+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
PVC geomembrane is a critical component in various construction and environmental projects, offering a robust solution for waterproofing and containment. This article provides an in-depth understanding of PVC geomembrane, its unique properties compared to other materials like HDPE, and other essential aspects to consider when choosing the right geomembrane for your project.
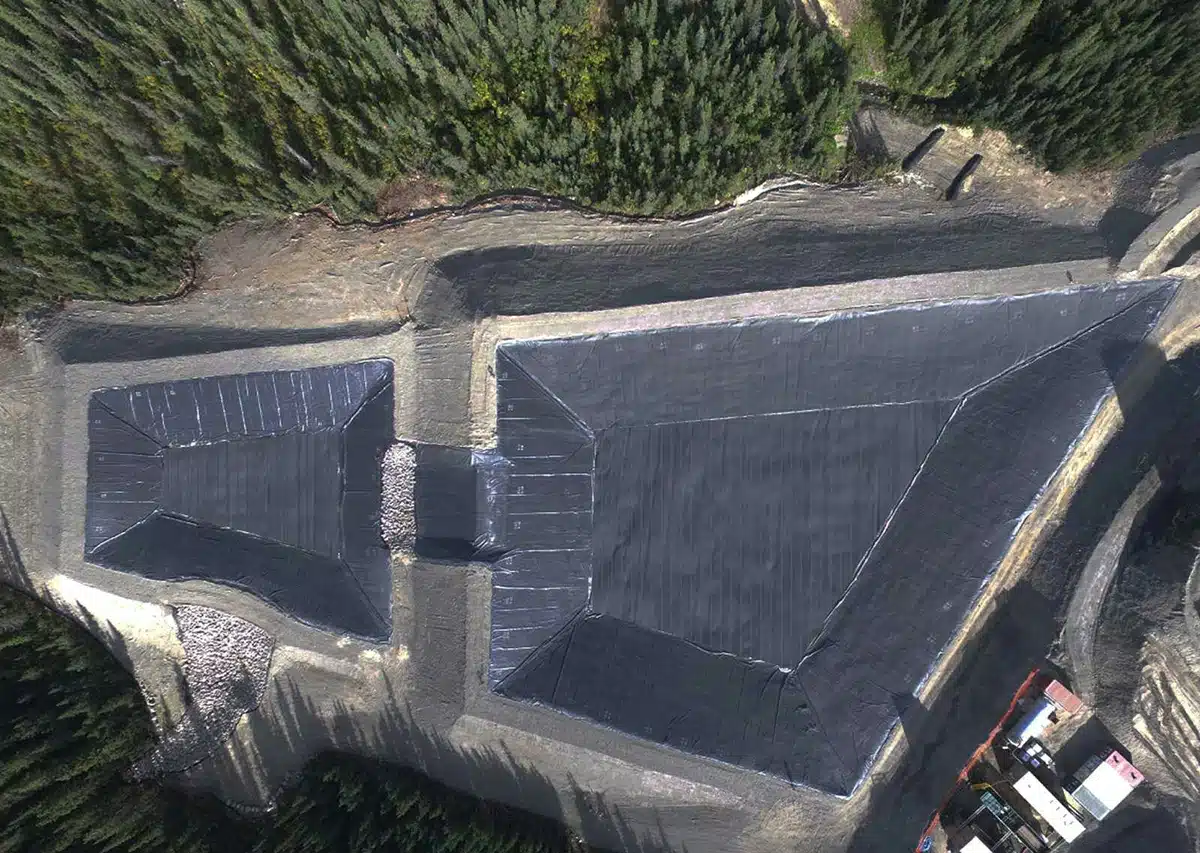

What is PVC Geomembrane?
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) geomembrane is a type of synthetic liner made from polyvinyl chloride, commonly used in various civil engineering and environmental protection applications. PVC geomembranes are designed to create a waterproof barrier, preventing the passage of liquids or gases. They are known for their flexibility, durability, and resistance to chemicals, making them suitable for a wide range of uses.
Key Characteristics of PVC Geomembranes:
- Flexibility: PVC geomembranes are highly flexible, allowing them to conform to the contours of the surfaces they cover. This flexibility makes them ideal for applications where the geomembrane needs to adapt to uneven or shifting surfaces.
- Chemical Resistance: PVC geomembranes offer excellent resistance to a wide range of chemicals, including acids, alkalis, and salts. This property is particularly valuable in industrial settings, where the geomembrane may be exposed to potentially harmful substances.
- Durability: PVC geomembranes are designed to withstand the effects of weathering, UV radiation, and mechanical stress. They have a long service life, making them a reliable choice for long-term applications.
