+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
When it comes to geotextiles, two commonly used terms are geogrid and geonet, which are often compared due to their similar functions in civil engineering and construction projects. While both materials serve vital roles, they have distinct differences and applications. In this article, we will explore the key distinctions between geogrid vs geonet, their respective uses, why geogrid is not considered a geotextile, and delve into the role of geonet within the realm of geotextiles.
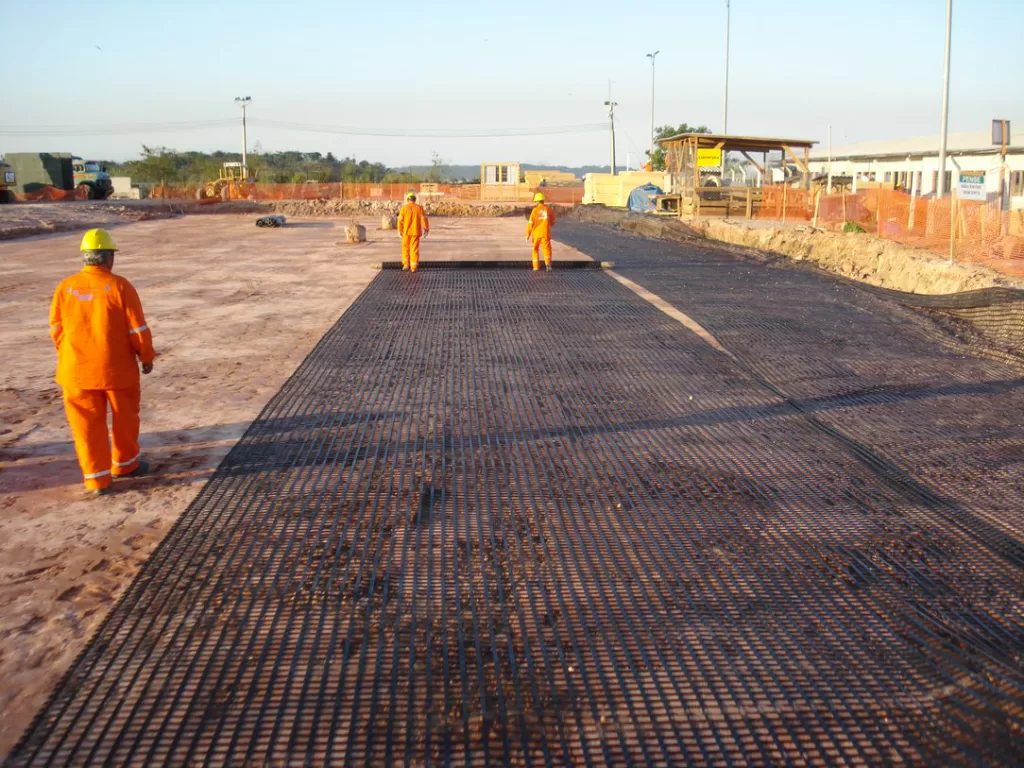

What is the difference between geotextile and geonet?
Geotextiles and geonets are both types of geosynthetic, Geotextiles and geonets differ in structure and function:
| Geotextile | Geonet | |
| Structure | Permeable fabric (woven or non-woven) | Separation, filtration, reinforcement, and erosion control. |
| Functions | Grid-like, 3D polymer grid with open channels. | Drainage and fluid flow management. |
What Is a Geonet Used For?
- Drainage Systems: Installed in landfills, roadbeds, and retaining walls to collect and convey water, preventing clogging and reducing hydrostatic pressure.
- Erosion Control: Allows rapid water drainage while maintaining soil stability, helping prevent surface erosion on slopes and embankments.
- Landfill Leachate Collection: Placed between geomembranes to safely manage leachate and protect surrounding soil and groundwater from contamination.
- Underground Construction: Used in tunnels, basements, and foundations to control groundwater and relieve pressure against structures.
- Road and Railway Drainage: Minimizes water buildup beneath pavements, improving stability and extending the life of transportation infrastructure.
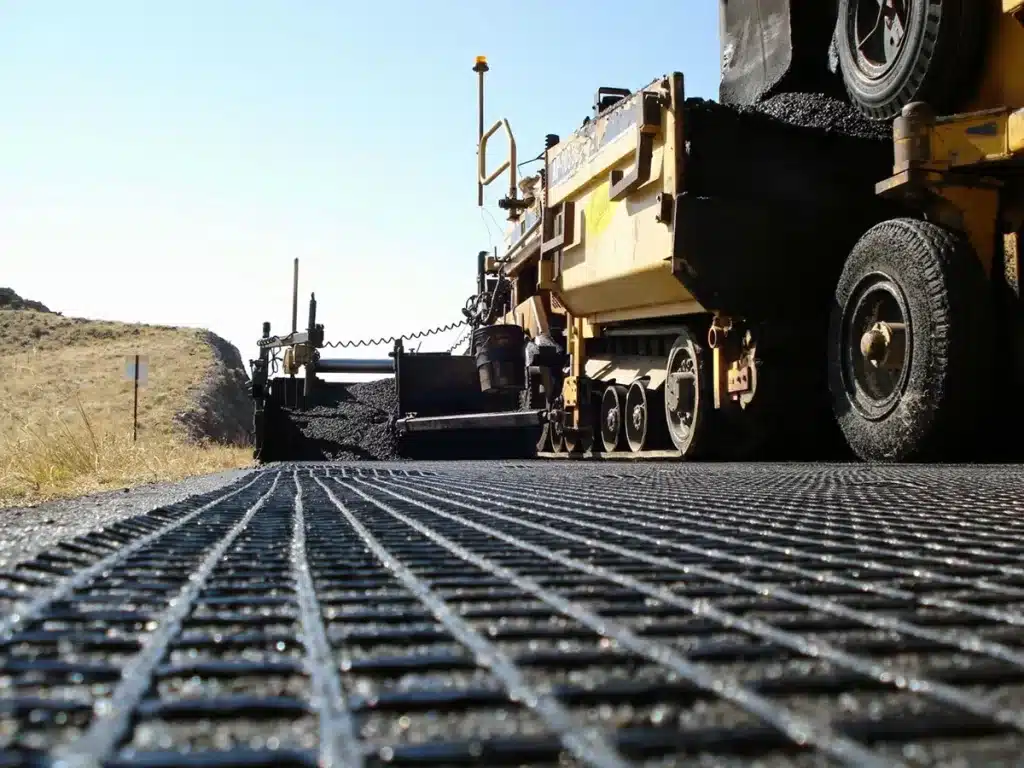

