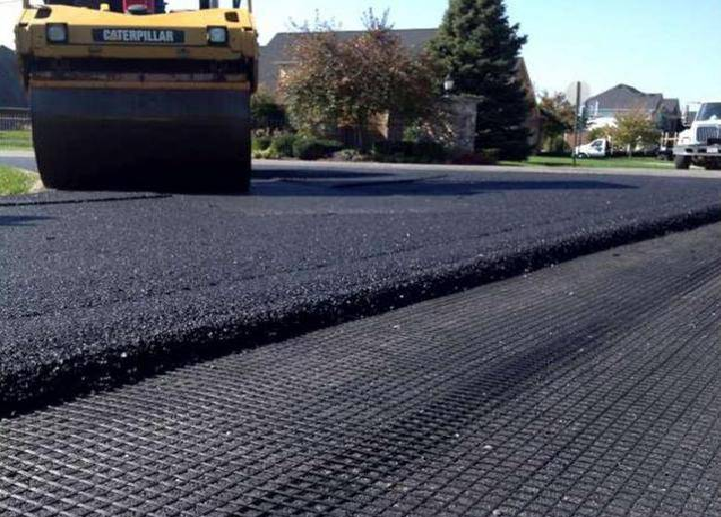

Real-World Case Examples
- Highway Base Stabilization, USA:In a Midwest highway project, engineers compared the performance of geogrids vs geotextiles over weak clay subgrades. Geogrids reduced the required aggregate thickness by 20% and significantly decreased rutting, while geotextiles improved drainage but offered minimal structural reinforcement.
- Railway Embankment Reinforcement, Europe:A soft clay embankment for a European railway line employed geogrids for lateral soil stabilization and load distribution. Geotextiles were installed in drainage layers to prevent fine soil migration into the ballast .
- Temporary Construction Roads, Wind Farm Projects:On peat and organic soils, temporary access roads utilized geogrids to provide reinforcement and load-bearing capacity. Geotextiles were installed underneath for separation and erosion prevention. Engineers found that combining both materials in their respective roles led to faster construction and reduced maintenance costs.
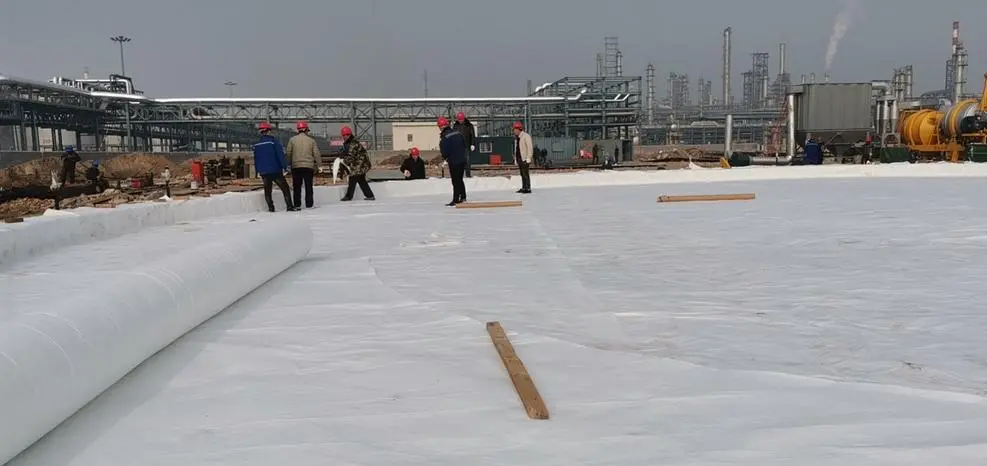

Key Takeaways
- Structural reinforcement: Geogrids excel in load-bearing applications, making them ideal for pavements, embankments, and slope stabilization.
- Separation and filtration: Geotextiles prevent soil contamination of aggregates, maintain drainage, and control erosion.
- Project optimization: Selecting between geogrid vs geotextile, or using them in combination, depends on project goals, soil conditions, and load requirements.
The comparison of geogrid vs geotextile highlights the importance of understanding material properties and project-specific needs. Real-world cases in highways, railways, and temporary construction roads show that engineers can optimize soil performance, reduce costs, and improve infrastructure longevity by choosing the appropriate geosynthetic solution.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