- Waterproofing: As a primary function, PVC geomembranes provide an effective barrier against water, making them ideal for lining ponds, reservoirs, canals, and other water containment structures.
- Ease of Installation: PVC geomembranes are relatively easy to install, as they can be welded or seamed together to create a continuous barrier. Their flexibility also simplifies handling and installation in various environments.
Common Applications of PVC Geomembranes:
- Landfills: These are used as liners to prevent the leachate from contaminating the surrounding soil and groundwater.
- Ponds and Reservoirs: Lining of water bodies to retain water and prevent seepage into the ground.
- Canals and Dams: These are used in irrigation and water management projects to reduce water loss and reinforce structures.
- Mining Operations: Serve as containment barriers for hazardous liquids and tailings.
- Wastewater Treatment: Used in treatment ponds and lagoons to contain and treat wastewater safely.
- Tunnel Waterproofing: PVC geomembranes are used to waterproof tunnels, ensuring that they remain dry and stable over time.
Advantages of PVC Geomembranes:
- Cost-Effective: PVC geomembranes offer a balance between performance and cost, making them an economical choice for many projects.
- Long Service Life: With proper installation and maintenance, PVC geomembranes can last for decades.
- Versatile: Suitable for a wide range of applications across different industries.
Disadvantages of PVC Geomembranes:
- Susceptibility to Punctures: While durable, PVC geomembranes can be punctured by sharp objects, requiring careful handling and installation.
- Environmental Impact: The production and disposal of PVC involve the use of chemicals that may have environmental impacts, making recycling and proper disposal important considerations.
In summary, PVC geomembranes are a versatile and effective solution for various waterproofing and containment applications, offering a combination of flexibility, chemical resistance, and durability.
What is the difference between HDPE and PVC geomembrane?
HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) and PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) geomembranes are both widely used in environmental protection and containment applications, but they have distinct differences that make them suitable for different uses.
Material Composition:
- HDPE Geomembrane: Made from high-density polyethylene, HDPE is known for its strength, durability, and resistance to a wide range of chemicals. It is a semi-crystalline material, making it more rigid.
- PVC Geomembrane: Made from polyvinyl chloride, PVC is more flexible due to the addition of plasticizers, which allow it to conform to various shapes and surfaces easily.
Flexibility:
- HDPE Geomembrane: Less flexible compared to PVC. This rigidity can be advantageous for applications requiring a strong, puncture-resistant liner, but it can make installation more challenging, especially in areas with complex contours.
- PVC Geomembrane: Highly flexible, making it easier to install in areas with intricate shapes and uneven surfaces. This flexibility also makes it more adaptable to settlement and ground movement.
Chemical Resistance:
- HDPE Geomembrane: Excellent chemical resistance, particularly to aggressive chemicals, solvents, and a wide range of hazardous substances. This makes HDPE a preferred choice for hazardous waste containment and chemical ponds.
- PVC Geomembrane: Good chemical resistance, but generally not as robust as HDPE. It is suitable for less aggressive environments and is often used in water containment and non-hazardous waste landfills.
Durability and Longevity:
- HDPE Geomembrane: Typically more durable and resistant to environmental stress cracking, UV degradation, and extreme temperatures. It has a longer lifespan, often exceeding 50 years in many applications.
- PVC Geomembrane: While durable, PVC is more susceptible to UV degradation and may require a protective cover to extend its lifespan. It generally has a shorter lifespan compared to HDPE, around 20-30 years depending on exposure conditions.
Cost:
- HDPE Geomembrane: Generally more cost-effective in the long term due to its durability and lower maintenance needs. However, the initial installation cost may be higher due to its rigidity.
- PVC Geomembrane: Typically less expensive upfront due to its ease of installation and material cost, but may require more frequent maintenance or replacement over time.
Environmental Impact:
- HDPE Geomembrane: Considered more environmentally friendly as it does not require plasticizers, which can leach out over time. It is also recyclable.
- PVC Geomembrane: Contains plasticizers that can potentially leach into the environment. PVC is also less recyclable compared to HDPE, and its production involves chlorine, which has environmental concerns.
Applications:
- HDPE Geomembrane: Commonly used in landfill liners, mining operations, hazardous waste containment, and large-scale water reservoirs.
- PVC Geomembrane: Often used in smaller-scale projects such as decorative ponds, water features, and non-hazardous waste containment.
In summary, the choice between HDPE and PVC geomembranes depends on the specific requirements of the project, including the need for chemical resistance, flexibility, durability, and cost considerations.
How is the PVC Geomembrane Installed?
Installing a PVC geomembrane requires careful planning and attention to detail to ensure a durable and effective result. Here is a step-by-step guide to the installation process:
Site Preparation
- Clear the Area: Remove any vegetation, debris, or large rocks from the installation site to prevent punctures and ensure a smooth surface.