Why geogrid is not geotextile?
- Estructura de red: formado por capas de polímeros, normalmente polietileno o polipropileno, soldados para crear una malla de costillas interconectadas;
- Drenaje eficiente: permite el paso rápido del agua, reduciendo la presión hidrostática en estructuras como vertederos, muros de contención y carreteras;
- Capas de drenaje geosintético: combinado con geotextiles, el geonet actúa como núcleo de drenaje mientras que el geotextil filtra partículas de suelo para evitar obstrucciones;
- Control de erosión: facilita el drenaje del agua y aporta cierta estabilidad mecánica, ayudando a prevenir el desplazamiento del suelo;
- Sistemas de revestimiento de vertederos: se utiliza para recolectar lixiviados y transportar el agua contaminada de manera segura.
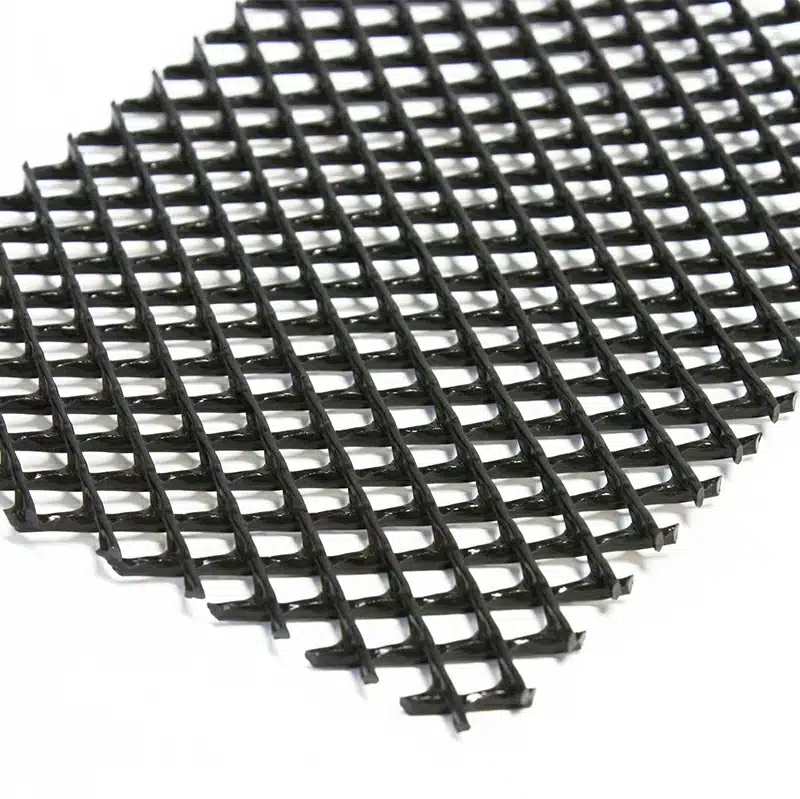
What is Geonet in geotextile?
A geonet is a type of geosynthetic material used in conjunction with geotextiles, but it differs in its structure and primary function. Geonets are made from layers of polymeric materials, typically polyethylene or polypropylene, that are welded together to form a network of interconnected ribs or strands. The result is a grid-like structure that is designed primarily for drainage applications.
Geonets are often used for:
- Drainage Systems: Due to their open, grid-like structure, geonets provide efficient water flow through the material. They are commonly used in landfill drainage systems, retaining walls, and road construction to facilitate the movement of water away from the structure and reduce hydrostatic pressure.
- Geosynthetic Drainage Layers: When used in combination with geotextiles, geonets act as a core drainage element. The geotextile typically surrounds the geonet to filter water while preventing soil particles from entering and clogging the drainage paths.
- Erosion Control: In some applications, geonets can be used as part of erosion control systems, where they allow water to drain while providing some mechanical stability to prevent soil movement.
- Landfill Liner Systems: Geonets are often used in landfill liner systems for leachate collection, helping manage and transport contaminated water that accumulates in landfills.
Because of their structure, geonets provide high flow capacity in a relatively lightweight material, making them suitable for a variety of civil engineering, environmental, and infrastructure projects.
In conclusion, understanding the difference between geogrid and geonet in geotextiles is crucial for selecting the right materials for construction and civil engineering projects. Geogrids offer reinforcement, while geonets facilitate drainage. Geonets can also be integrated into geotextiles to provide combined filtration and drainage capabilities, making them versatile solutions in various applications.

Get Free Sample
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)






















