+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
Geogrid is a key soil reinforcement material widely selected by contractors, engineers, and project buyers when building stable foundations for concrete footings, pavements, and paver systems. By improving load distribution and strengthening weak soils, geogrid helps prevent settlement, cracking, and structural deformation. Understanding how geogrid works in foundation applications allows construction professionals to choose the right reinforcement solution for long-term durability and performance.
¿Se puede usar Geogrid con concreto?
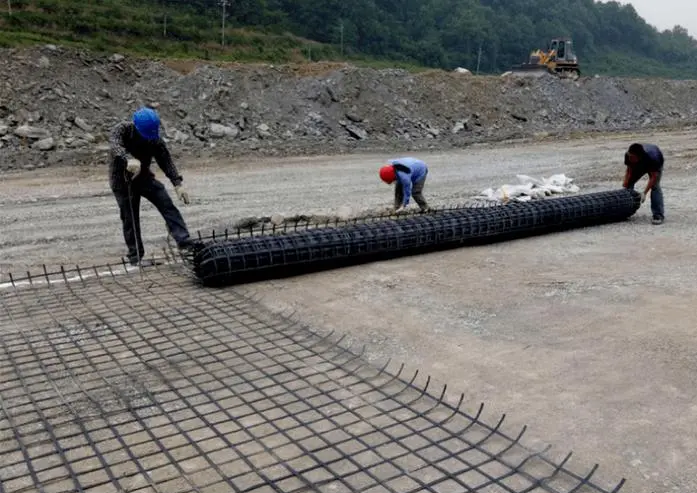

Sí, se puede usar Geogrid con concreto, aunque su aplicación depende del tipo de proyecto y del propósito deseado. El geogrid se coloca estratégicamente debajo de los cimientos de concreto o losas para reforzar el suelo, mejorar la distribución de cargas y reducir el riesgo de asentamientos o agrietamiento.
Principales usos incluyen:
- Refuerzo del suelo bajo concreto: Los geogrids fortalecen el suelo que soporta losas o pavimentos, distribuyendo mejor las cargas y disminuyendo el riesgo de asentamientos diferenciales.
- Refuerzo de concreto: Aunque no sustituyen al acero (rebar) dentro del concreto, pueden integrarse en capas delgadas o sobreposiciones de concreto para mejorar la resistencia a la tracción y controlar grietas.
- Superficies inclinadas o shotcrete: En taludes o muros de contención proyectados con concreto, el geogrid aumenta la estabilidad del material y refuerza la estructura.
En resumen, el Geogrid se utiliza principalmente para reforzar el suelo que soporta el concreto o como parte de sistemas compuestos, mejorando la estabilidad, la capacidad de carga y la durabilidad de la construcción, aunque no reemplaza el refuerzo tradicional dentro del concreto.
What Is Geogrid in a Foundation?
A geogrid in a foundation is a geosynthetic soil reinforcement material installed within or beneath the subgrade to improve ground stability and load-bearing capacity. Made from high-strength polymers such as polypropylene (PP) or polyester (PET), geogrids feature an open grid structure that interlocks with surrounding soil or aggregate.
- Soil Reinforcement: Geogrids provide tensile strength to weak or loose soils, limiting lateral soil movement and improving overall foundation support.
- Load Distribution: By spreading structural loads over a wider area, geogrids reduce stress concentrations and minimize the risk of differential settlement.
- Settlement Control: The interlocking mechanism between soil and geogrid helps control vertical and horizontal deformation, protecting foundations from uneven settling.
- Foundation Stability: Geogrids enhance bearing capacity, making them especially effective for foundations built on soft soils or areas with variable ground conditions.
- Drainage Compatibility: The open structure allows water to pass through freely, supporting proper drainage and reducing pore water pressure beneath foundations.
Geogrids are widely used in building foundations, pavements, embankments, retaining walls, and slabs-on-grade to improve long-term performance, structural safety, and durability.
Can I use Geogrid under pavers?
Yes, you can use a geogrid under pavers. Geogrid is commonly used in construction to improve soil stabilization and support structures like roadways, walkways, and patios made with pavers. Here’s how it can be beneficial:
- Enhanced Load Distribution: Geogrid helps distribute the load evenly across the surface, which reduces the risk of pavers sinking or becoming uneven over time.
- Soil Stabilization: It prevents the soil beneath the pavers from shifting, which is especially important in areas with soft or unstable soil.
- Improved Durability: By stabilizing the base, geogrid can extend the lifespan of the paved area, making it more resistant to wear and tear.
- Weed and Erosion Control: Geogrid can also help minimize weed growth and prevent erosion under the pavers.
Installing geogrid involves laying it down over the prepared sub-base before the bedding sand and pavers are placed. This adds an extra layer of stability and can be particularly useful in high-traffic areas or places with frequent moisture exposure.
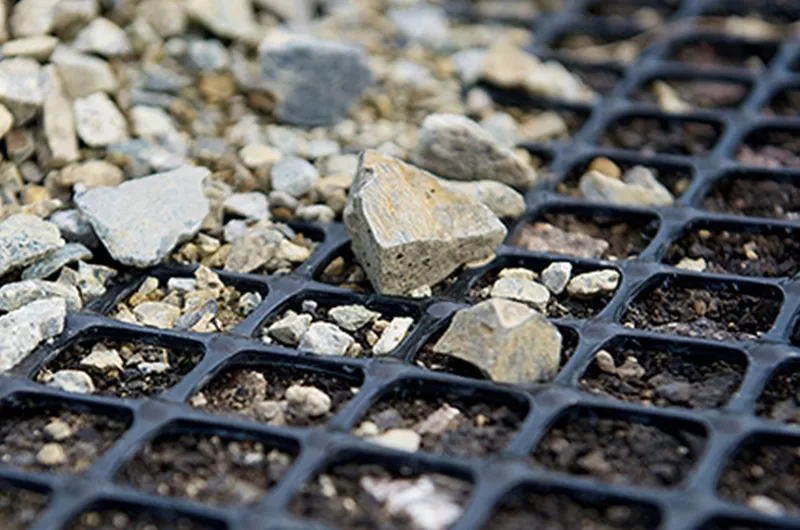

What is the difference between geogrid and geotextile?
| Feature | Geogrid | Geotextile |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Grid/mesh structure | Fabric-like sheet |
| Function | Reinforcement | Filtration, separation, drainage |
| Material | Polymers (e.g., PP, PET) | Woven/nonwoven synthetic fibers |
| Key Uses | Roads, walls, soil support | Soil separation, drainage, erosion |
Both can be used together in some engineering projects to maximize soil performance
In summary, the utilization of geogrids beneath concrete footings, pavers, or other foundation applications significantly improves the structural integrity of constructions. Their ability to reinforce soil, distribute loads, and reduce the risk of settlement or cracking makes them a valuable addition to various construction projects. Understanding the distinction between geogrids and geotextiles enables builders and engineers to choose the most suitable material for specific needs, ensuring the longevity and stability of their structures.


Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















