+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
Geotextile form bags have become increasingly popular in civil engineering and construction due to their versatility and effectiveness. In this article, we will delve into the world of geotextile bags, understanding what they are, their applications, and their drawbacks. We will also explore the different types of geotextiles available.
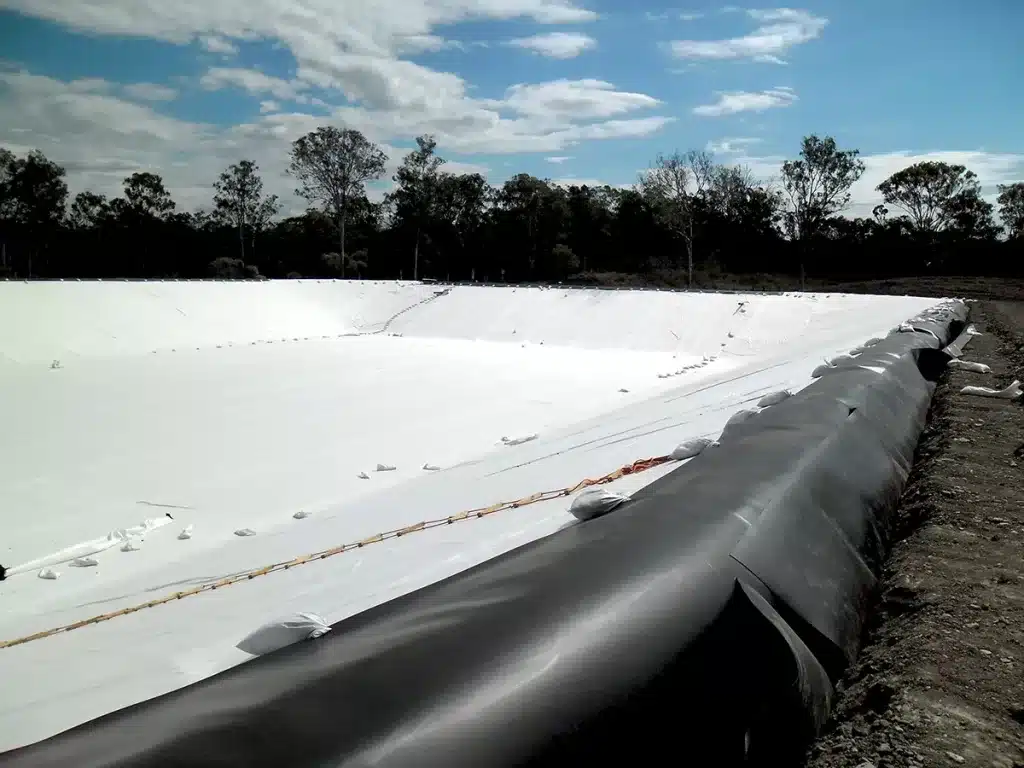

What Is a Geotextile Bag?
A geotextile bag is a container made from permeable geotextile fabric, designed to hold sand, soil, gravel, or sediment while allowing water to pass through. It is widely used in civil engineering and environmental projects for erosion control, filtration, and ground stabilization.
- Function: The permeable fabric retains solid materials while releasing water, helping control erosion and manage sediment.
- Typical applications: Geotextile bags are commonly used along riverbanks, shorelines, slopes, and construction sites for erosion protection, flood control, dewatering, and soil stabilization.
- Key advantages: They are flexible, easy to install, and adaptable to different site conditions, making them an effective solution for both temporary and long-term engineering works.
Where Should Geotextile Bags Be Used?
Geotextile bags are best used in applications that require controlled containment of soil or sediment while allowing water to drain freely. Their permeable structure and flexibility make them suitable for a wide range of temporary and permanent engineering works.
Common and effective use cases include:
- Erosion control: Geotextile bags are widely installed along riverbanks, coastlines, channels, and slopes to reduce erosion caused by flowing water, waves, or rainfall. They absorb hydraulic energy and help stabilize exposed soil surfaces.
- Dewatering and sediment containment: In construction, dredging, and environmental remediation projects, geotextile bags are used to dewater sludge, contaminated sediments, or slurry. Water drains through the fabric while solids are retained, simplifying handling and disposal.
- Flood protection and emergency works: Filled geotextile bags can be stacked to form temporary flood barriers, cofferdams, or diversion structures during storm events, high water levels, or emergency response situations.
- Slope and soil stabilization: On unstable slopes or embankments, geotextile bags provide additional weight and confinement, reducing soil movement and improving short-term stability during construction or remediation.
