+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
Retaining walls play a crucial role in civil engineering and landscaping, providing stability and preventing soil erosion in various scenarios. From enhancing the aesthetics of your garden to supporting massive highway structures, retaining walls come in different types, each tailored to specific needs.
Retaining walls are available in various types, shapes, and sizes, catering to diverse project requirements and site conditions. They range from simple gravity walls to bored pile walls for basements and reinforced soil walls utilizing geogrids.
The most common retaining walls include brick, concrete, stone, and wood. Some modern walls use a geosynthetic material called geogrids to stabilize and create reinforced soil.
Geogrid is used in almost every type of hardscape—from driveways to walkways to patios and everything in between. However, it is essential in retaining walls, particularly those above three or four feet. Geogrid should be implemented whenever you want your hardscape to last and stay structurally sound.
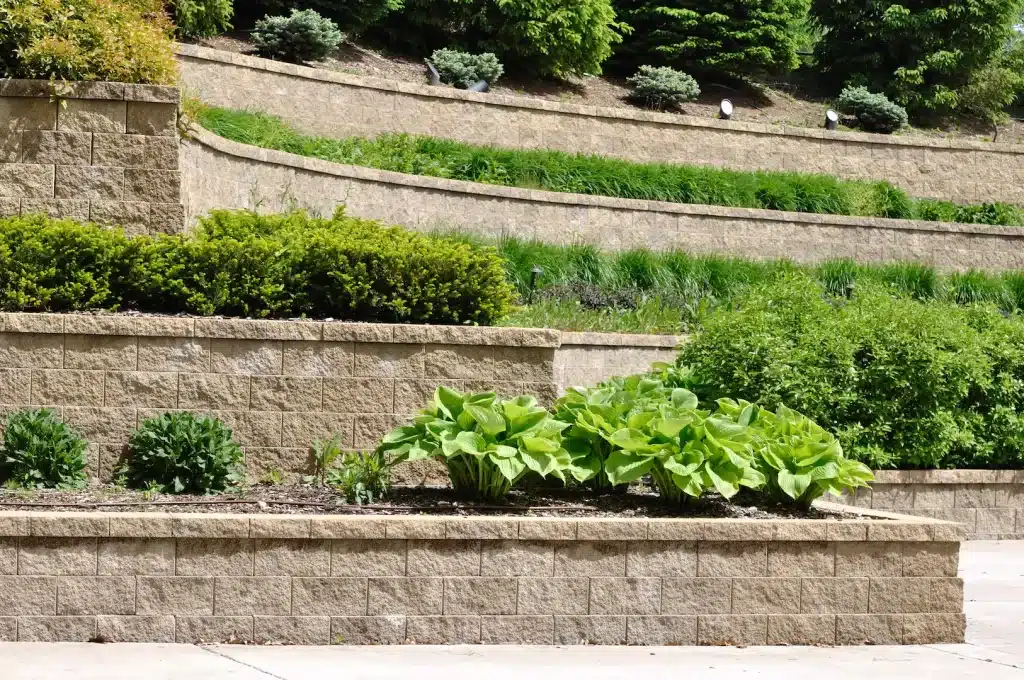

What are various types of retaining walls?
Types of retaining walls:
- Gravity Walls: These rely on their weight and mass to retain soil and are suitable for shorter structures.
- Cantilever Walls: Supported by a base slab, cantilever walls use leverage to counteract the pressure of the retained soil.
- Sheet Pile Walls: Composed of interlocking sheets, typically made of steel or vinyl, these are ideal for tight spaces.
- Anchored Walls: These walls use cables or rods anchored into the earth behind the wall to provide additional support.
- Reinforced Soil Walls: Also known as geogrid or mechanically stabilized earth walls, these utilize layers of soil reinforced with geosynthetic materials for added strength.
- Gabion Walls: Constructed by stacking wire mesh baskets filled with stones, gabion walls are both functional and aesthetically pleasing.
What is the most commonly used retaining wall?
The most commonly used type of retaining wall is the gravity wall. These walls rely on their sheer weight to resist the pressure of the soil behind them. They are simple to construct, cost-effective, and suitable for walls up to about 10 feet in height. Gravity walls often use materials like concrete blocks, stone, or even treated timber.
What is the cheapest style retaining wall?
The cheapest type of retaining wall is poured concrete. Prices start at $4.30 per square foot for poured concrete, $5.65 for interlocking concrete block, $6.15 for pressure-treated pine, and about $11 for stone. Installation or supplies, such as drainage stone or filter fabric, are not included.
What Is Geogrid And When To Use?
The choice of the best retaining wall depends on several factors, including the specific project requirements, site conditions, and budget. Here are some considerations:
- Height and Load: For taller walls or walls subjected to heavy loads, engineered options like cantilever or reinforced soil walls are often preferred.
- Space: In limited space scenarios, sheet pile walls or gabion walls might be the best fit.
- Aesthetics: If aesthetics are a significant concern, gabion walls or decorative concrete blocks can provide both functionality and visual appeal.
- Budget: Gravity walls are often the most economical choice for shorter walls. However, it’s essential to balance cost with the wall’s intended purpose and longevity.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















