+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
HDPE geonets, made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE) polymers, stand as indispensable assets in modern geotechnical engineering. Engineered with precision, these geonets boast a remarkable combination of strength, flexibility, and durability. Their net-like configuration, woven or extruded with meticulous attention, showcases a grid-like pattern with specific apertures. This innovative design not only reinforces stability in various soil types but also enables efficient drainage and filtration, making HDPE geonets a cornerstone solution in erosion control, landfill systems, roadways, and diverse civil engineering applications. Discover the unparalleled adaptability and performance of HDPE geonets reshaping the landscape of geotechnical solutions worldwide.
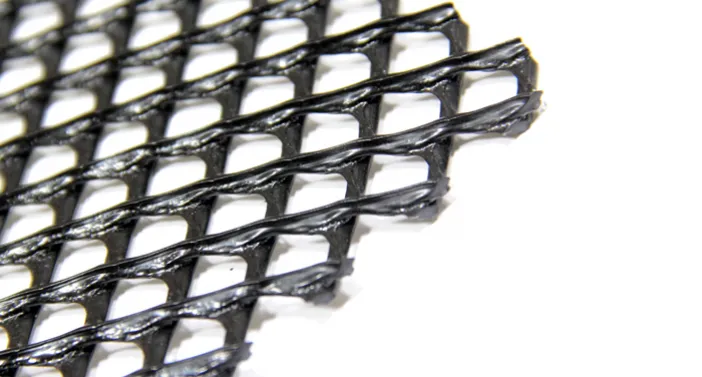
What is a geonet made of?
virgin high-density polyethylene (HDPE)
HDPE Geonets, a vital element in geotechnical engineering, are crafted from virgin high-density polyethylene (HDPE) polymers. These specialized polymers are intricately woven or extruded into a net-like structure, displaying a grid-like pattern with specific apertures. This distinctive design attributes strength, flexibility, and durability to the geonet, rendering it an optimal solution for a wide array of geotechnical applications.
What are the properties of geosynthetic materials?
The versatility of HDPE Geonets spans multiple domains, including road construction, road widening, asphalt work, building construction and foundations, retaining walls, dams, artificial ponds, water reservoirs, and many more, finding extensive applications in:
- Drainage Systems: Geonets facilitate effective subsurface drainage by allowing water to flow freely while preventing soil particles from clogging the system.
- Landfill Engineering: They serve as a barrier and drainage layer in landfill construction, enhancing stability and mitigating environmental risks by managing leachate and gas migration.
- Erosion Control: Geonets reinforce soil structures, preventing erosion and promoting vegetation growth in slopes and embankments.
- Road Construction: Their use in roadways assists in stabilizing soil, reducing lateral movement, and improving overall pavement performance.
- Environmental Protection: Geonets act as protective layers in reservoirs, retaining walls, and coastal structures, offering erosion control and structural support.
What is the difference between geogrids and geonets?
Geogrids and Geonets, despite serving similar functions in geotechnical applications, possess distinctive structural variances:
- Composition: Geogrids are typically made of polyester, polyethylene, or polypropylene, and and formed into grid-like configurations. Conversely, Geonets consist of HDPE polymers woven into a net-like structure.
- Functionality: Geogrids primarily provide tensile reinforcement and soil stabilization by interlocking with soil particles. Geonets focus on drainage, filtration, and soil confinement through their open mesh design.
- Application: Geogrids are more commonly used for soil reinforcement and load distribution in retaining walls, pavements, and embankments. Geonets excel in drainage and erosion control systems.
What is the difference between geotextile and Geonet?
Geotextiles and Geonets serve distinct yet complementary purposes in geotechnical projects:
- Structure: Geotextiles are woven or non-woven fabrics made from synthetic materials like polypropylene, polyester, or polyethylene. On the other hand, Geonet is a geosynthetic material with a grid-like structure made of HDPE, consisting of integrally connected parallel sets of ribs overlying similar sets at various angles.
- Function: Geotextiles primarily act as separators, filters, or protectors, preventing soil erosion, promoting drainage, and providing reinforcement. Geonets focus on drainage and filtration while also offering structural support and soil stabilization.
- Application: Geotextiles are commonly used in road construction, erosion control, and as cushioning or protection layers. Geonets are prevalent in drainage systems, landfill engineering, and erosion control structures.
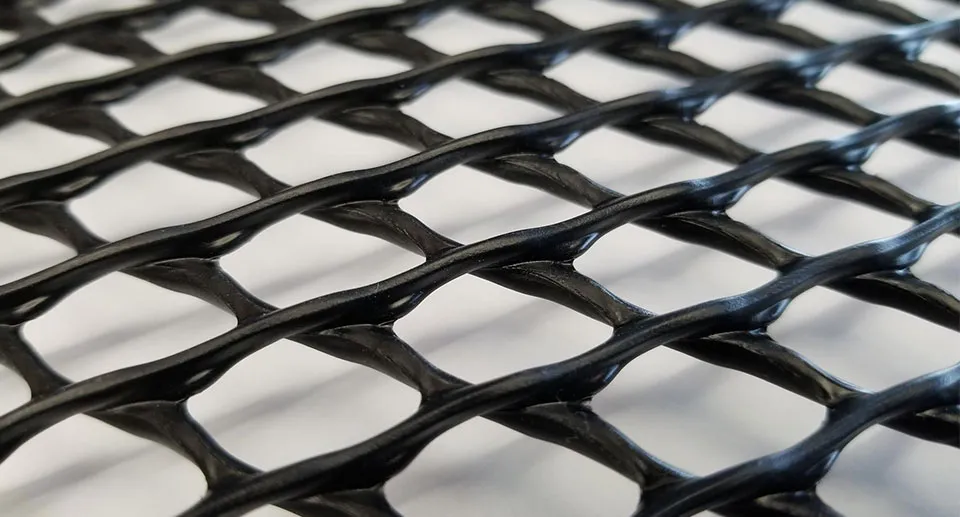
In conclusion, HDPE Geonets stand as a fundamental solution in geotechnical engineering, offering a blend of drainage efficiency, structural reinforcement, and environmental sustainability across diverse applications. Understanding their composition, applications, and distinctions from geogrids and geotextiles is pivotal for harnessing their full potential in construction and environmental projects.

Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