- Coastal and hydraulic applications: They are used in shoreline protection, breakwater cores, and scour prevention around hydraulic structures where flexible, permeable protection is required.
Overall, geotextile bags are most effective in projects involving erosion mitigation, water management, sediment control, and temporary structural support, particularly where adaptability and ease of installation are important.
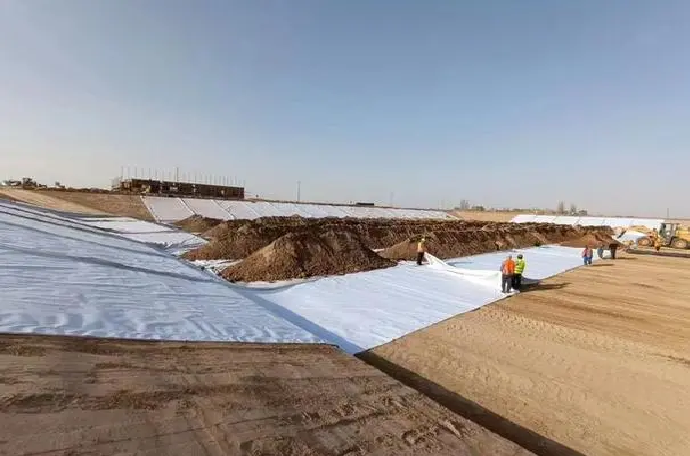

What Are the Limitations and Design Considerations of Geotextile Bags?
While geotextile bags provide flexible and efficient solutions for erosion control, dewatering, and soil stabilization, their performance is highly dependent on proper design, material selection, and installation. Key limitations and considerations include:
- UV exposure and weathering: When geotextile bags are left exposed, prolonged ultraviolet radiation can reduce fabric strength. For long-term applications, UV-resistant materials or protective cover layers are required.
- Mechanical damage risk: Geotextile bags may be punctured or torn by sharp rocks, debris, or improper handling during filling and placement, potentially compromising filtration and containment performance.
- Limited structural capacity: Unlike rigid structures, geotextile bags rely on mass and confinement rather than structural stiffness. They are not suitable for applications requiring high load-bearing or permanent structural support without supplemental systems.
- Clogging potential: Fine sediments, organic matter, or contaminated soils can clog the fabric pores over time, reducing permeability and drainage efficiency if filtration criteria are not properly designed.
- Installation sensitivity: Incorrect filling ratios, poor placement, or inadequate compaction can lead to deformation, displacement, or reduced effectiveness under hydraulic forces.
- Service life variability: Environmental conditions such as chemical exposure, biological activity, and hydraulic loading can significantly influence the long-term durability of geotextile bags.
Geotextile bags are highly effective when used within their design limits, but successful performance depends on correct fabric selection, proper installation practices, and realistic expectations regarding service life and structural function.
Where Should a Geotextile Bag Be Used?
Geotextile bags, made from permeable fabrics, are versatile engineering tools designed for projects requiring sediment retention, erosion control, and water filtration. They are most effective in applications where soil or slurry containment must occur simultaneously with controlled drainage. Typical scenarios include:
- Erosion Control: Geotextile bags are placed along riverbanks, beaches, canals, or deltas to dissipate hydraulic energy and stabilize exposed soils under wave, current, or rainfall action.
- Dewatering and Sediment Management: In dredging, environmental remediation, and construction, these bags are filled with sludge or contaminated sediment. Water drains through the fabric while solids remain inside, simplifying transport and disposal.
- Flood and Emergency Barriers: During storm events or high-water conditions, stacked geotextile bags form temporary cofferdams, diversion structures, or flood protection walls.
- Slope and Soil Stabilization: On embankments or unstable slopes, geotextile bags add mass, confinement, and reinforcement to reduce sliding or erosion.
- Coastal and Hydraulic Works: Used in breakwaters, scour protection, and shoreline reinforcement where flexible, permeable, and rapidly deployable structures are preferred.
In summary, geotextile bags are suitable for environmental, hydrological, and civil engineering projects where sediment control, structural confinement, and drainage performance are simultaneously required.
In conclusion, geotextile form bags offer a versatile and effective solution for various engineering and construction challenges. Their applications span from erosion control to dewatering, making them valuable tools in the field of civil engineering. However, it’s essential to understand their limitations and choose the appropriate type of geotextile for a given project to ensure optimal performance and longevity.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