- Grade the Surface: The area should be graded to prevent water pooling or uneven stress on the geomembrane. Any sharp protrusions should be smoothed or removed to avoid damage during installation.
- Compaction: Ensure the subgrade is properly compacted to provide a stable foundation for the geomembrane.
- Install a Cushion Layer: In some cases, a geotextile fabric or sand cushion is placed beneath the PVC geomembrane to protect it from sharp objects or rough surfaces.
Material Handling
- Check the PVC Geomembrane: Before installation, inspect the geomembrane for any visible defects or damage. Ensure it meets the specifications required for the project.
- Roll Handling: PVC geomembranes come in large rolls. Handle them carefully using appropriate equipment to avoid creasing, folding, or excessive bending, which can damage the material.
Installation Techniques
- Unroll the Geomembrane: Begin unrolling the PVC geomembrane along the prepared site. Ensure it is laid flat and straight to minimize the number of seams required.
- Seaming the Geomembrane:
- Hot Air Welding: The most common method for joining PVC geomembranes is hot air welding, which involves using a heated air gun to melt the edges of the material, creating a strong bond.
- Extrusion Welding: For additional strength or when dealing with thicker seams, extrusion welding may be used. This involves feeding PVC welding rods into the seam during the welding process.
- Ensure Proper Alignment: While welding, make sure the edges of the geomembrane align properly and there are no gaps between adjacent sheets.
- Quality Control: Continuously monitor the welding process to ensure consistent weld quality. Visual inspection and air pressure tests (for seam integrity) are often performed.
Safety Precautions
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Ensure workers wear appropriate PPE, including gloves, safety glasses, and protective footwear, especially when working with hot air welders and other equipment.
- Ventilation: If working in confined spaces or using welding equipment, ensure proper ventilation to avoid inhaling fumes.
- Fire Safety: Since welding involves high temperatures, ensure there are fire extinguishers available and that the area is free of flammable materials.
Post-Installation Inspection
- Inspect Seams: After installation, carefully inspect all seams for any weak points or areas of concern. Perform tests, such as air pressure tests or vacuum tests, to confirm the seams are sealed.
- Final Surface Check: Inspect the entire geomembrane for any damage, such as punctures, tears, or holes. Repair any issues immediately to ensure the integrity of the installation.
- Backfilling and Coverage: If the PVC geomembrane is used in a landfill or pond lining project, ensure it is appropriately covered with soil or ballast to prevent movement or UV degradation.
Challenges and Troubleshooting
- Uneven Subgrade: If the subgrade is not smooth or contains sharp objects, it can damage the geomembrane. Ensure thorough site preparation and consider using additional protection layers, like geotextiles.
- Weather Conditions: Extreme heat, rain, or high winds can hinder installation. It is advisable to install geomembranes in mild weather conditions and avoid installation during rainy periods.
- Seam Failures: Poor welding can lead to seam failures. Regularly check the quality of the seams during installation and perform tests afterward to ensure durability.
Best Practices
- Overlap Seams: To ensure a secure bond, overlap seams by at least 4 inches (10 cm) before welding.
- Work in Sections: Break down the installation process into manageable sections, ensuring proper quality control and minimizing the risk of defects.
- Regular Maintenance: Inspect the geomembrane periodically for signs of wear, punctures, or degradation, especially if exposed to UV light or harsh weather conditions.
By following these detailed steps and precautions, PVC geomembranes can be installed efficiently and effectively, ensuring their long-term performance in environmental and construction applications.
What are the Environmental Considerations of Using PVC Geomembrane?
When considering PVC geomembrane for environmental projects, it’s important to understand its impact and sustainability. PVC is a type of plastic, and while it is durable and resistant to chemicals, it is not biodegradable. However, modern PVC formulations can be made more environmentally friendly through the use of plasticizers and stabilizers that are less harmful. Additionally, the longevity and effectiveness of PVC geomembrane in preventing leaks and contamination can significantly mitigate environmental risks associated with waste or water containment. Recycling and proper disposal of PVC geomembrane are also critical to minimizing its environmental footprint. As with any construction material, considering the full lifecycle, including production, usage, and disposal, is crucial for understanding its environmental impact.
By understanding the properties, differences, installation techniques, and environmental considerations of PVC geomembrane, stakeholders can make informed decisions for their specific needs, ensuring the longevity and success of their projects. Whether it’s for water containment, waste management, or other applications, PVC geomembrane offers a flexible and durable solution that can be tailored to a wide range of environmental conditions and requirements.



Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















